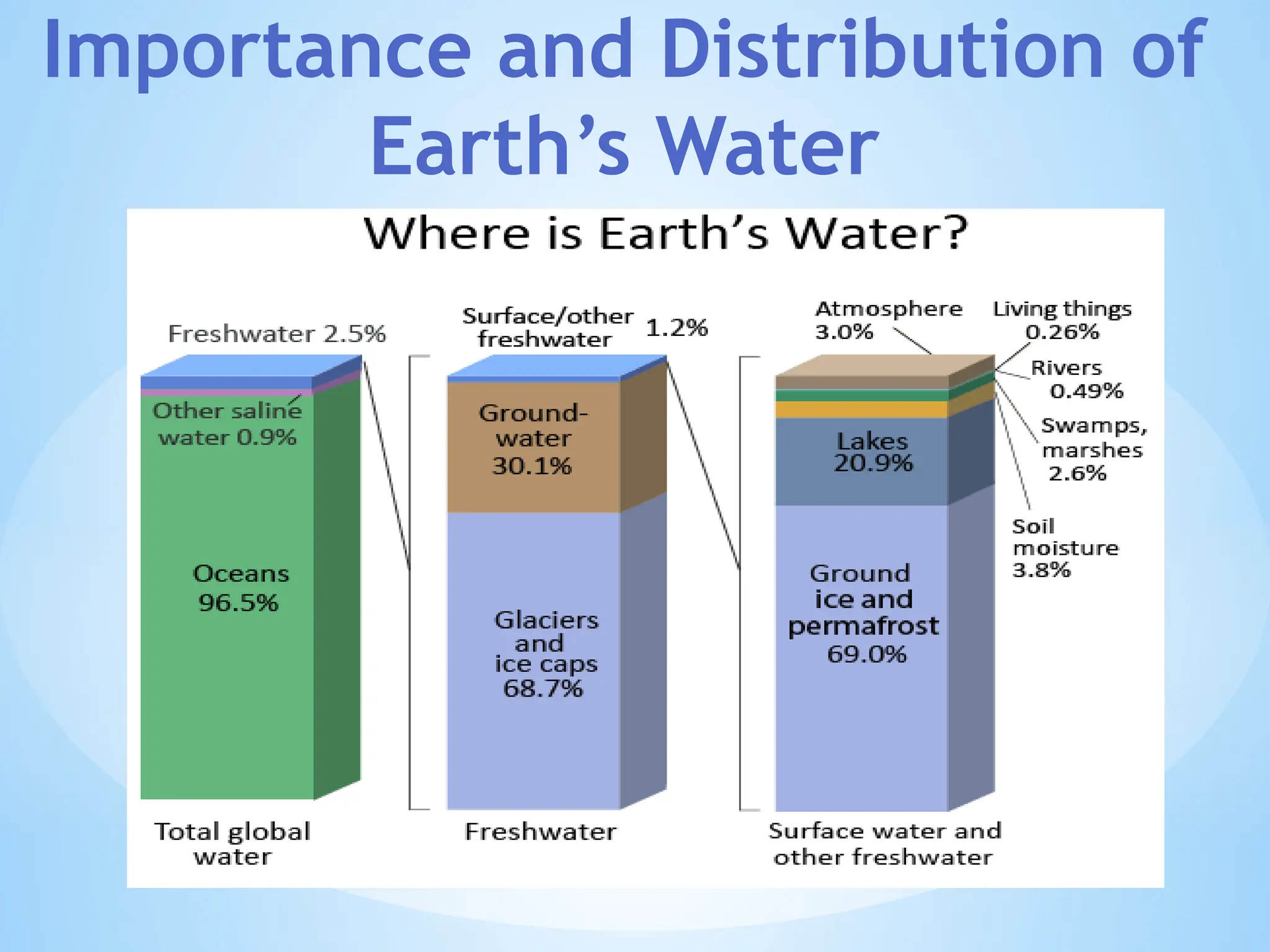
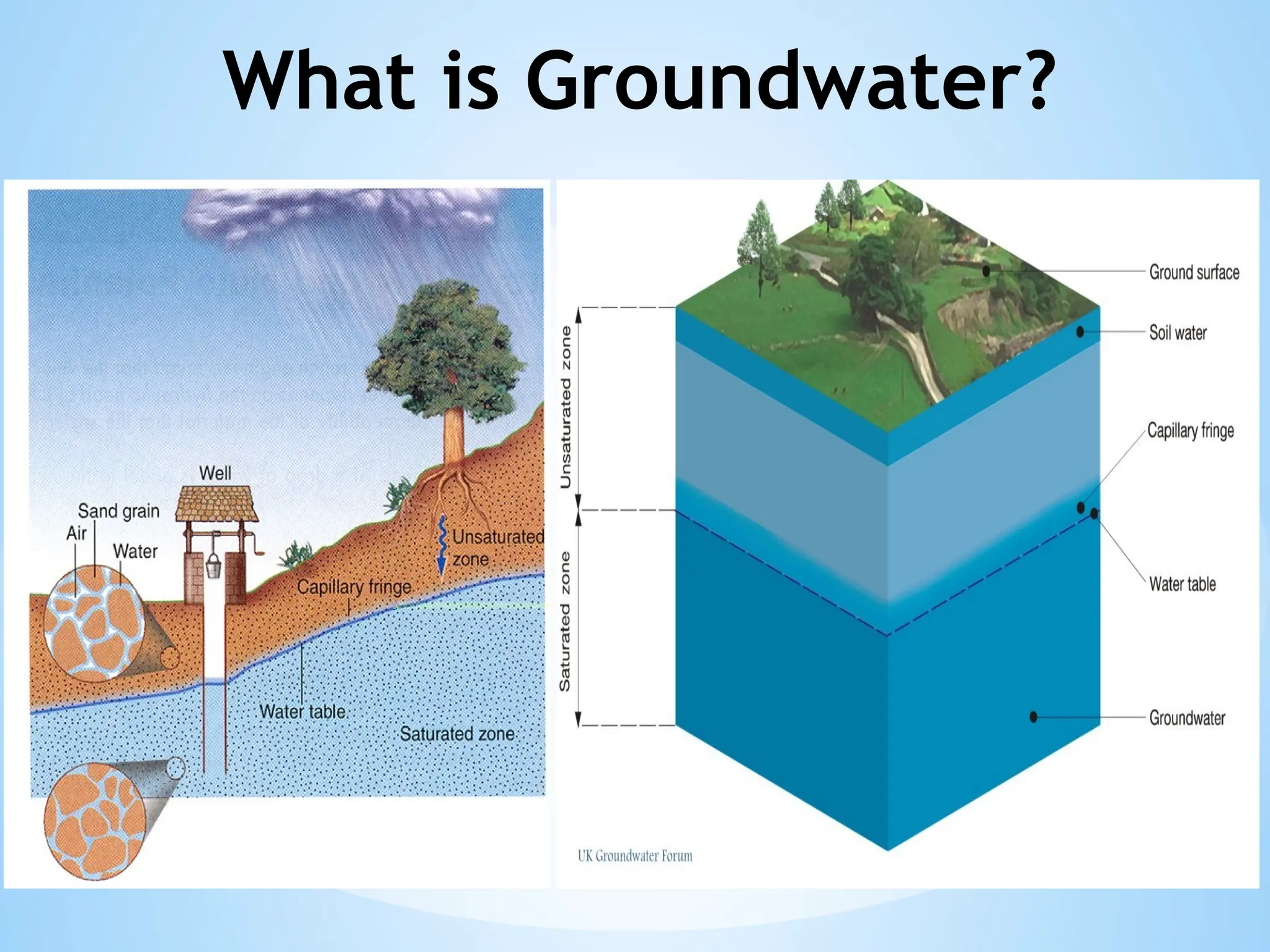
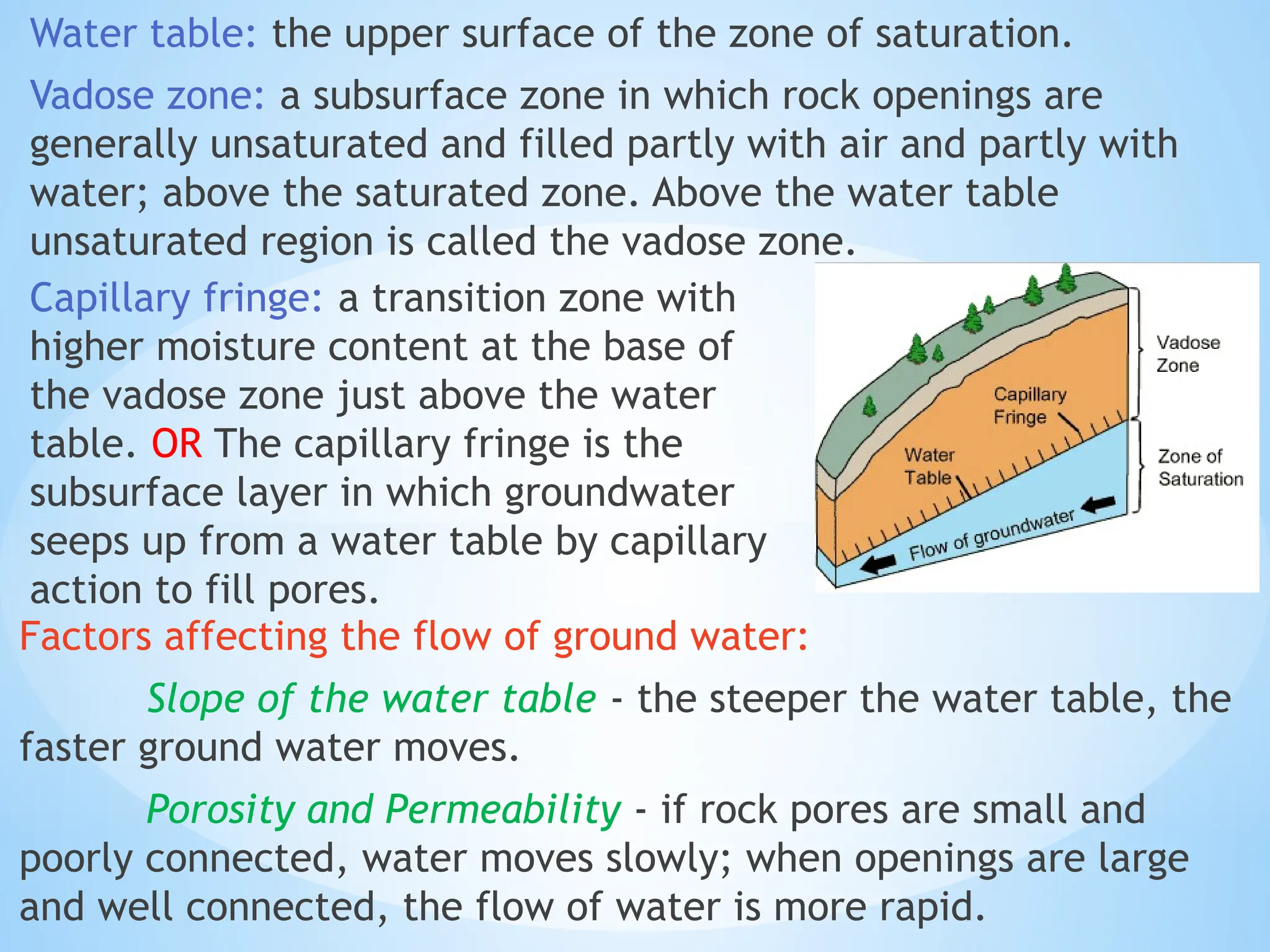
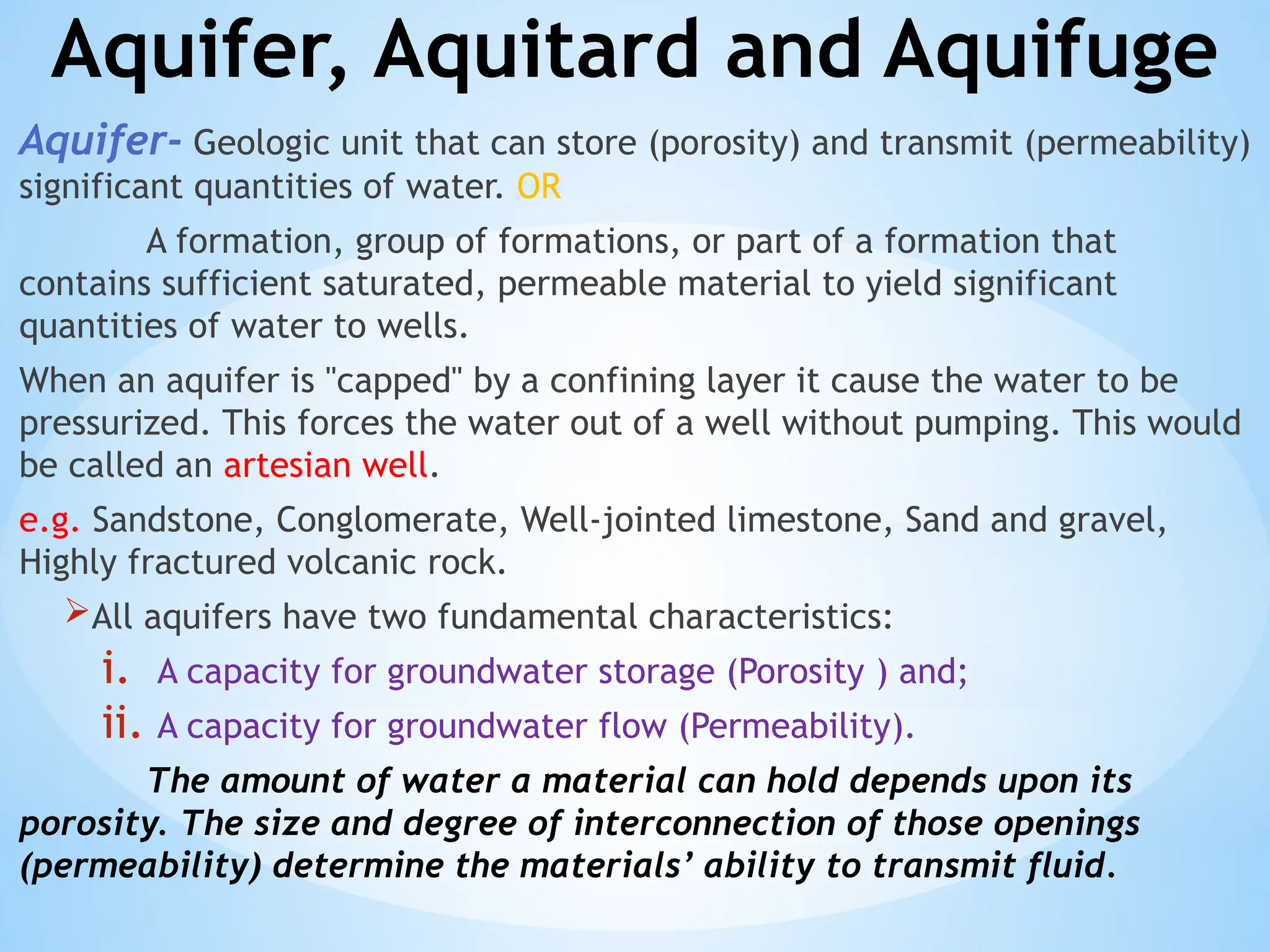
Hydrogeology is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust. It combines aspects of hydrology (the study of water) and geology (the study of Earth materials).
