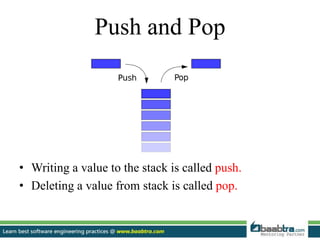
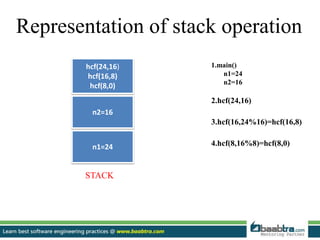
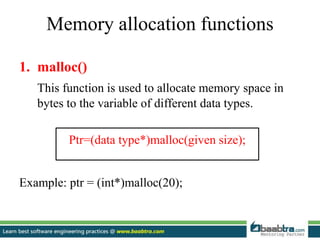
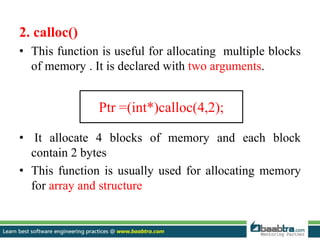
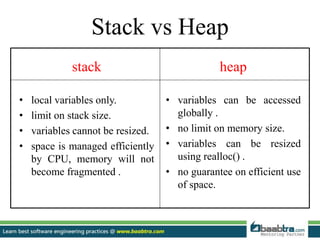
This document discusses stacks and heaps in computer memory. It defines a stack as a linear data structure where items are inserted and deleted from one end in LIFO order. Compiler stores local variables in the stack. Writing to the stack is called push and deleting is called pop. The heap is an area of dynamic memory allocation where space is allocated during program execution using functions like malloc(), calloc(), and realloc(). The stack has limits and fixed-size variables while the heap allows variable resizing and globally accessible variables of arbitrary size.