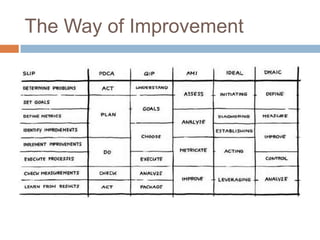
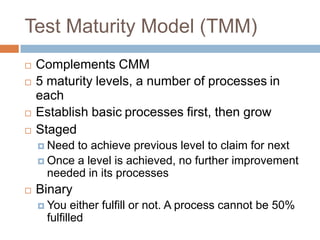
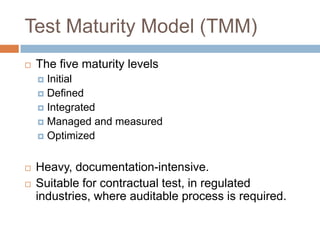
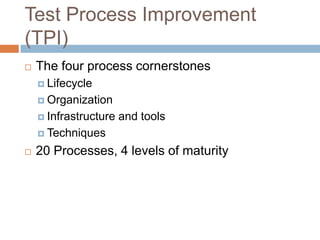
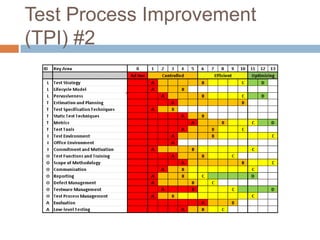
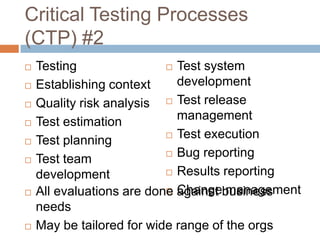
This document provides an overview of several test process improvement frameworks: Test Maturity Model (TMM), Test Process Improvement (TPI), Critical Testing Processes (CTP), and Systematic Test and Evaluation Process (STEP). TMM defines 5 maturity levels for testing processes. TPI focuses on 4 process cornerstones and allows incremental improvement. CTP identifies attributes of critical testing processes. STEP assesses test planning, implementation, and measurement with qualitative and quantitative metrics.