Here are the key concepts in hydrogeology:
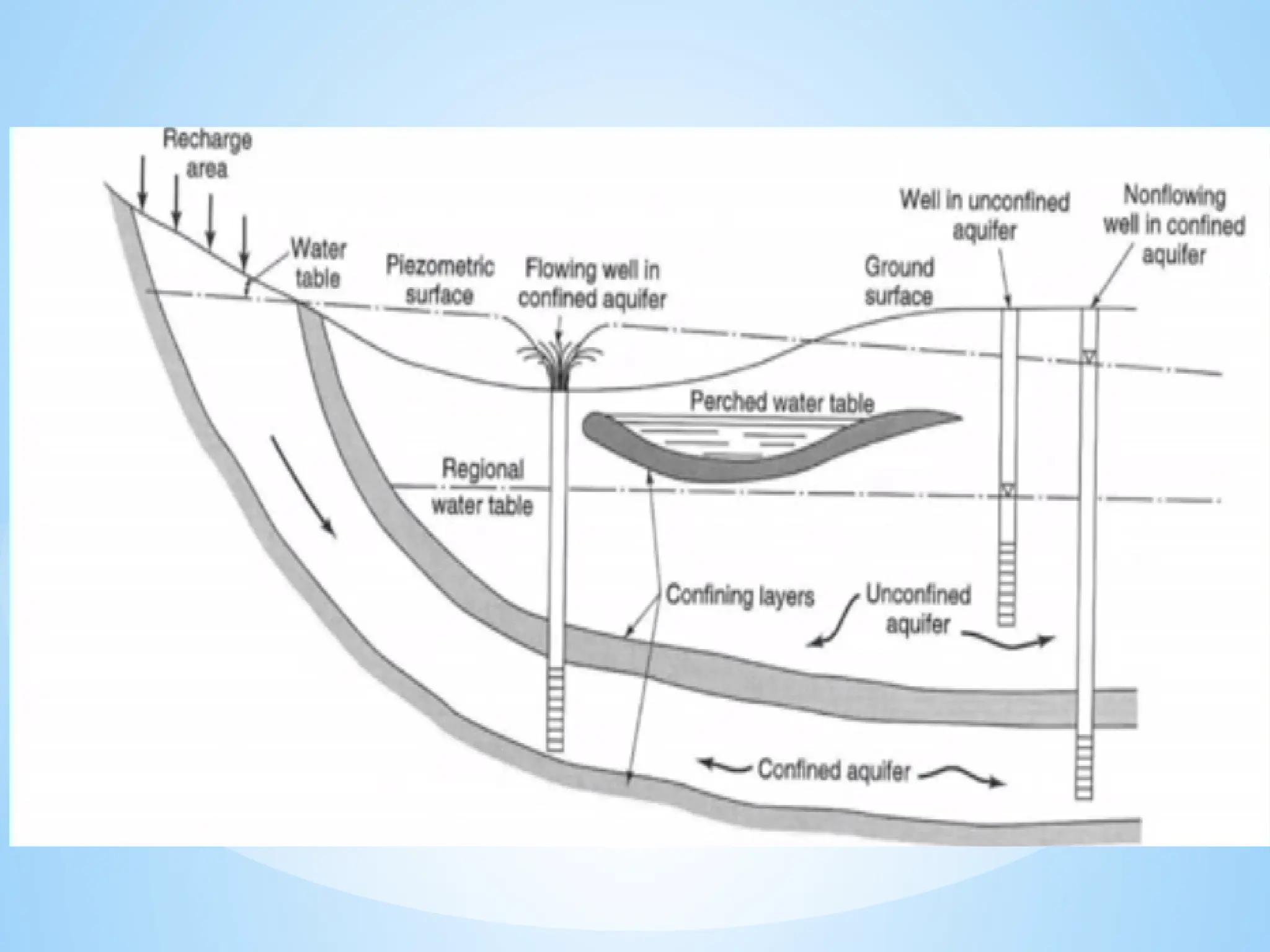
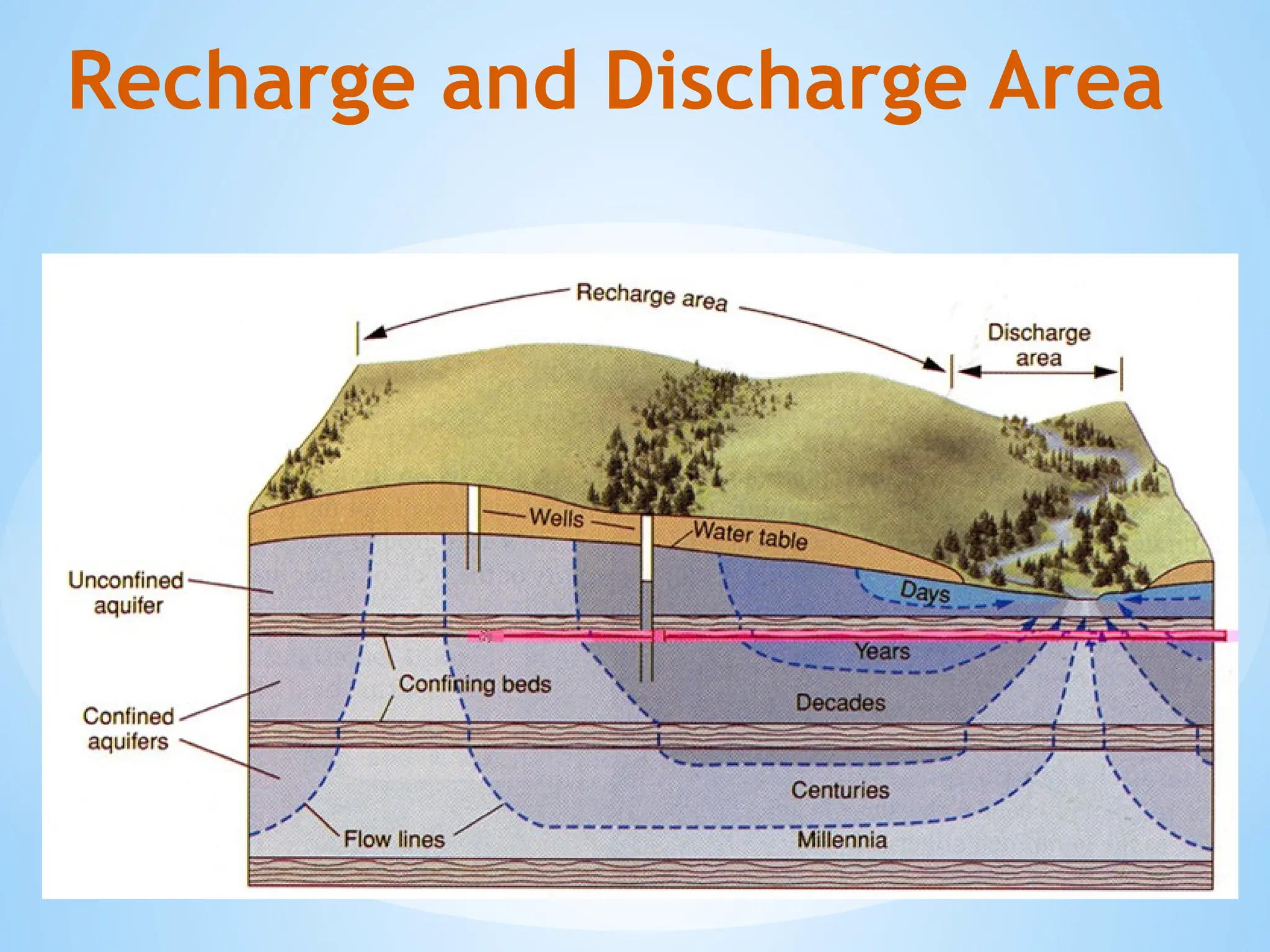
