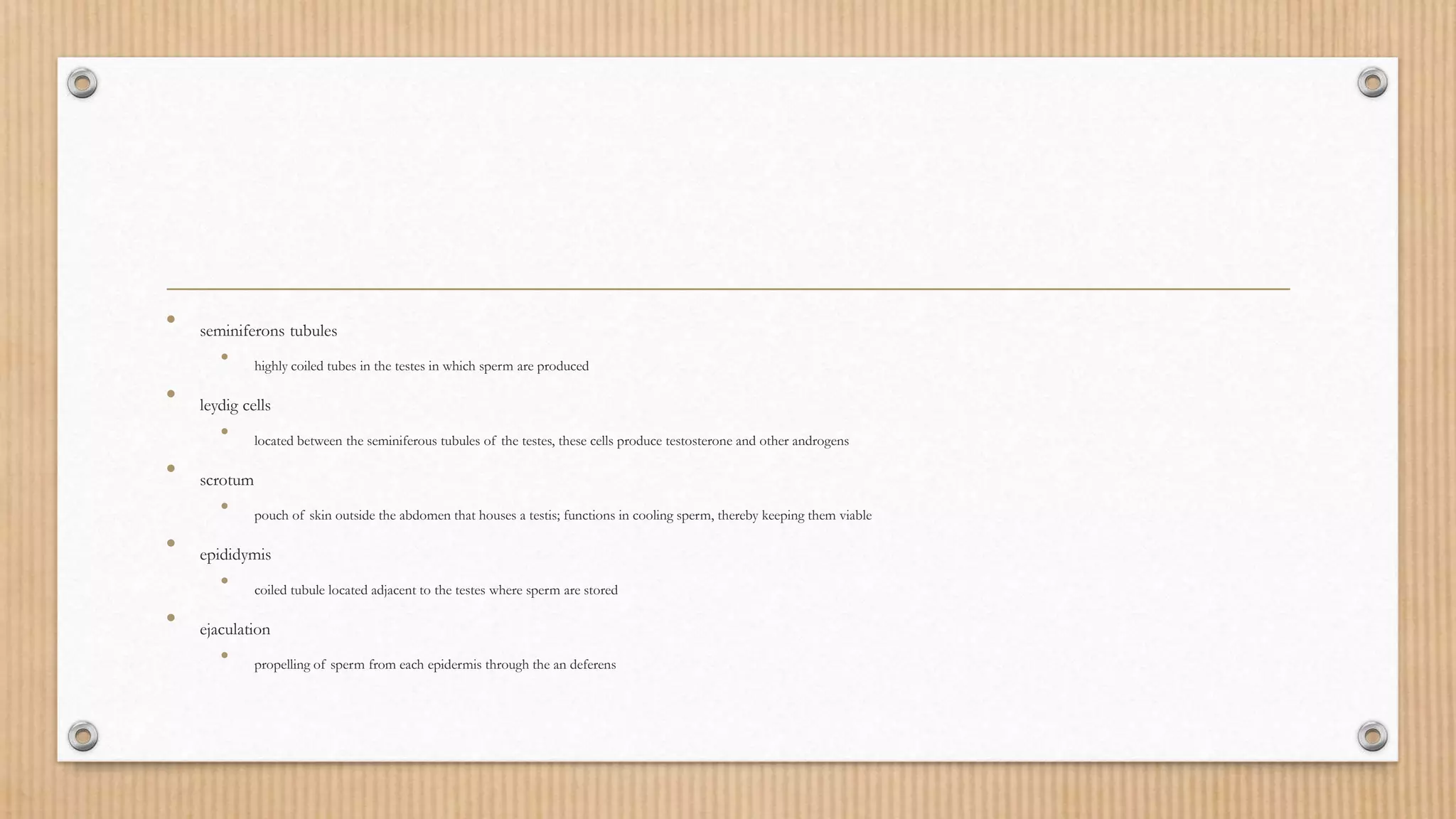
Sexual and asexual reproduction are the two main types of reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes to form offspring, while asexual reproduction requires only one individual and creates offspring without gamete fusion. Examples of asexual reproduction include budding, where new individuals arise from outgrowths of existing ones. Sexual reproduction can involve external fertilization, where eggs and sperm fuse outside the body, or internal fertilization within the female reproductive tract. Pregnancy in humans involves three trimesters of fetal development, labor and birth in the third trimester, and potential lactation afterwards. Contraception aims to prevent pregnancy through methods that block the release of eggs and sperm, keep them apart,