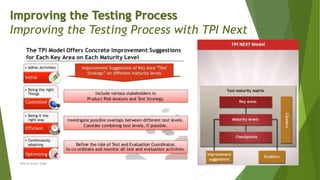
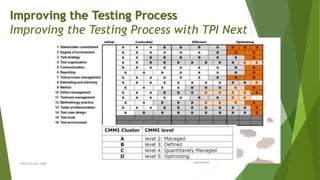
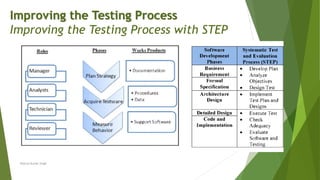
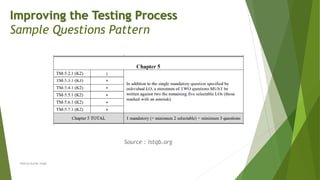
The document discusses the continuous improvement of software testing processes, emphasizing the role of test managers in implementing industry-accepted improvement models like TMMi, TPI Next, CTP, and STEP. Each model provides structured approaches for assessing and enhancing testing effectiveness, aiming to increase maturity and reduce costs associated with software testing. The text highlights the need for organizations to adopt a methodical approach to evaluation and improvement of their testing processes to ensure high-quality software deliverables.