1. Aquifers: Rock or sediment layers that hold and transmit groundwater.
Unconfined aquifer: Water table is open to the atmosphere.
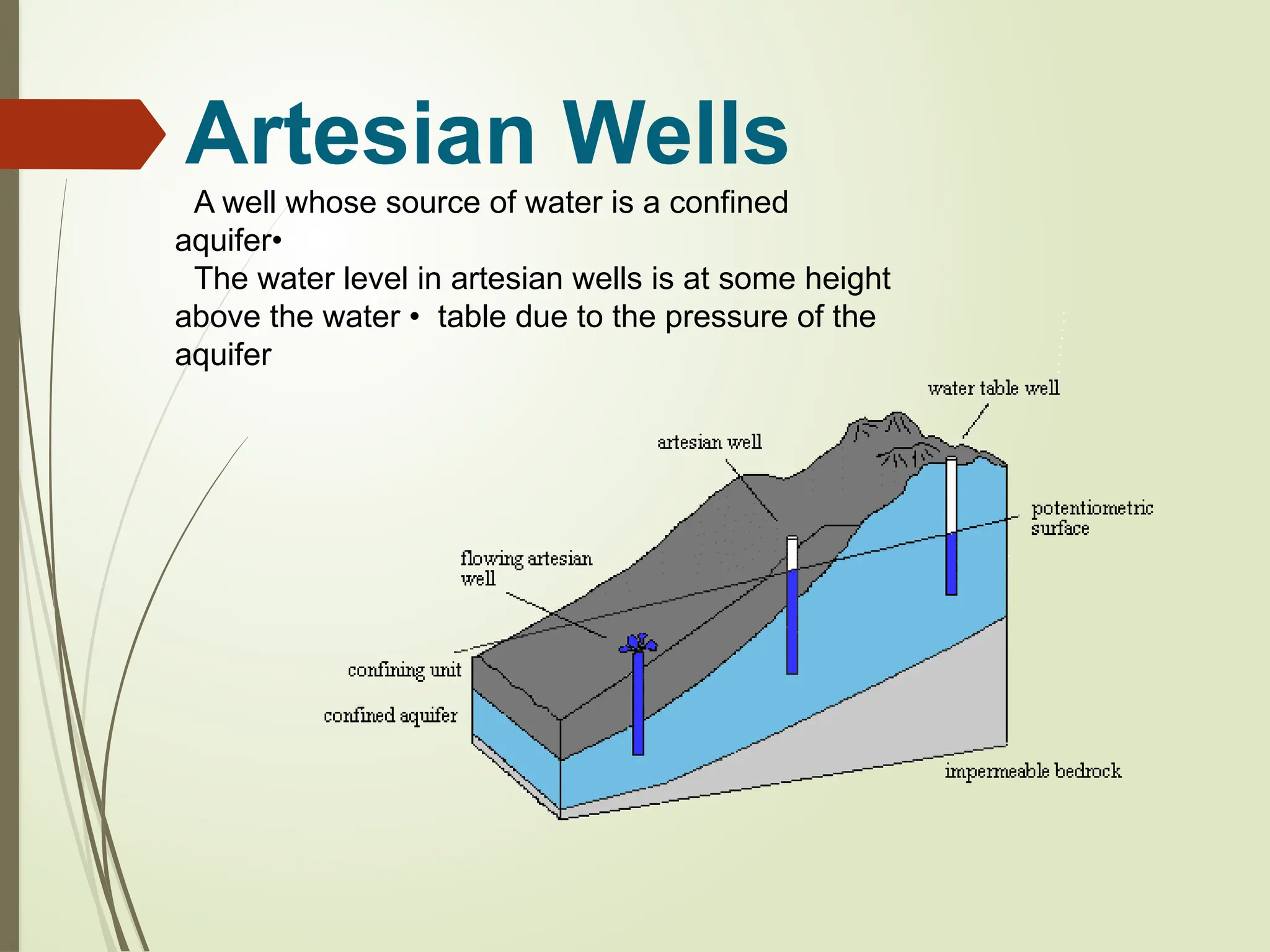
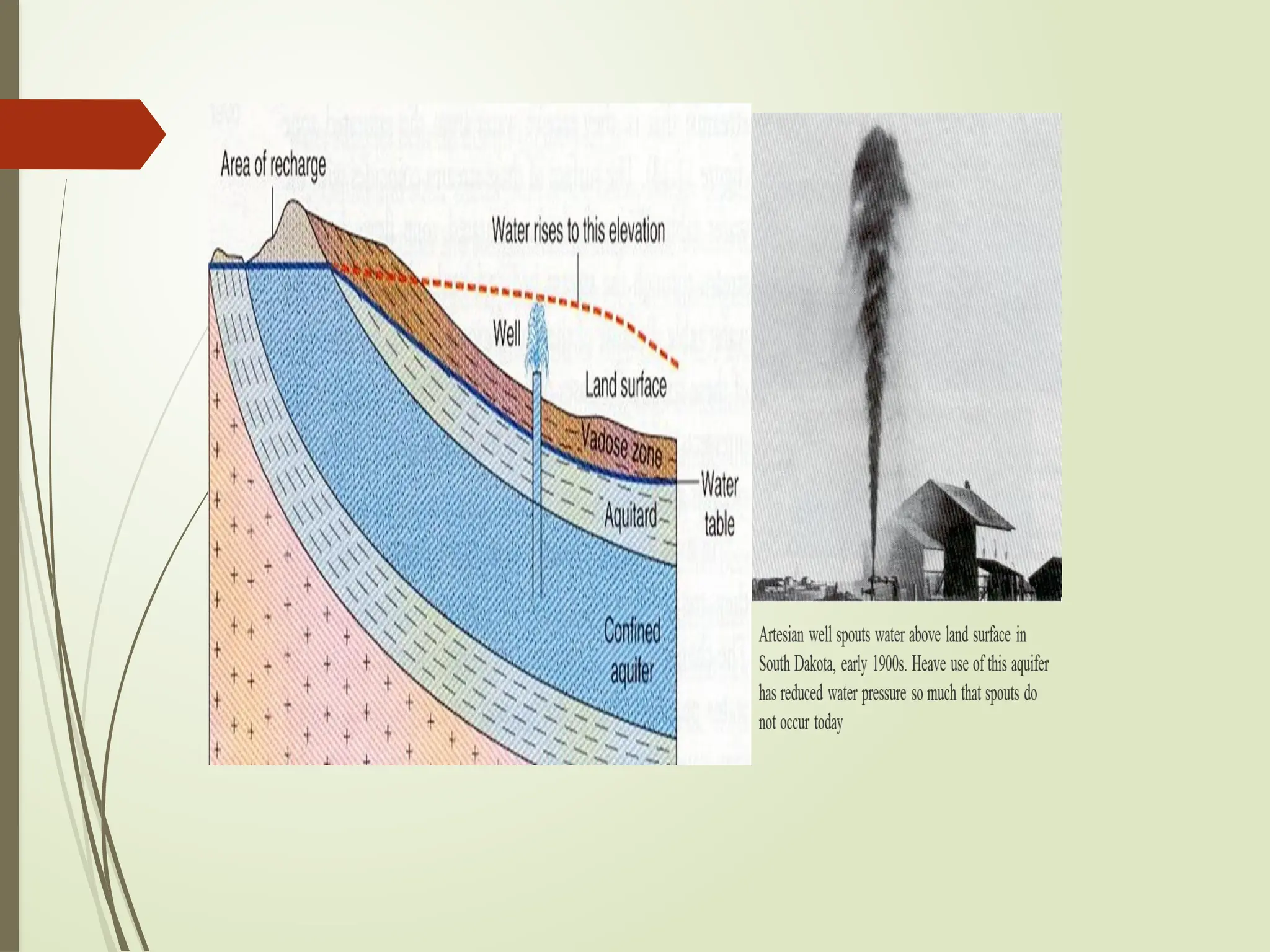
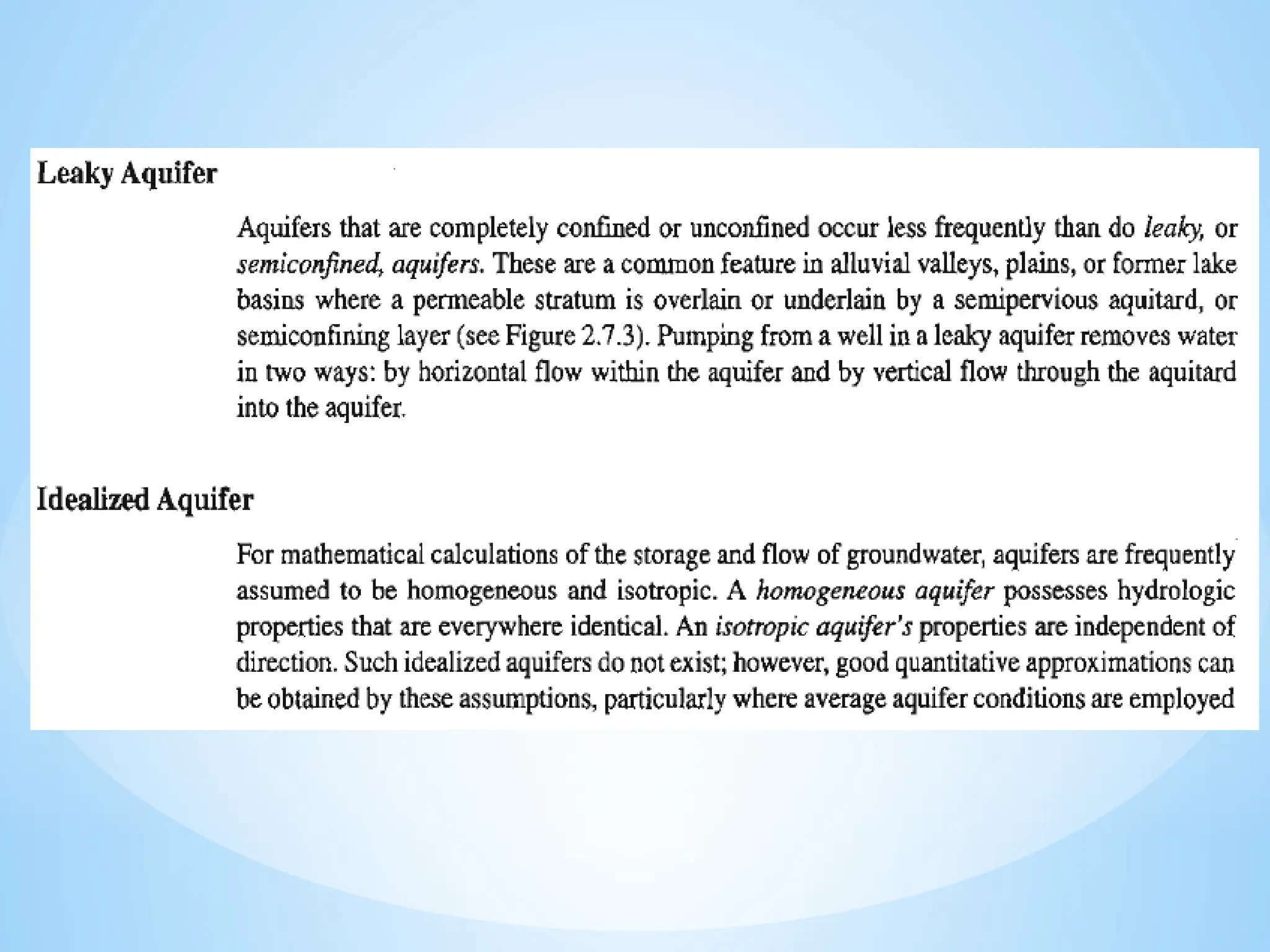
