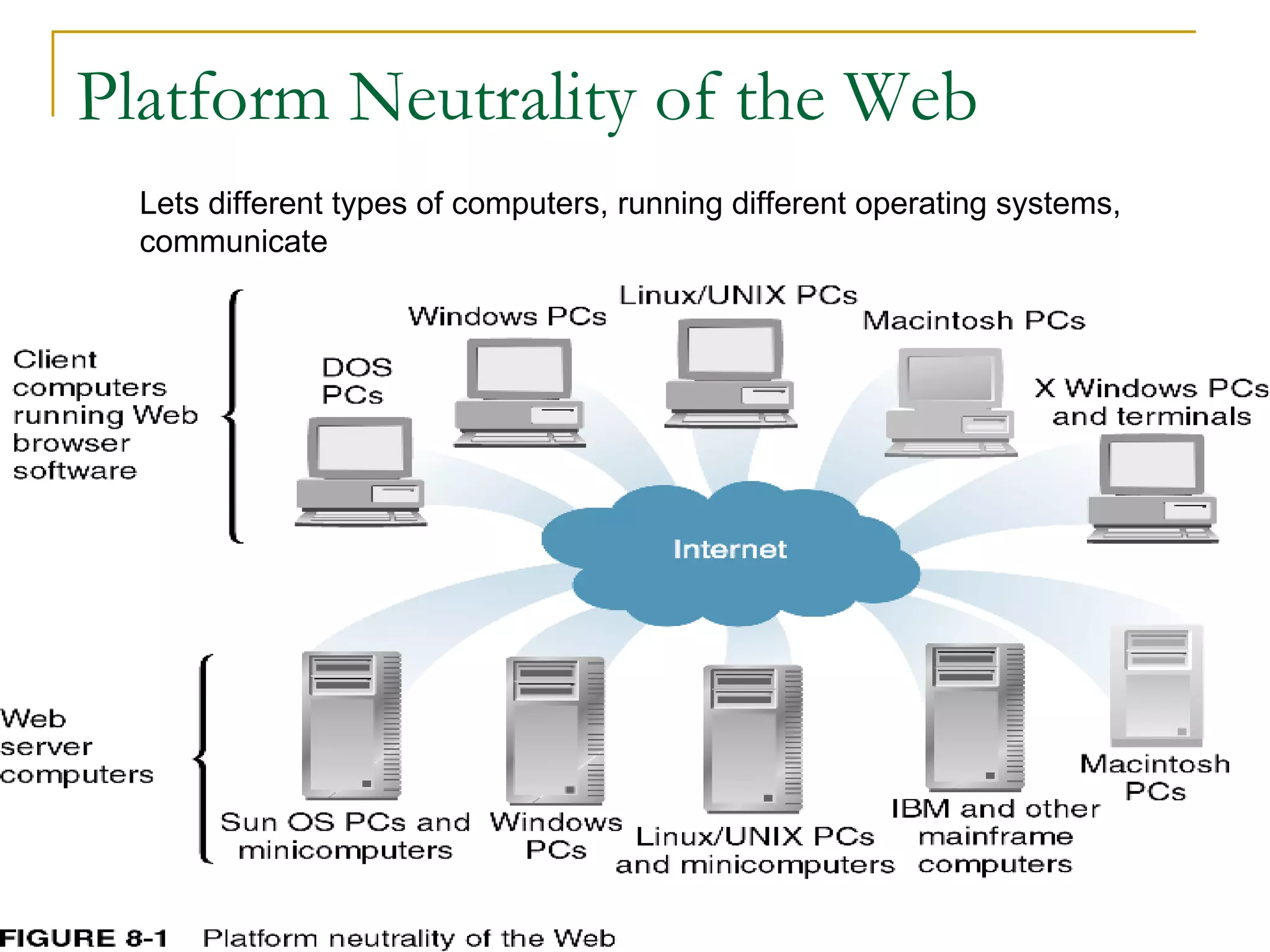
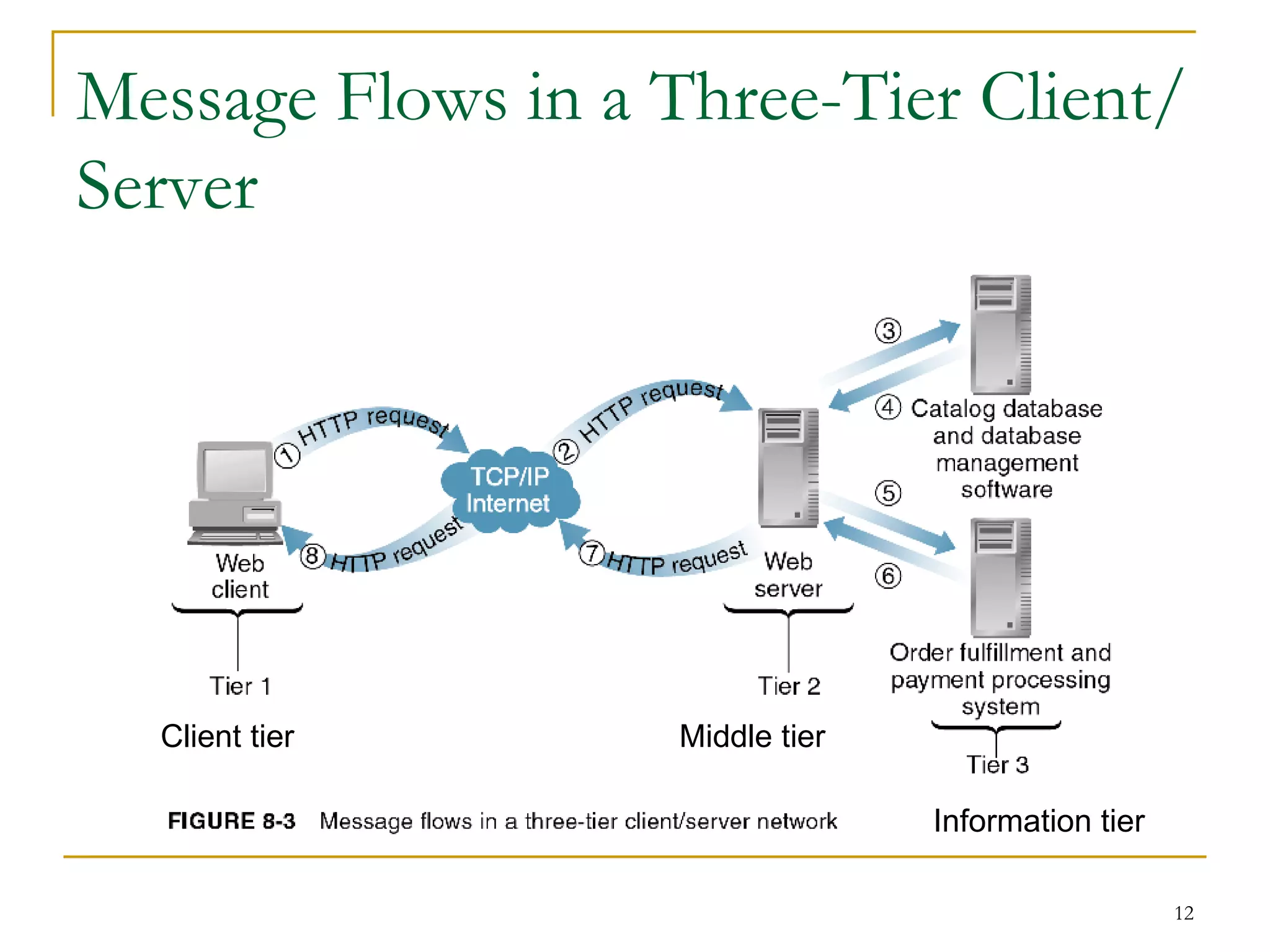
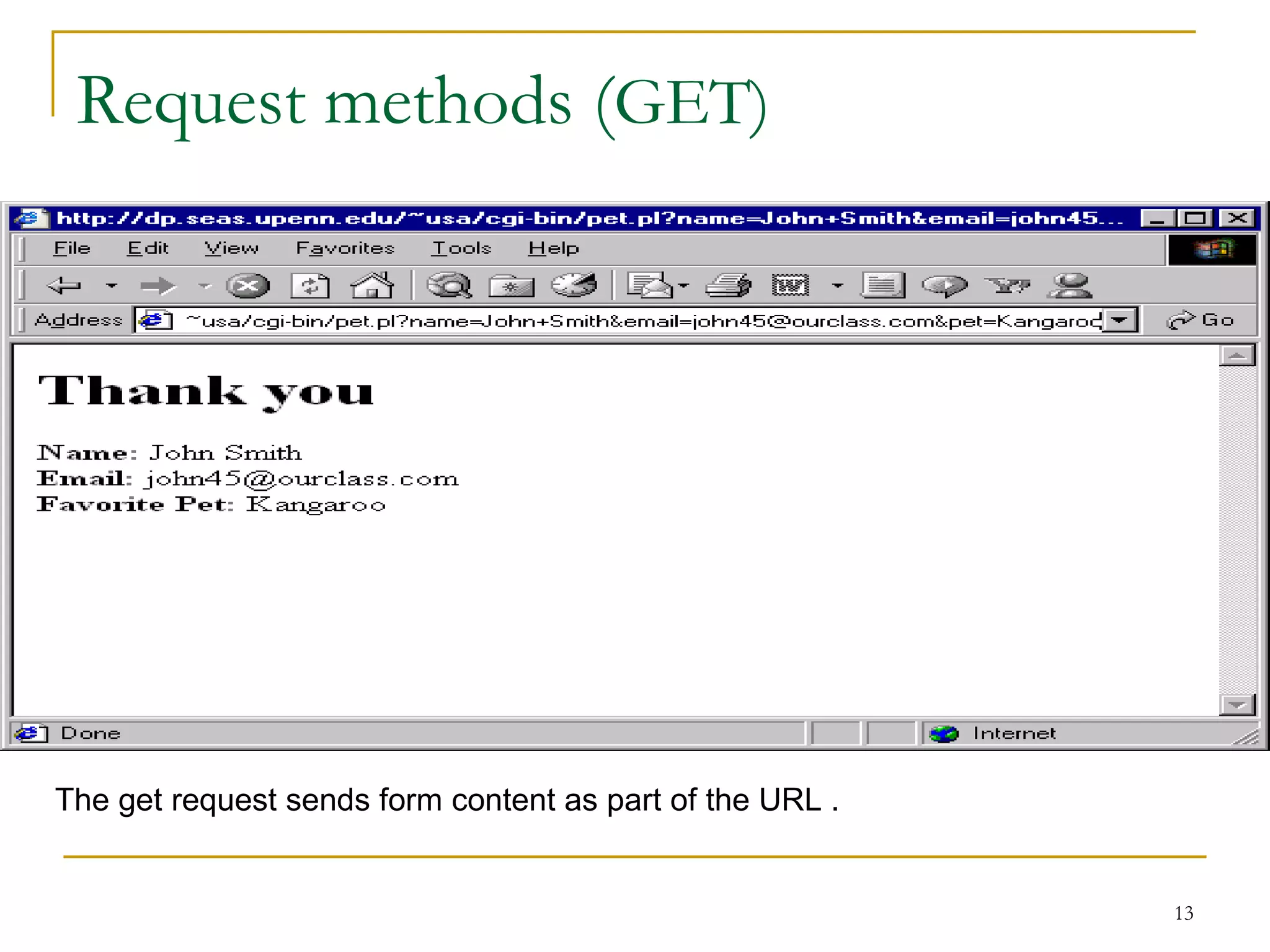
