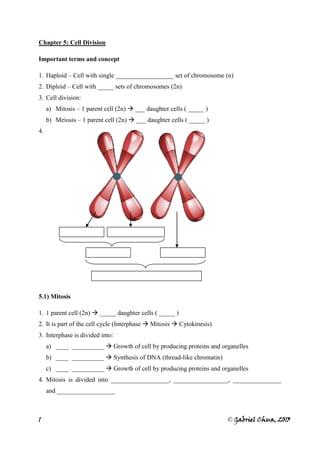
1. The document discusses cell division through mitosis and meiosis.
2. Mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cell and is important for growth, repair of damaged cells, and asexual reproduction. Meiosis produces four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes, and is important for sexual reproduction.
3. The key differences between mitosis and meiosis include the number of divisions, number of daughter cells produced, ploidy of daughter cells, and role in sexual versus asexual reproduction.