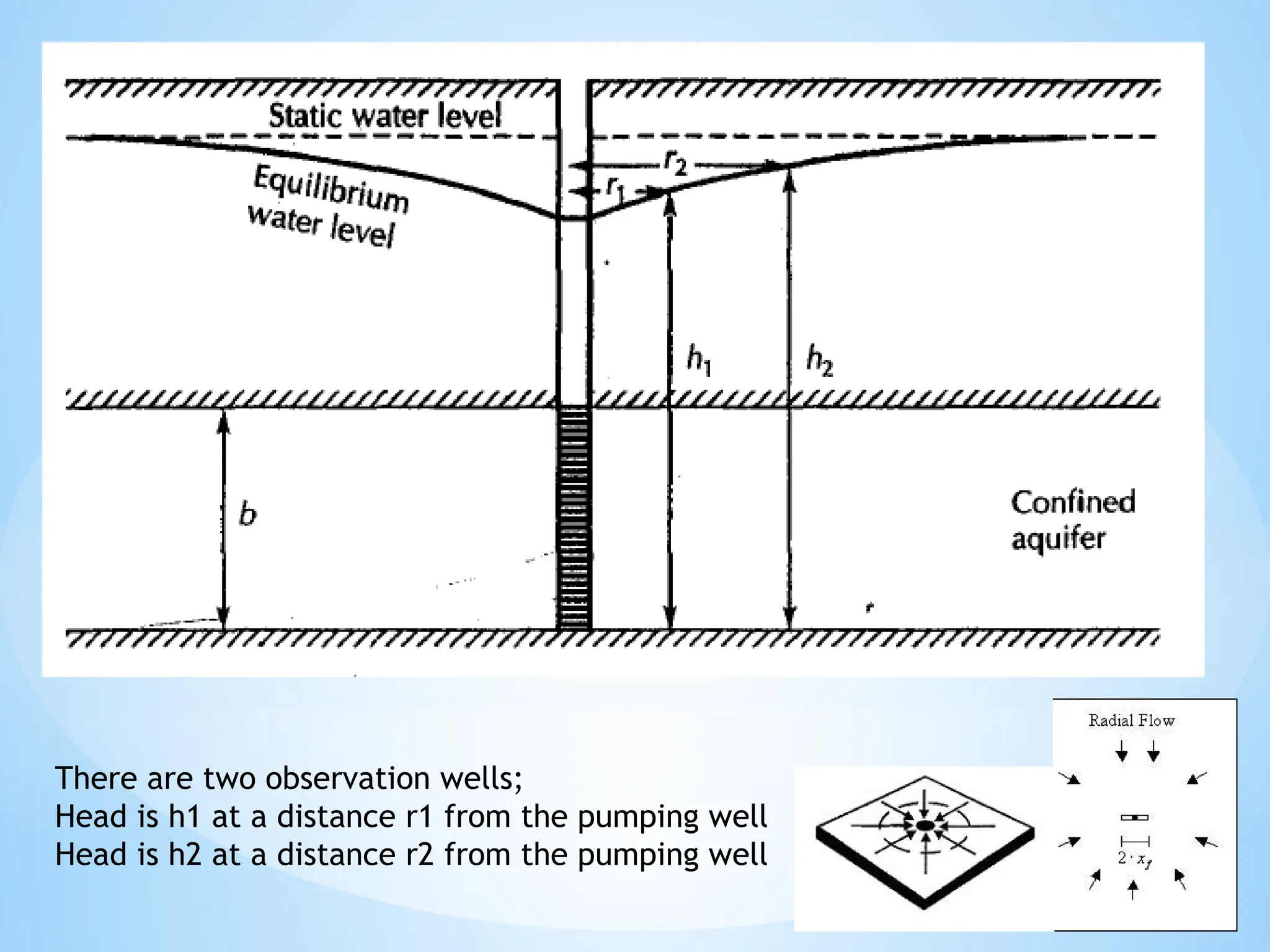
Confined aquifer: Water is under pressure between two impermeable layers.
