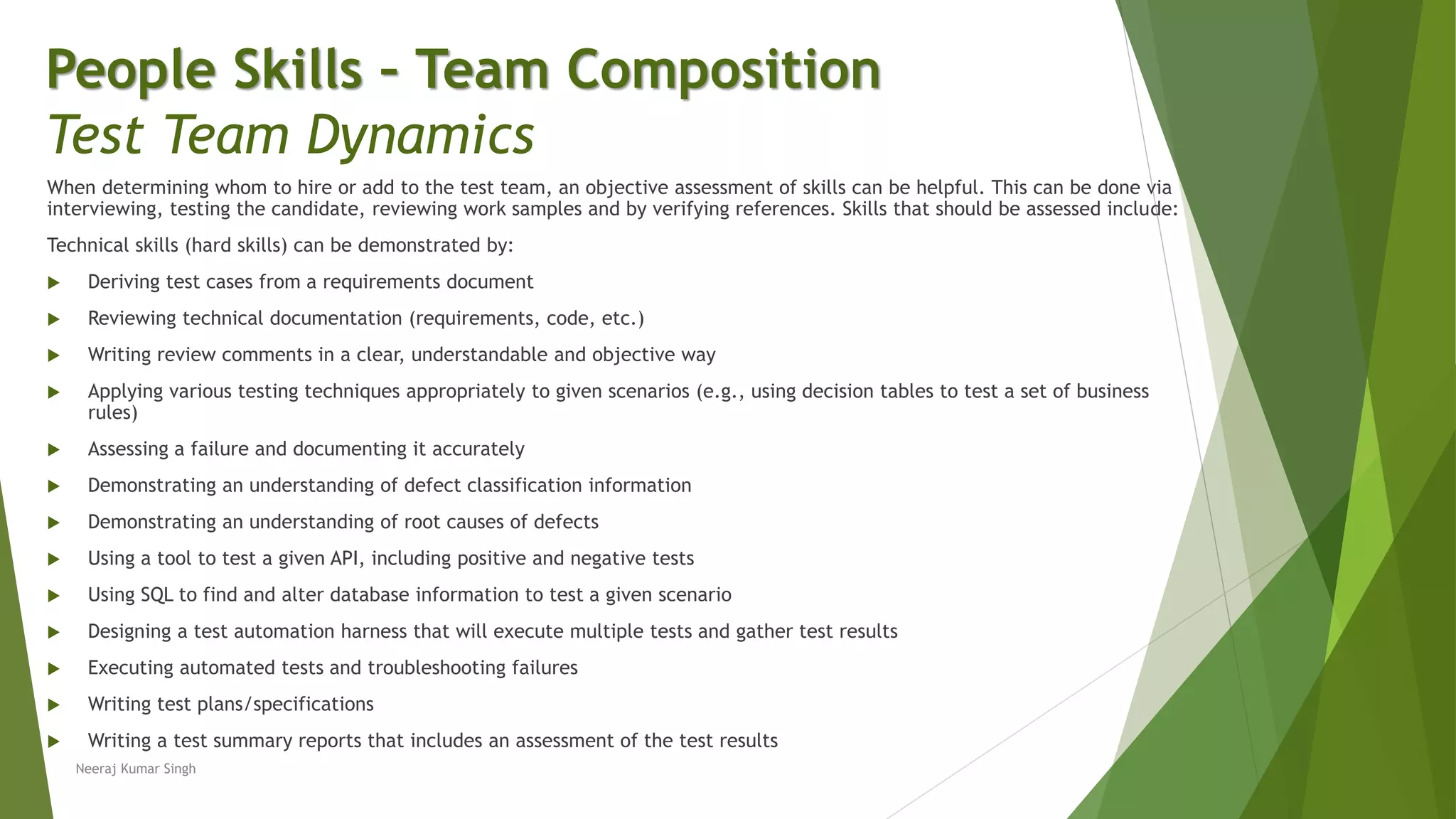
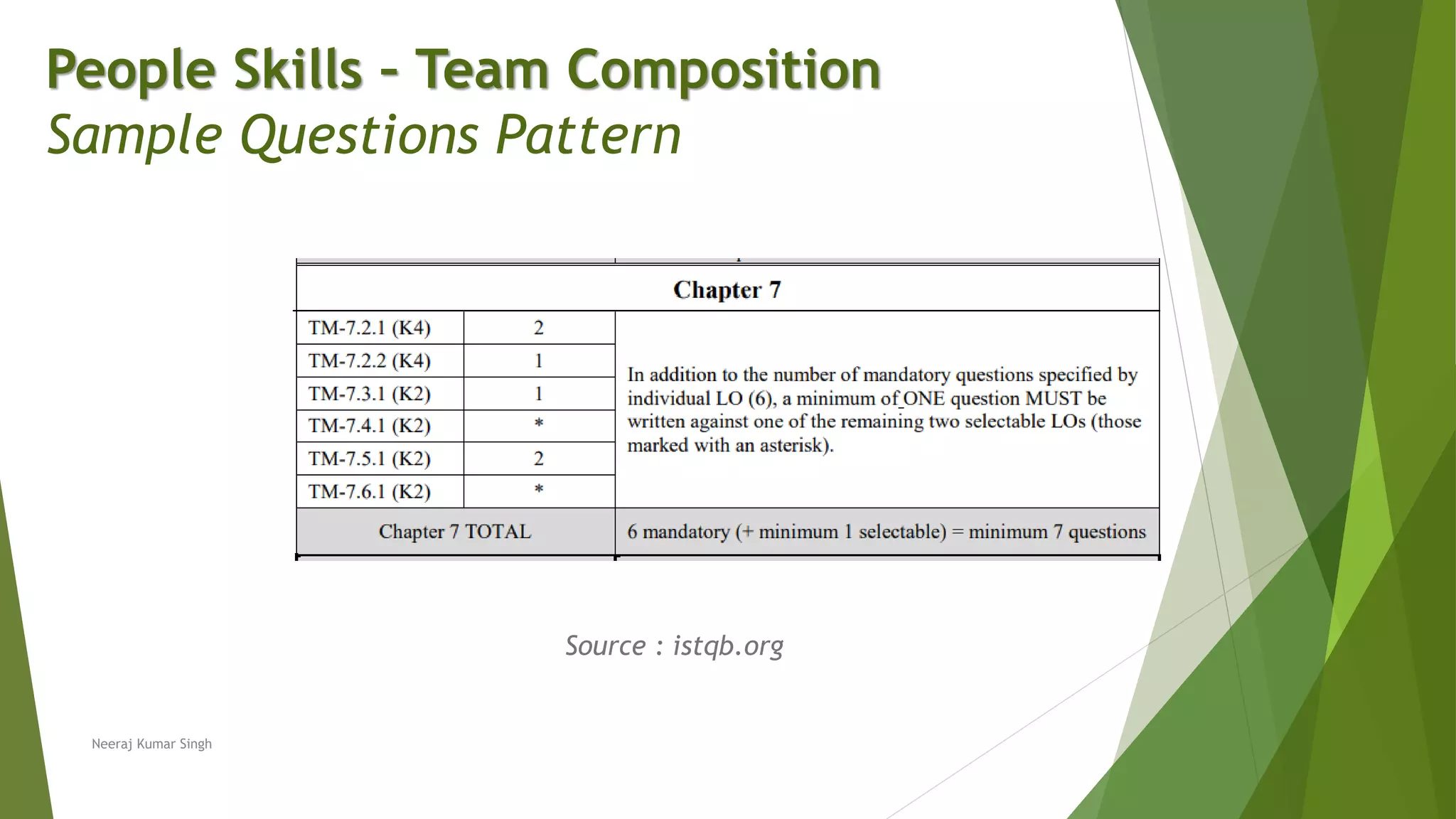
The document discusses the importance of people skills in test team composition and the role of test managers in recruiting, training, and retaining team members with the right mix of skills. It emphasizes assessing individual skills, maintaining effective communication, and motivating team members to achieve peak performance amidst high-pressure environments. Additionally, it highlights the need for understanding team dynamics and fitting testing within an organization to enhance overall software quality.