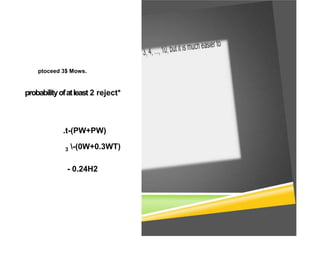
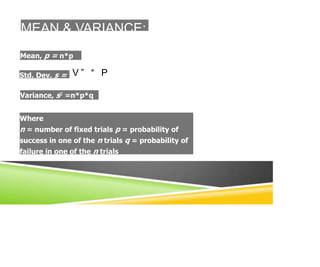
The document discusses the binomial probability distribution, which describes experiments with a fixed number of trials where each trial results in success or failure. The key properties are that the probability of success (p) is constant across trials and trials are independent. Examples show how to calculate the probability of different numbers of successes using the binomial distribution formula. Applications include clinical trials, personality assessments, and quality control.










![EXAMPLE 4:
The ratio of boys to girls at birth in Singapore is quite high at
1.09:1.
What proportion of Singapore families with exactly 6 children
will have at least 3 boys?
(Ignore the probability of multiple births.)
[Interesting and disturbing trivia: In most countries the
ratio of boys to girls is about 1.04:1, but in China it is
1.15:1.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binomialprobabilitydistribution-160303055131-230507101947-3040aa27/85/binomialprobabilitydistribution-160303055131-ppt-13-320.jpg)