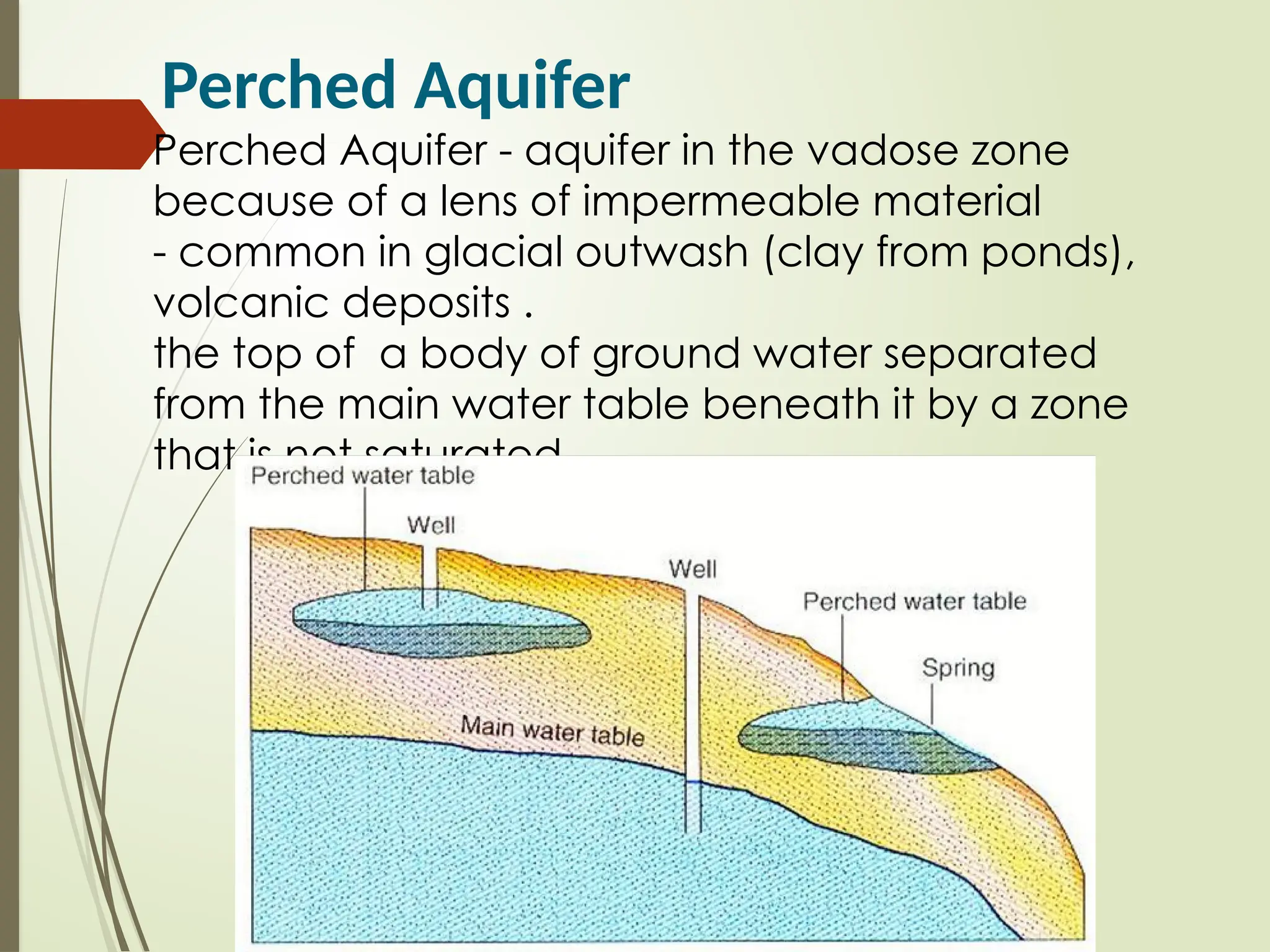
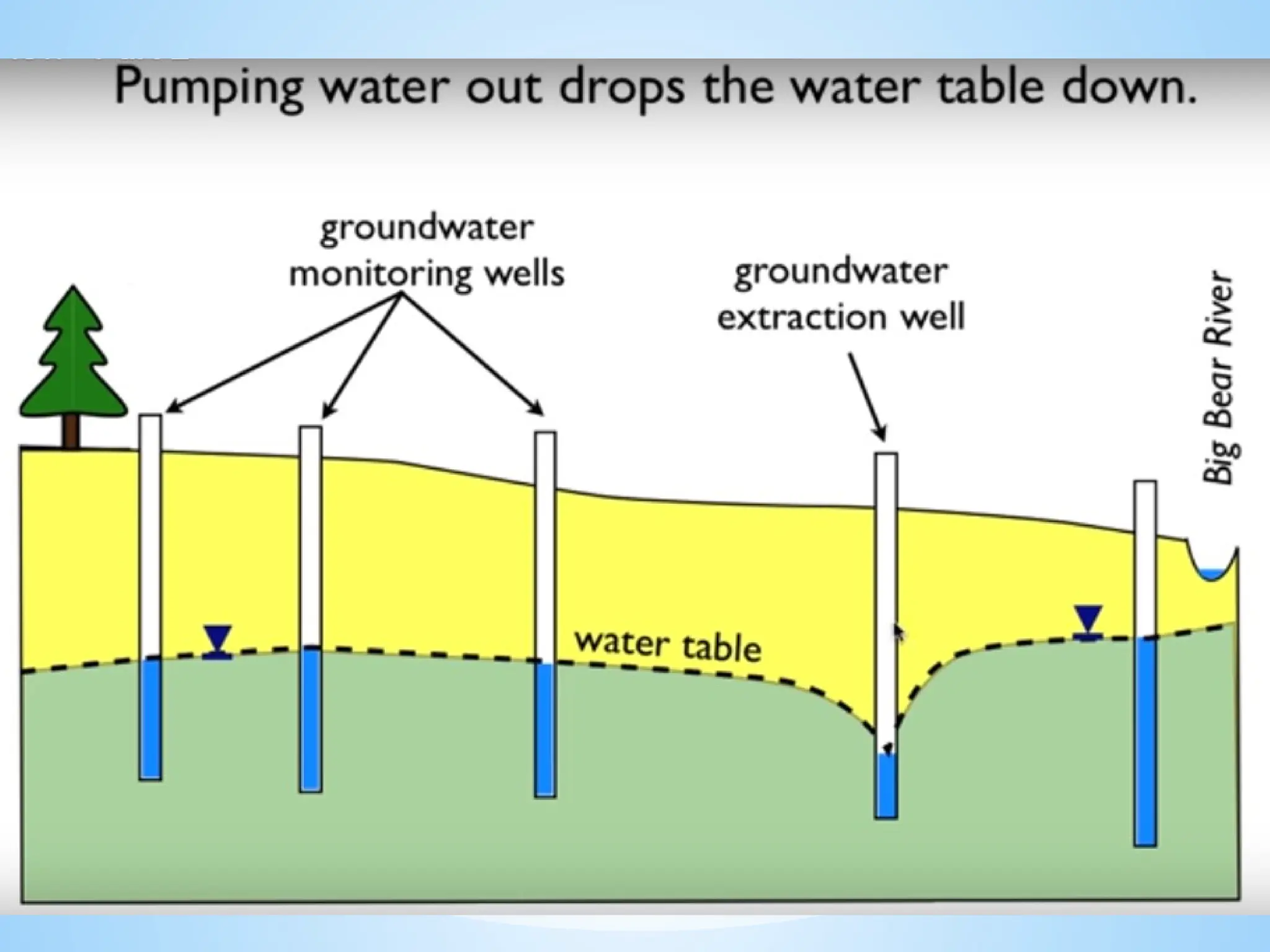
2. Water Table: The upper level of an underground surface in which the soil or rocks are permanently saturated with water.
