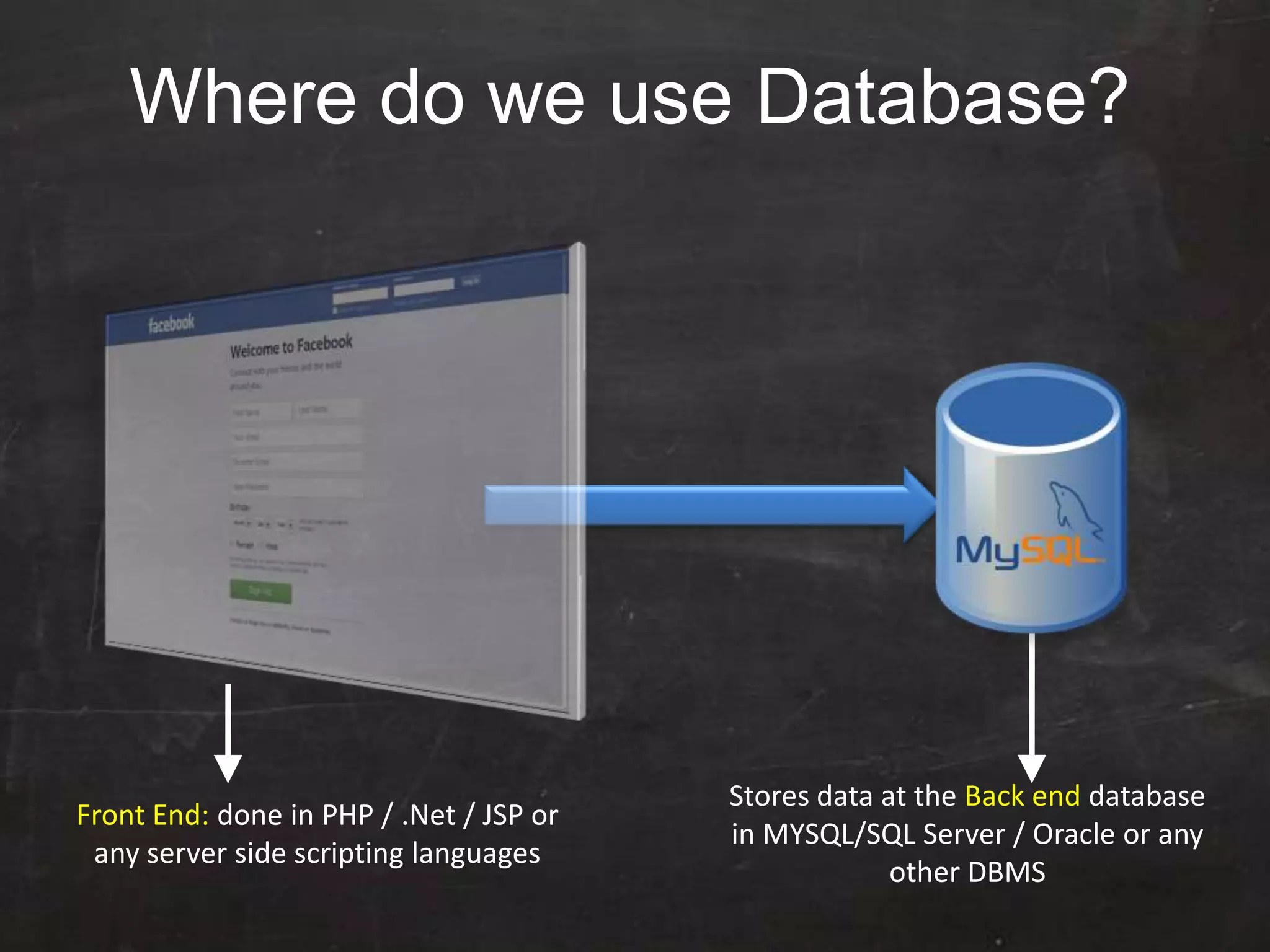
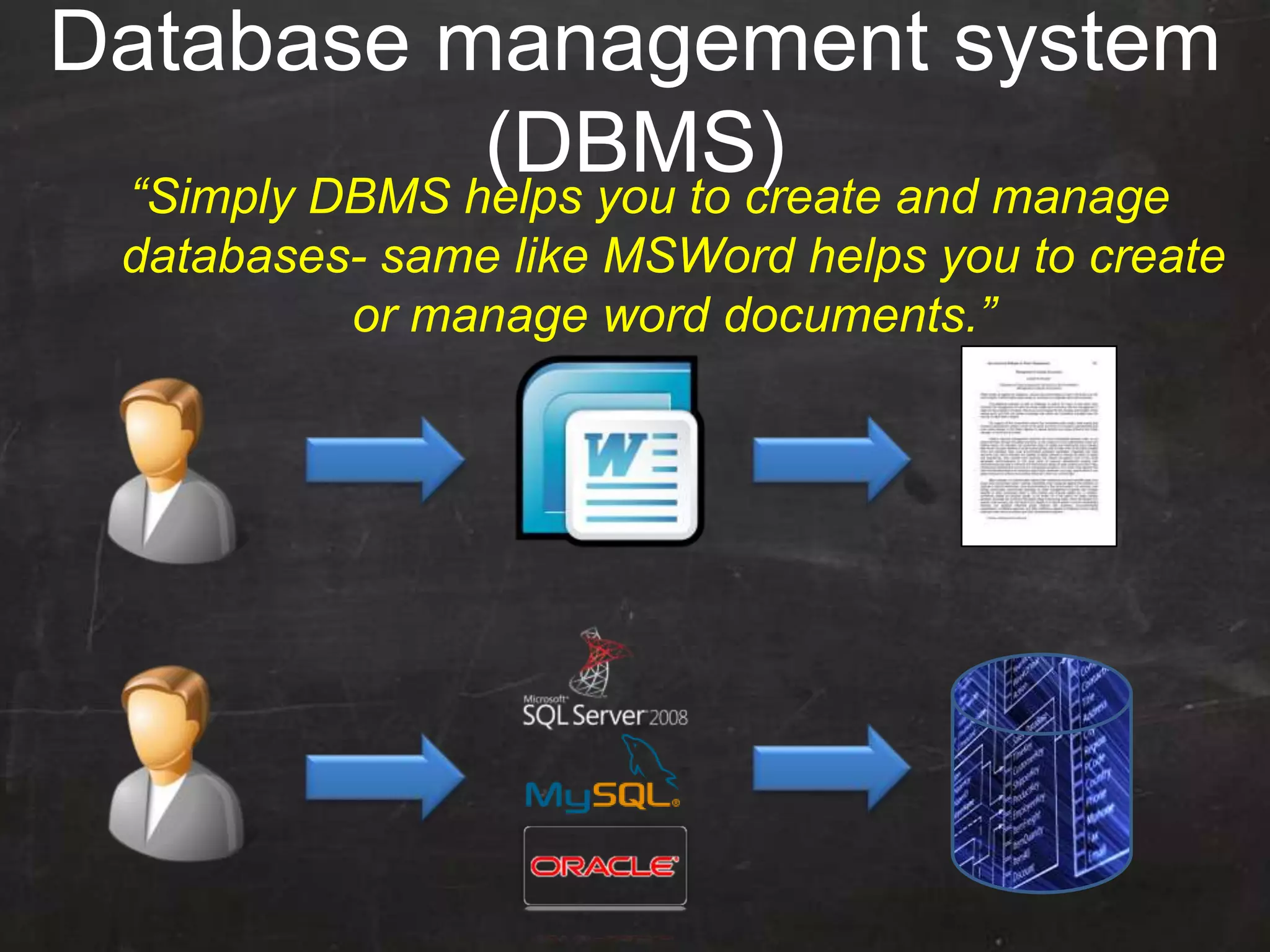
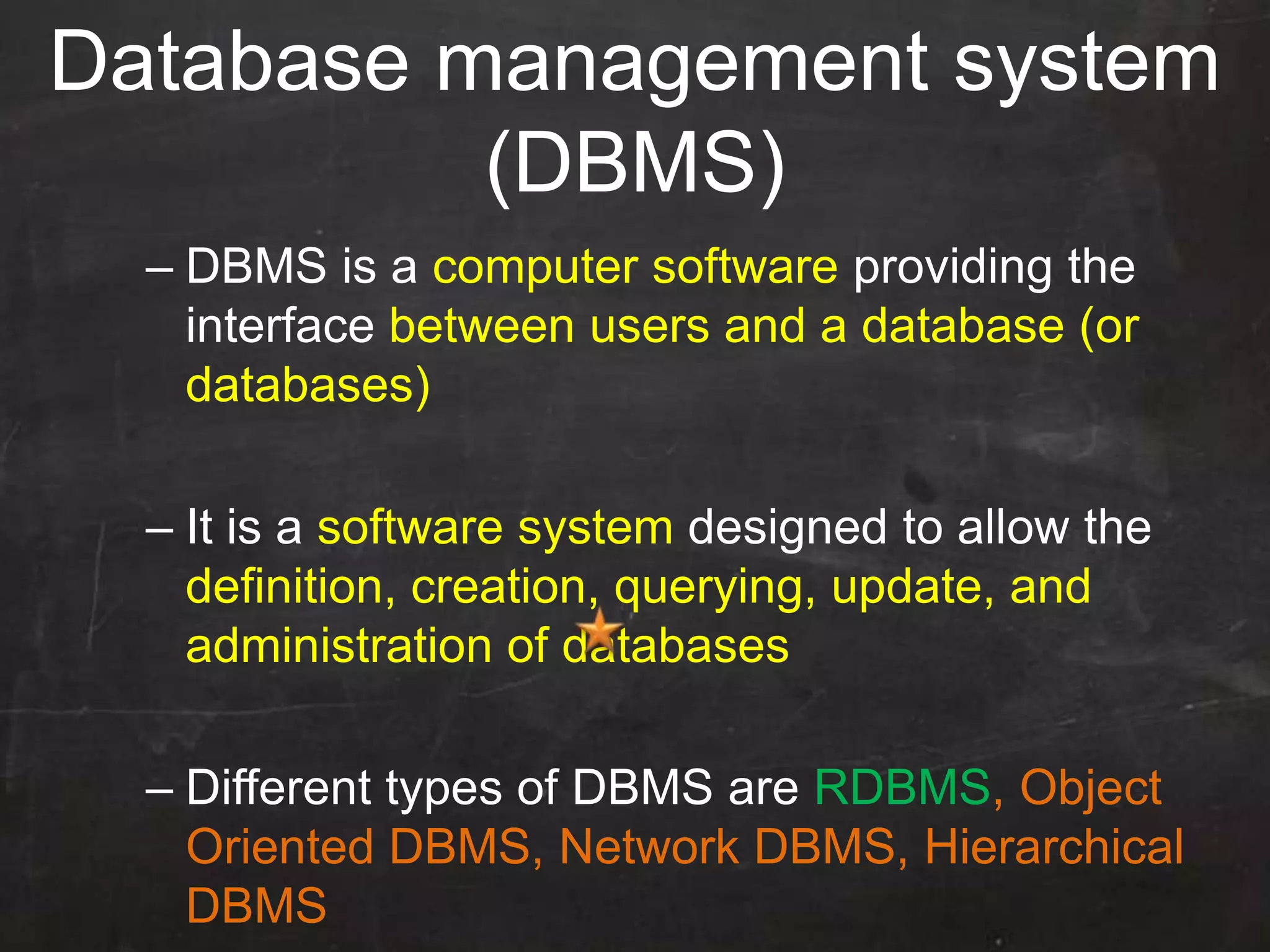
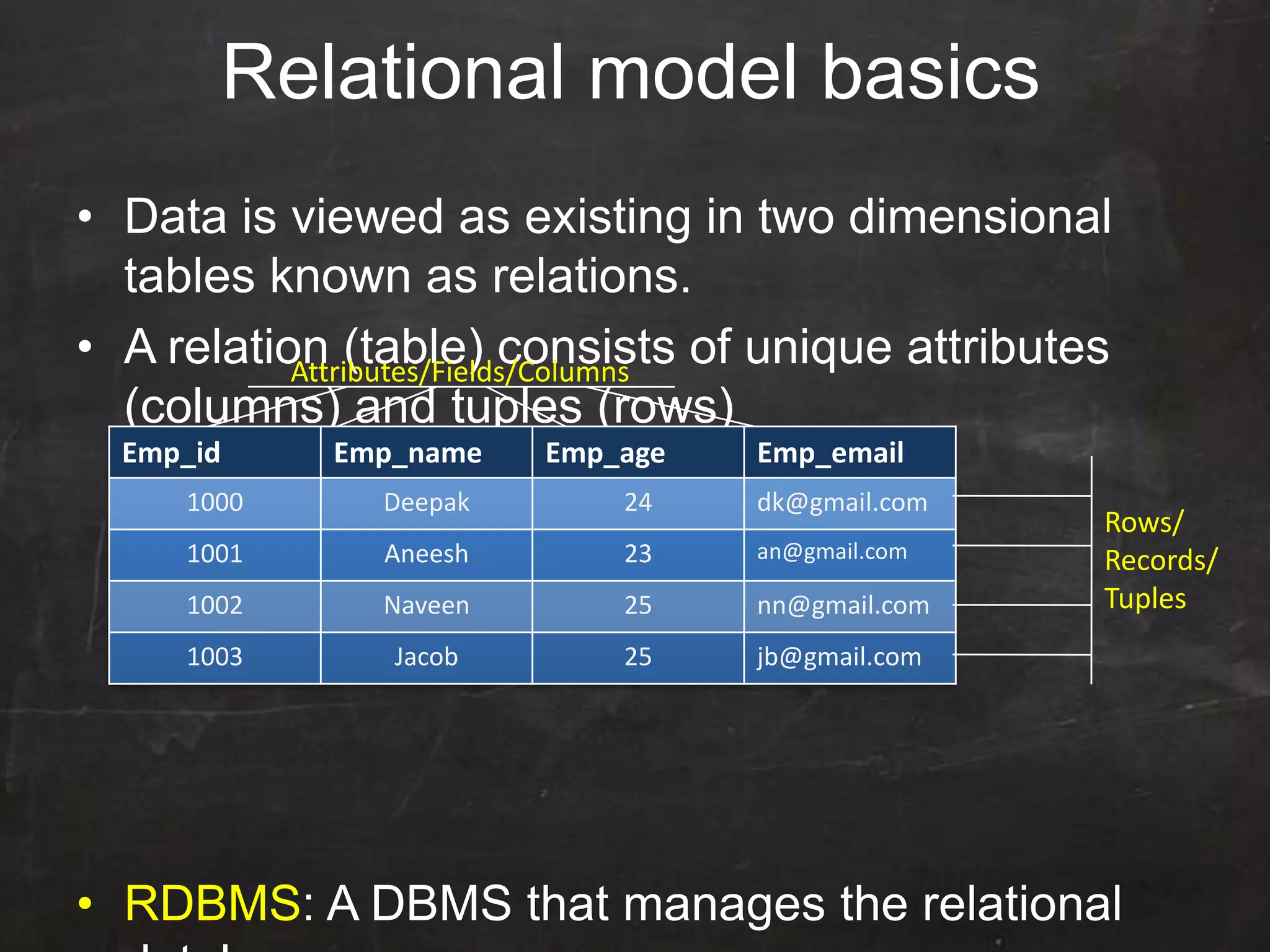