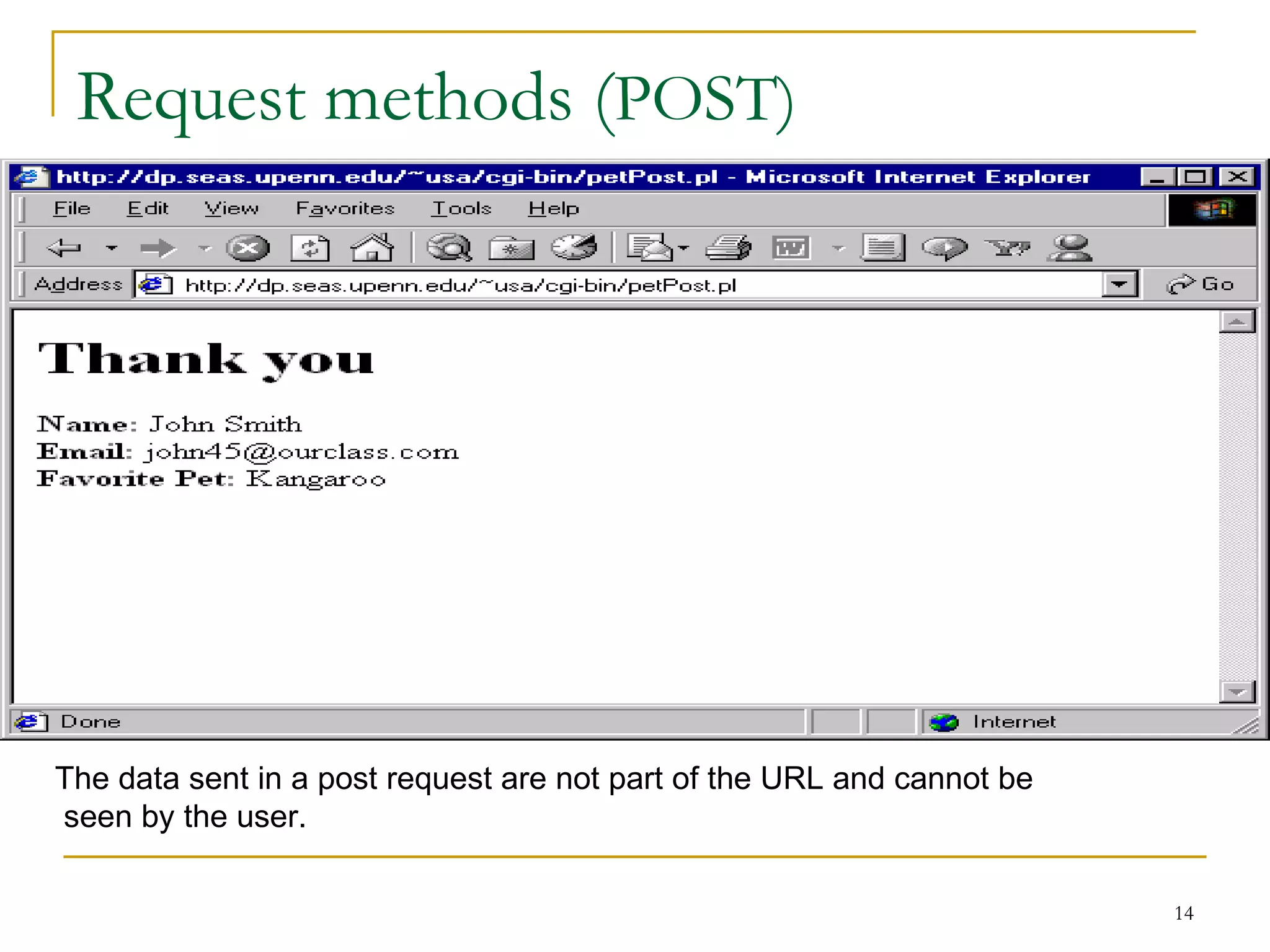
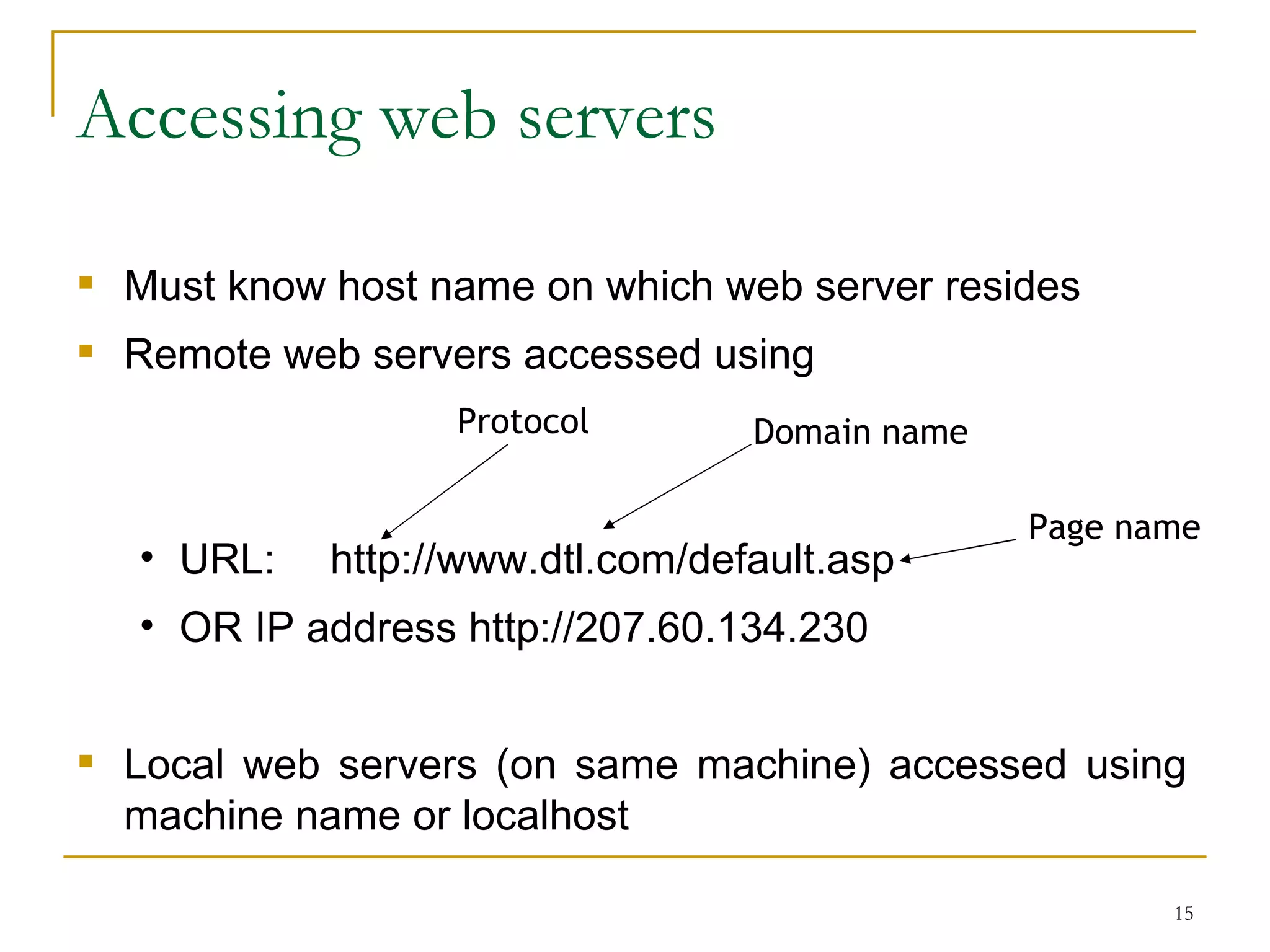
