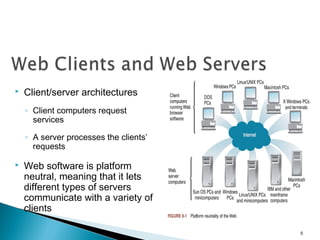
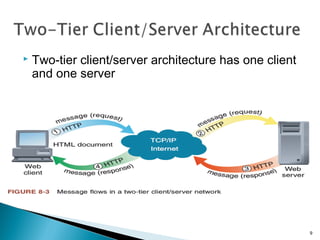
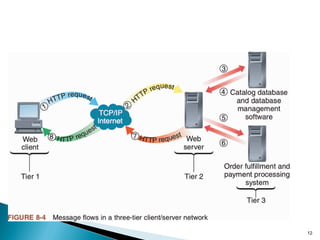
The document discusses various topics related to web servers including their basic functions, components, common types of websites, client-server architectures, static vs dynamic content, server-side scripting technologies, request messages, and multi-tier architectures. It also covers operating system tasks and mentions Linux as an open-source operating system option.