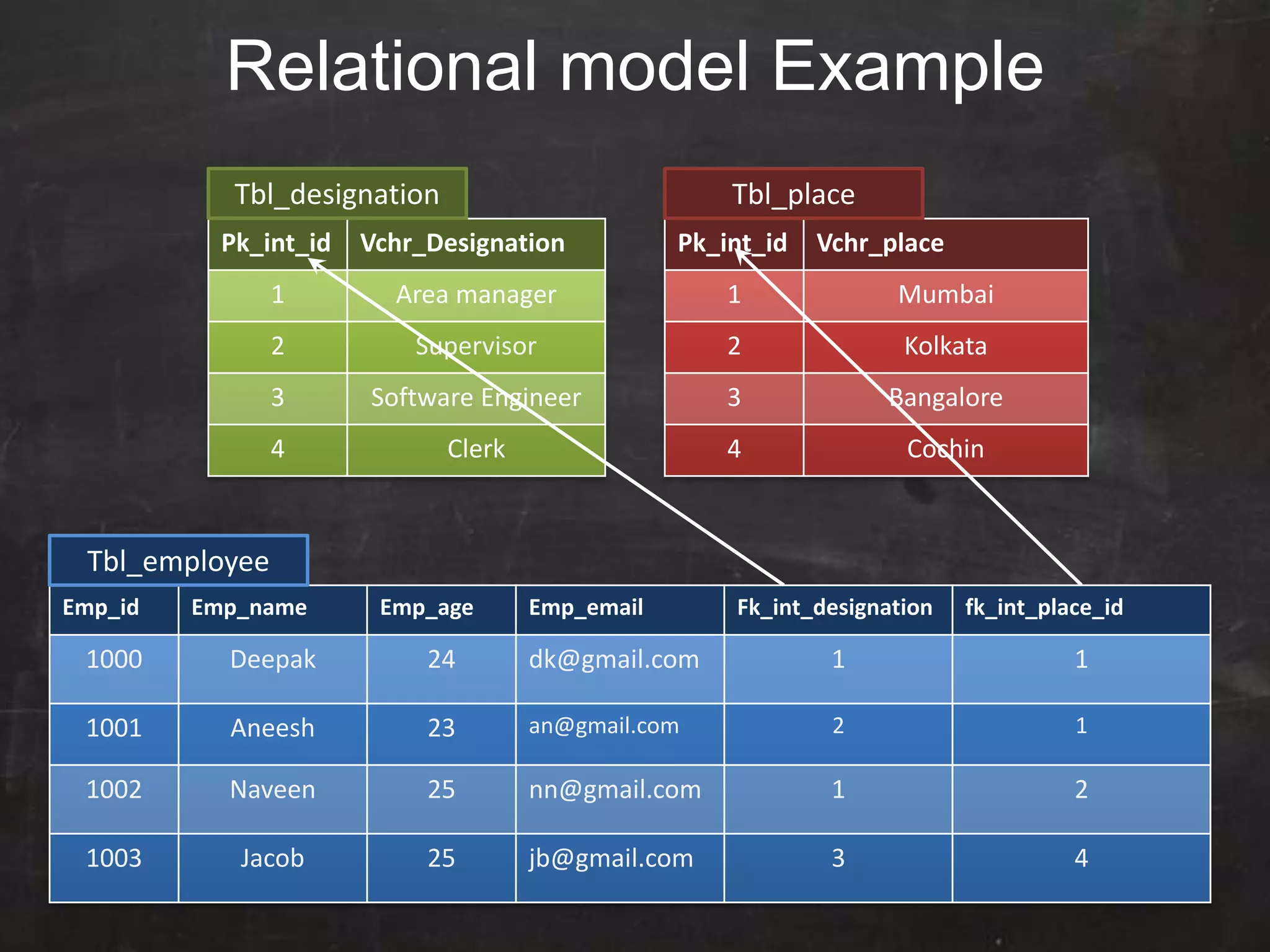
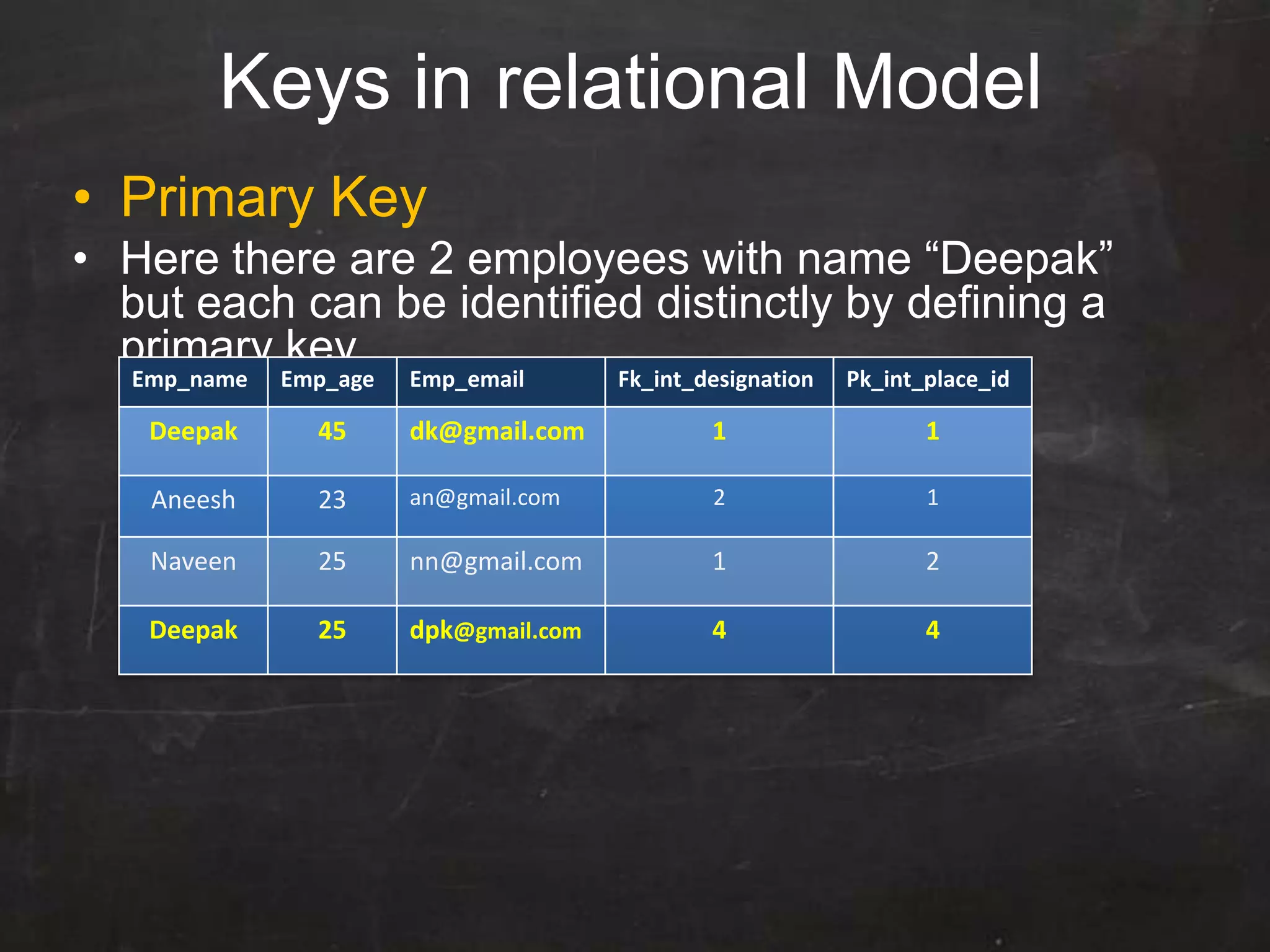
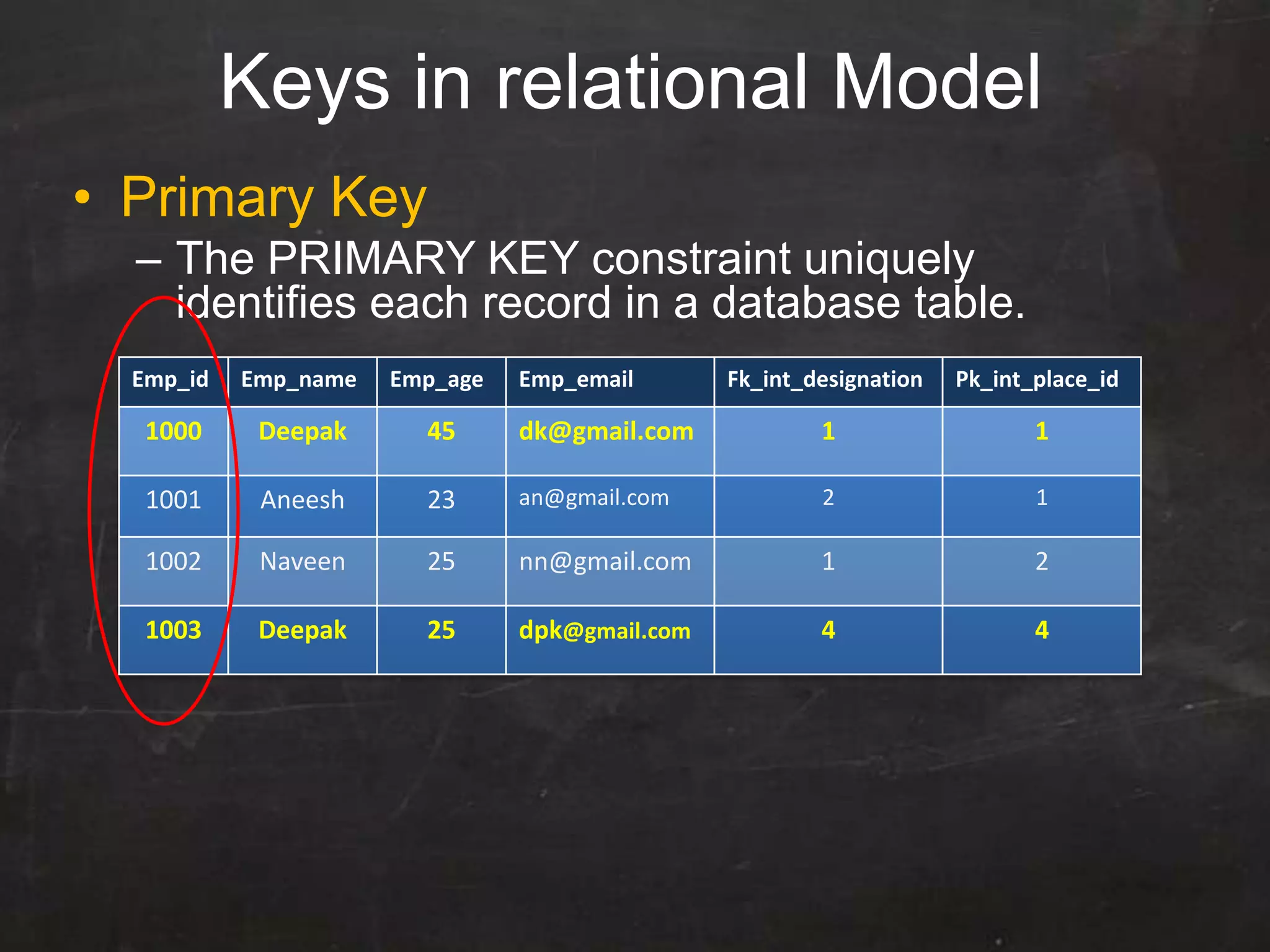