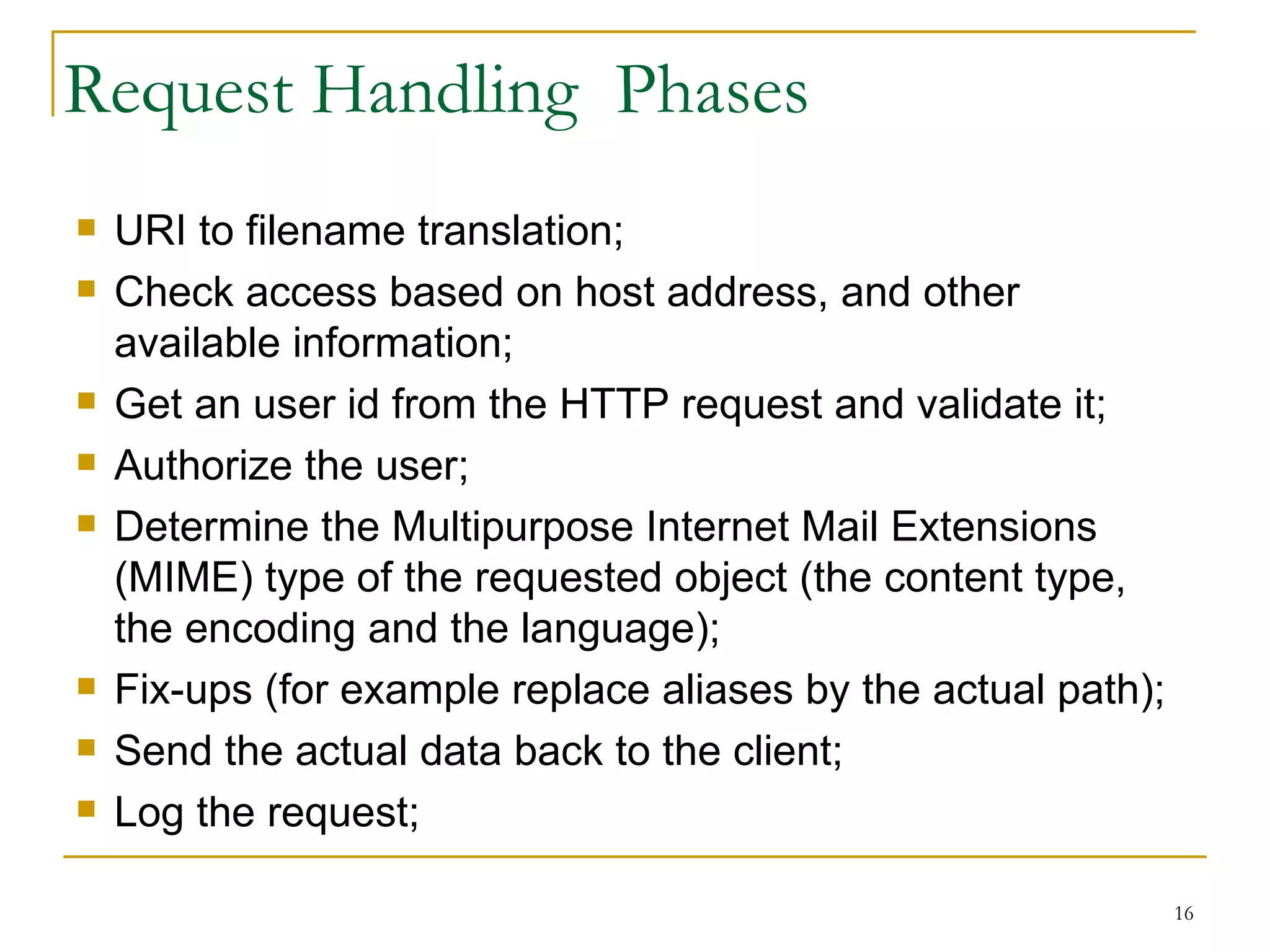
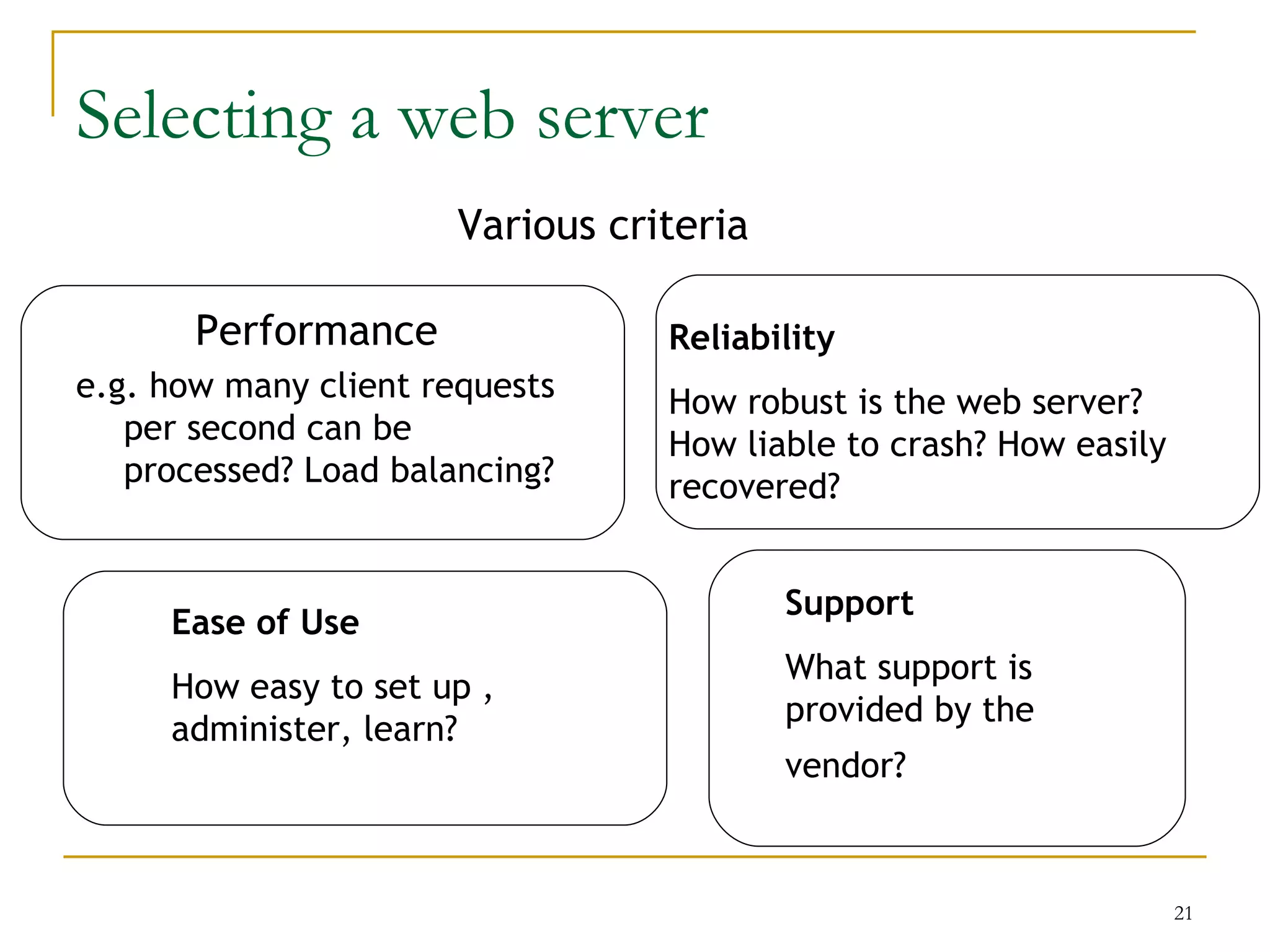
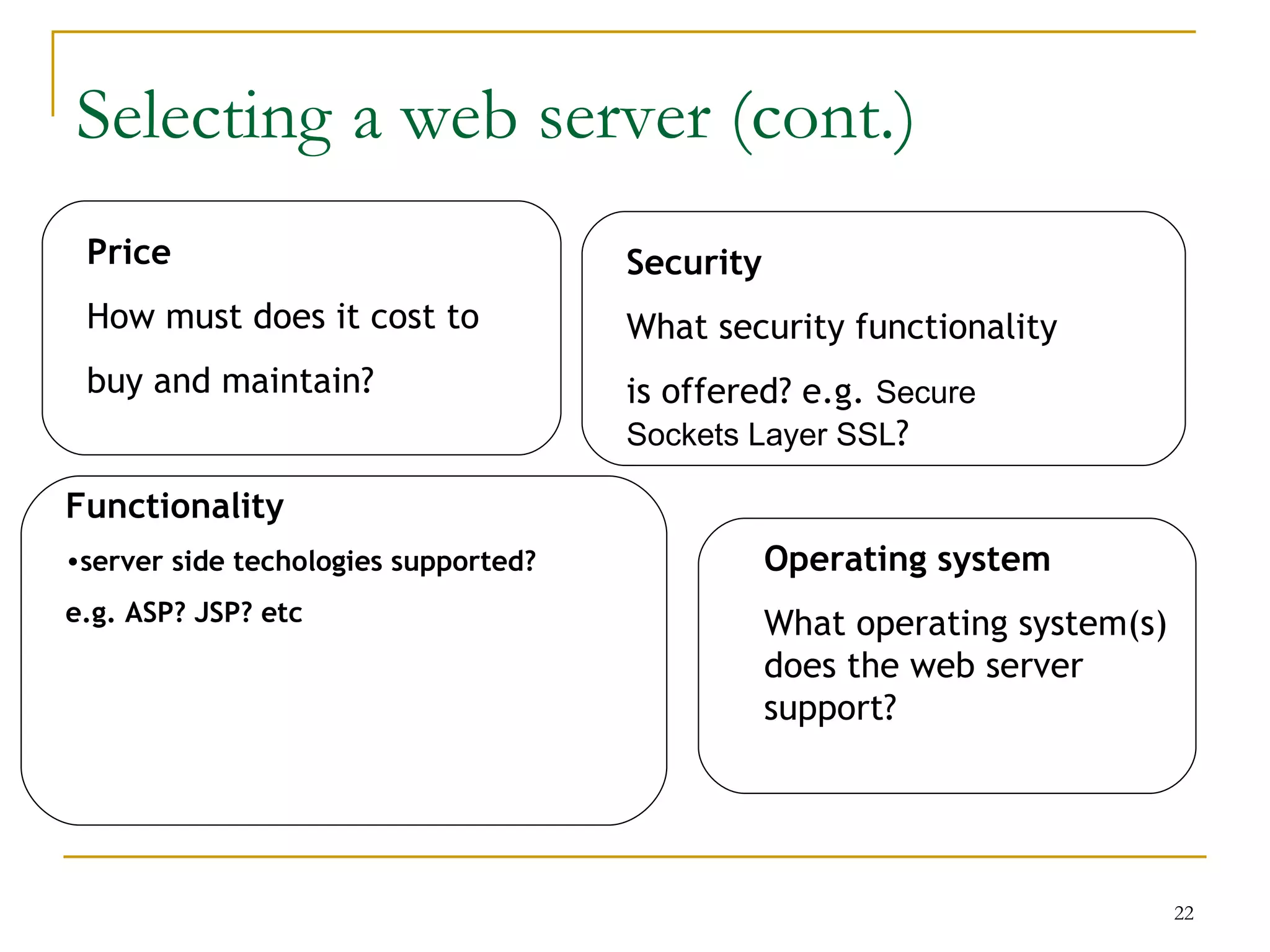
