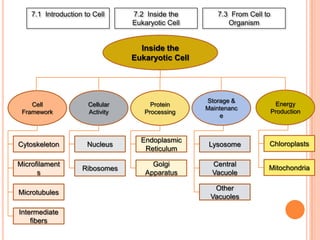
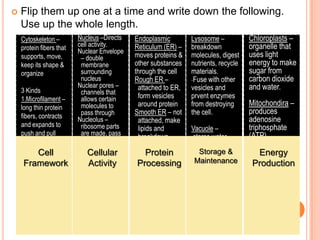
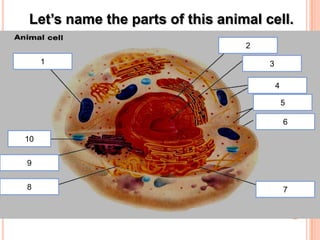
The document summarizes the major organelles and structures found within eukaryotic cells, including their functions. It describes the cytoskeleton which provides structure and organization to the cell. It also outlines the roles of the nucleus which directs cell activity, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus which process and package proteins, mitochondria which produce energy, lysosomes which break down molecules, vacuoles which store substances, and chloroplasts which perform photosynthesis in plant cells.