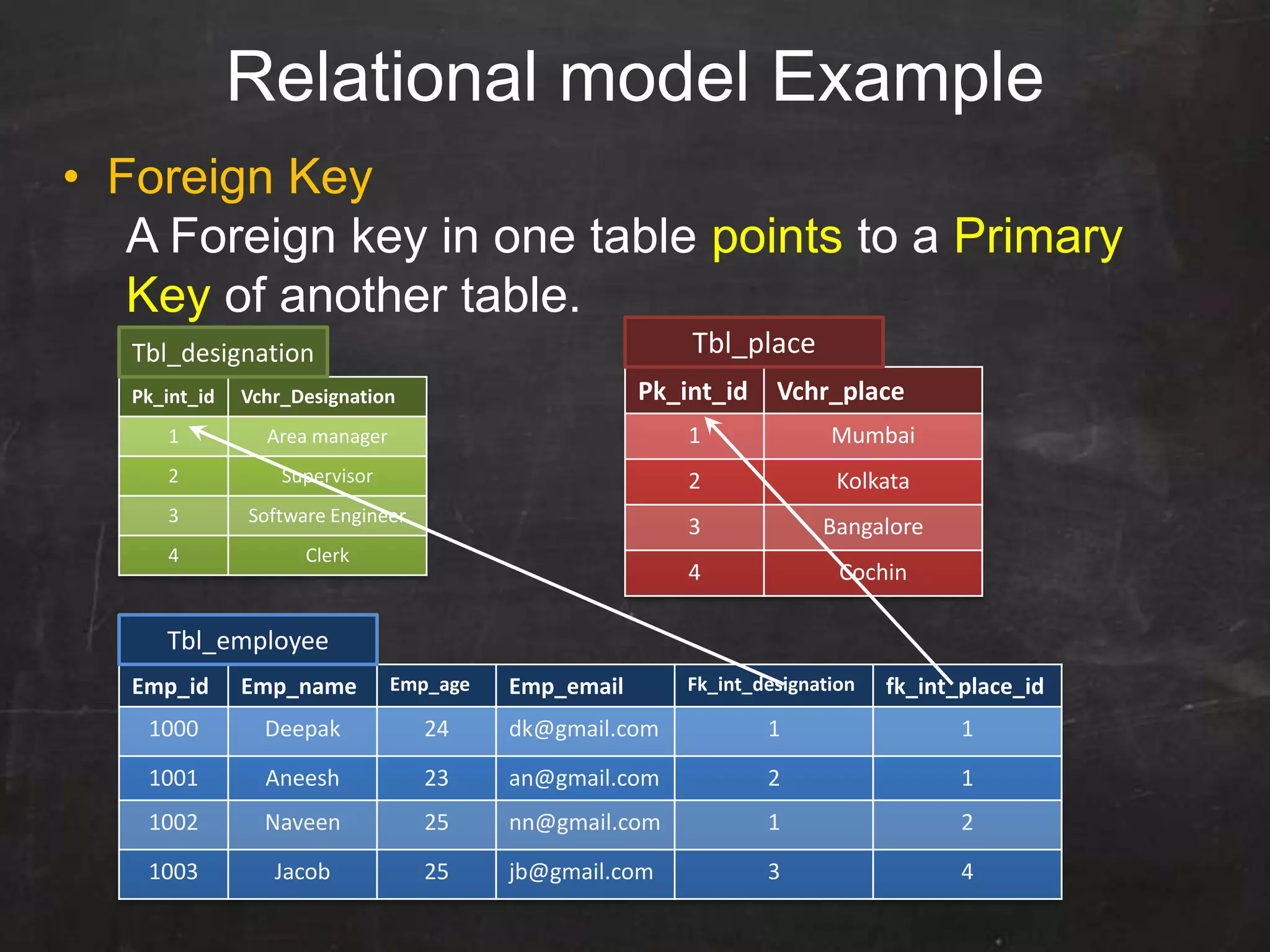
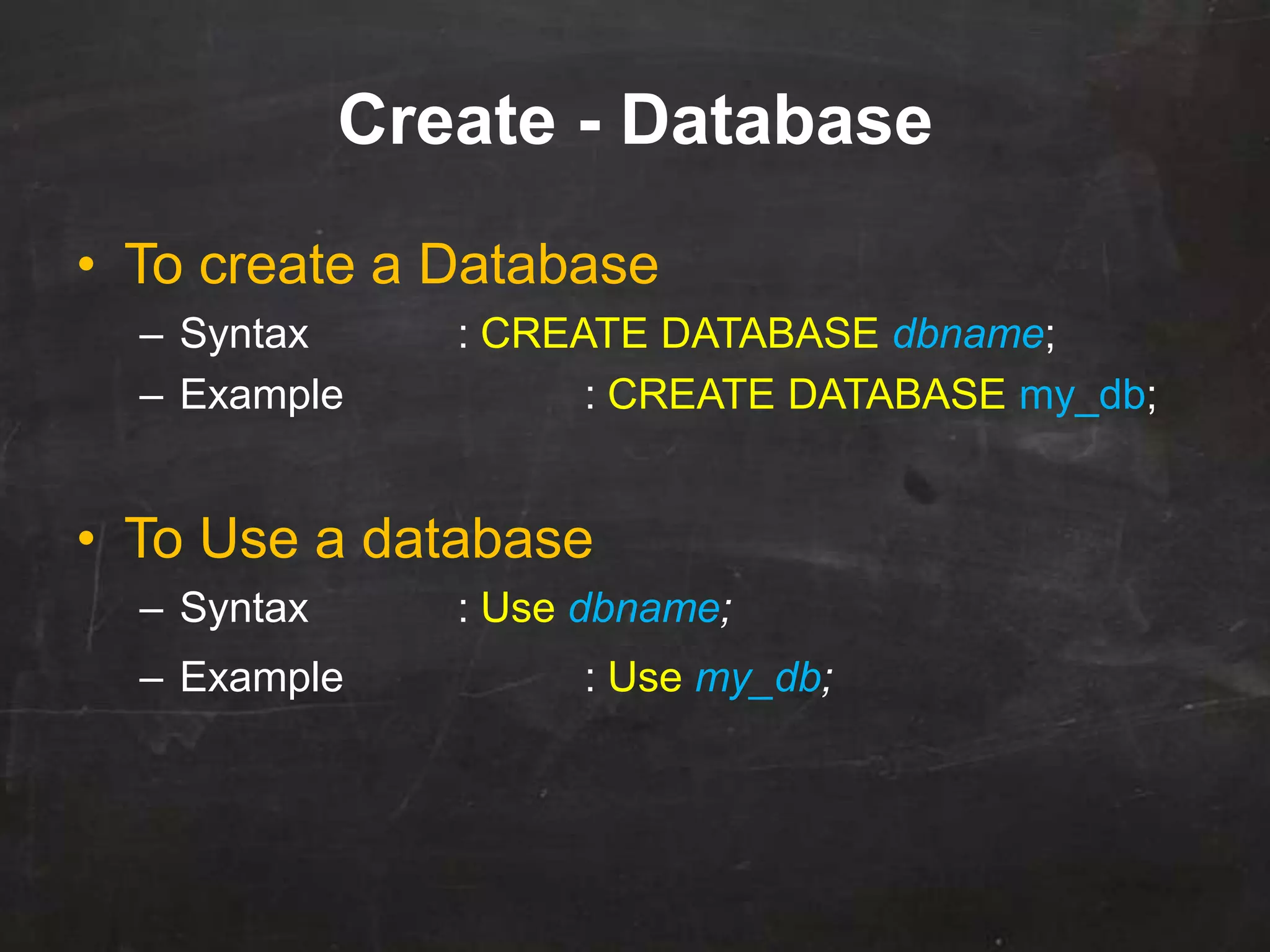
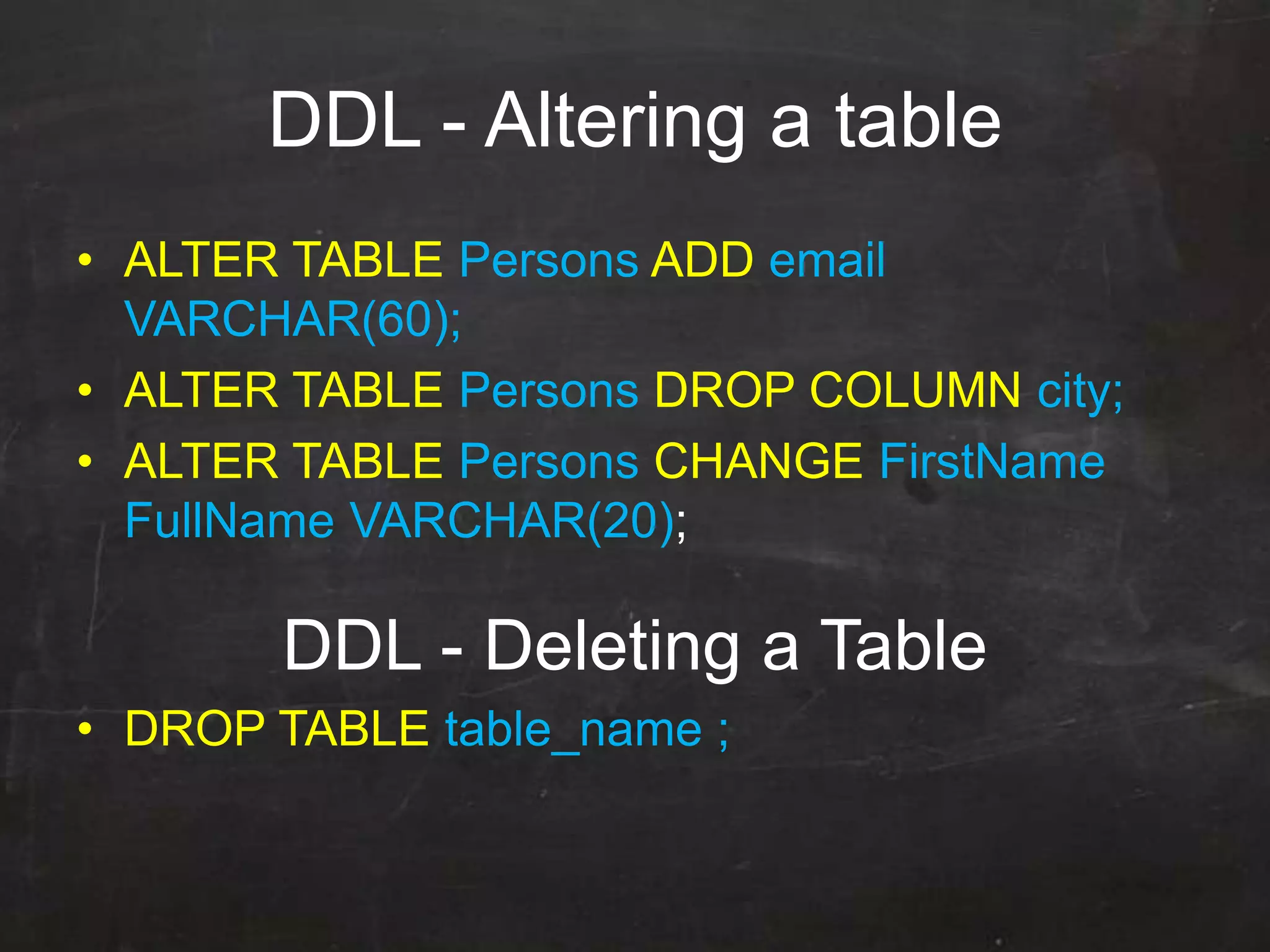
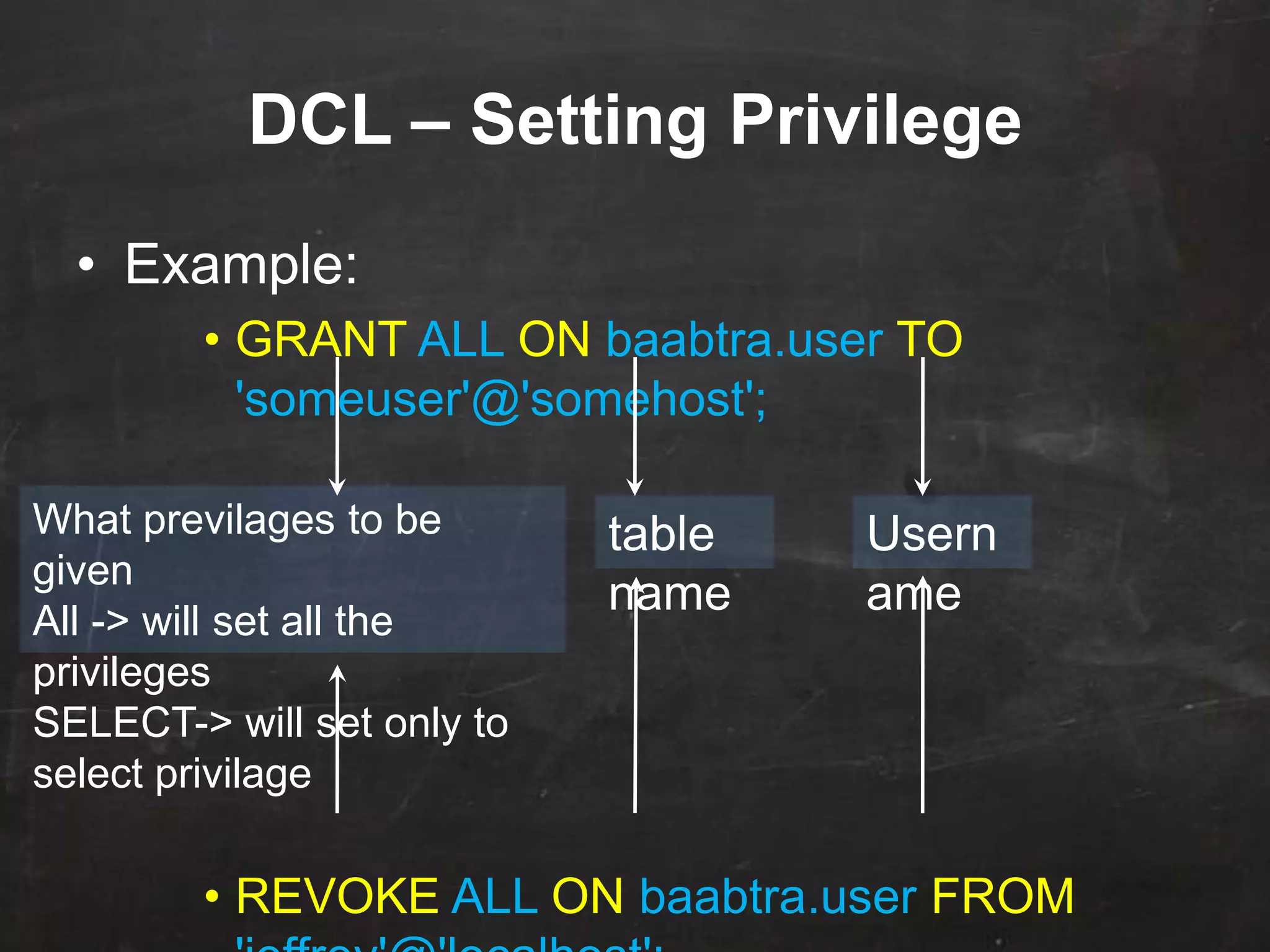
This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS) and MySQL. It defines a database as a collection of organized information that can be quickly accessed by a computer program. A DBMS helps create and manage databases, similar to how MS Word helps create documents. The document discusses the entity-relationship model and how entities are represented as tables with attributes as columns. It provides examples of creating tables, adding primary keys, and linking tables with foreign keys. It also explains the three types of SQL statements - DDL for defining the database structure, DML for managing data, and DCL for controlling access. Specific DDL, DML, and DCL commands are defined along with syntax examples.