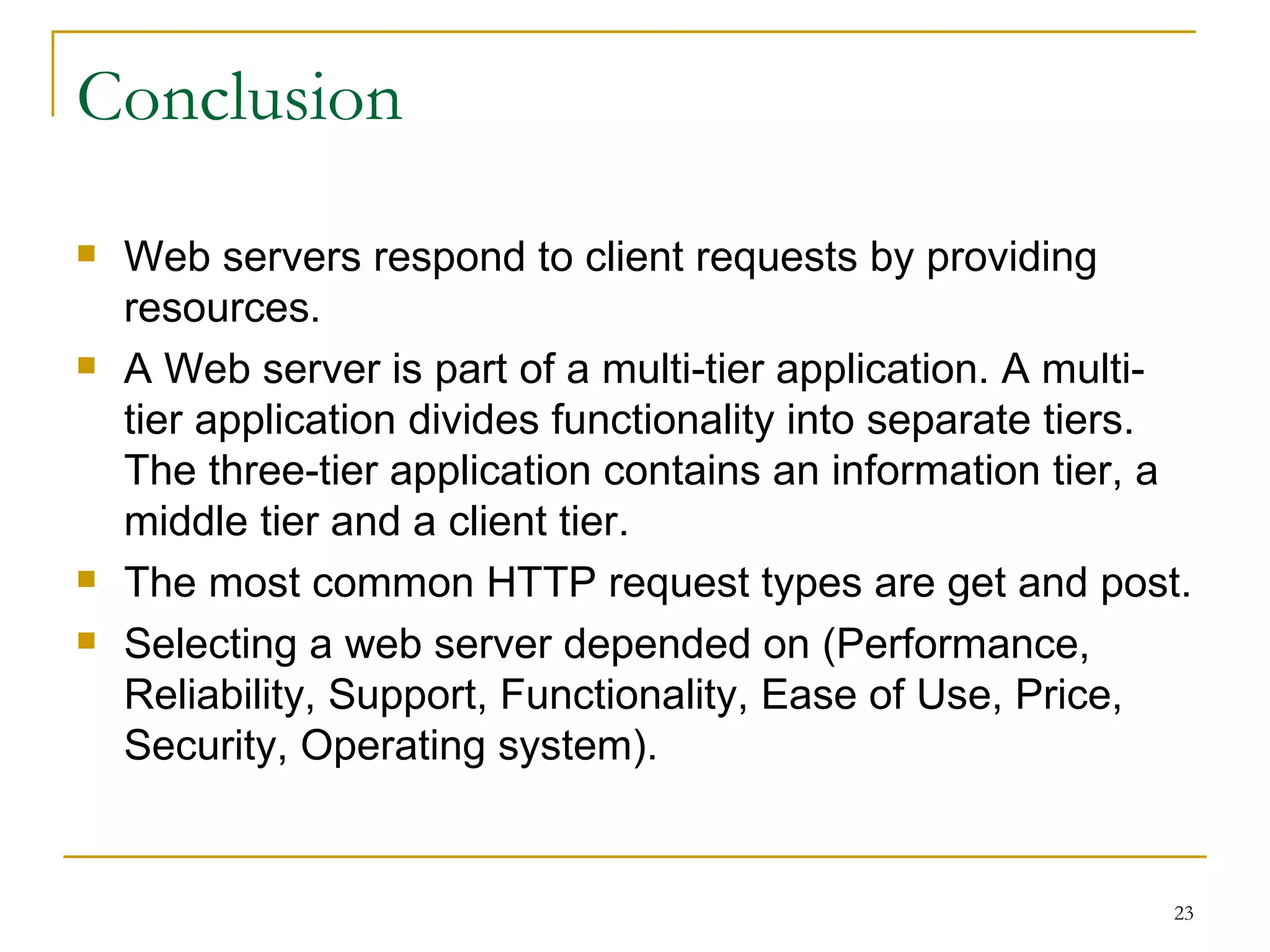
This document discusses web servers. It provides an overview of web clients and web servers, and describes how web servers handle static and dynamic content. The document outlines the typical architecture of a two-tier or three-tier client-server system for delivering web pages. It also discusses the GET and POST request methods, phases of request handling, popular web servers like Apache and IIS, and factors to consider when selecting a web server.