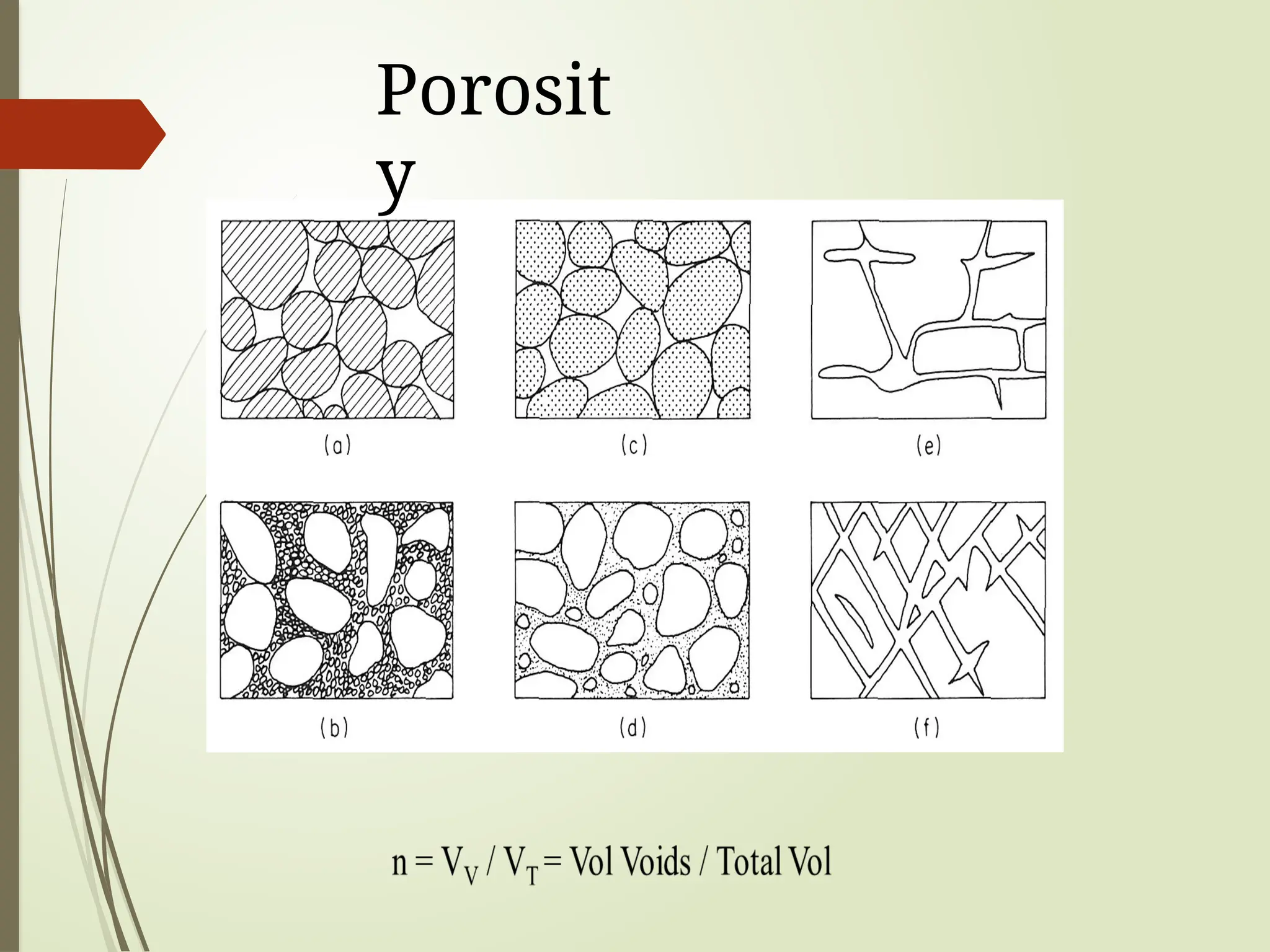
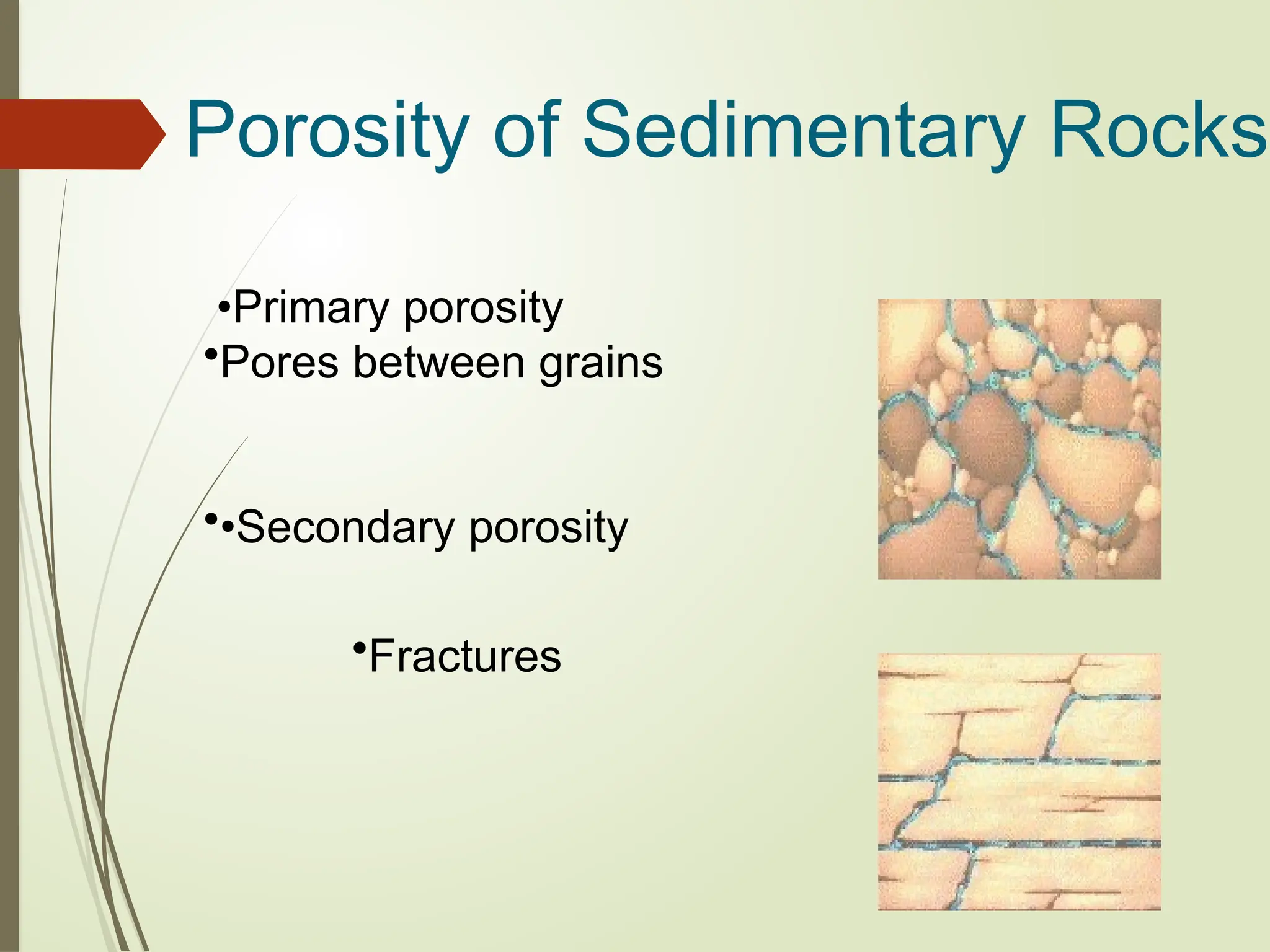
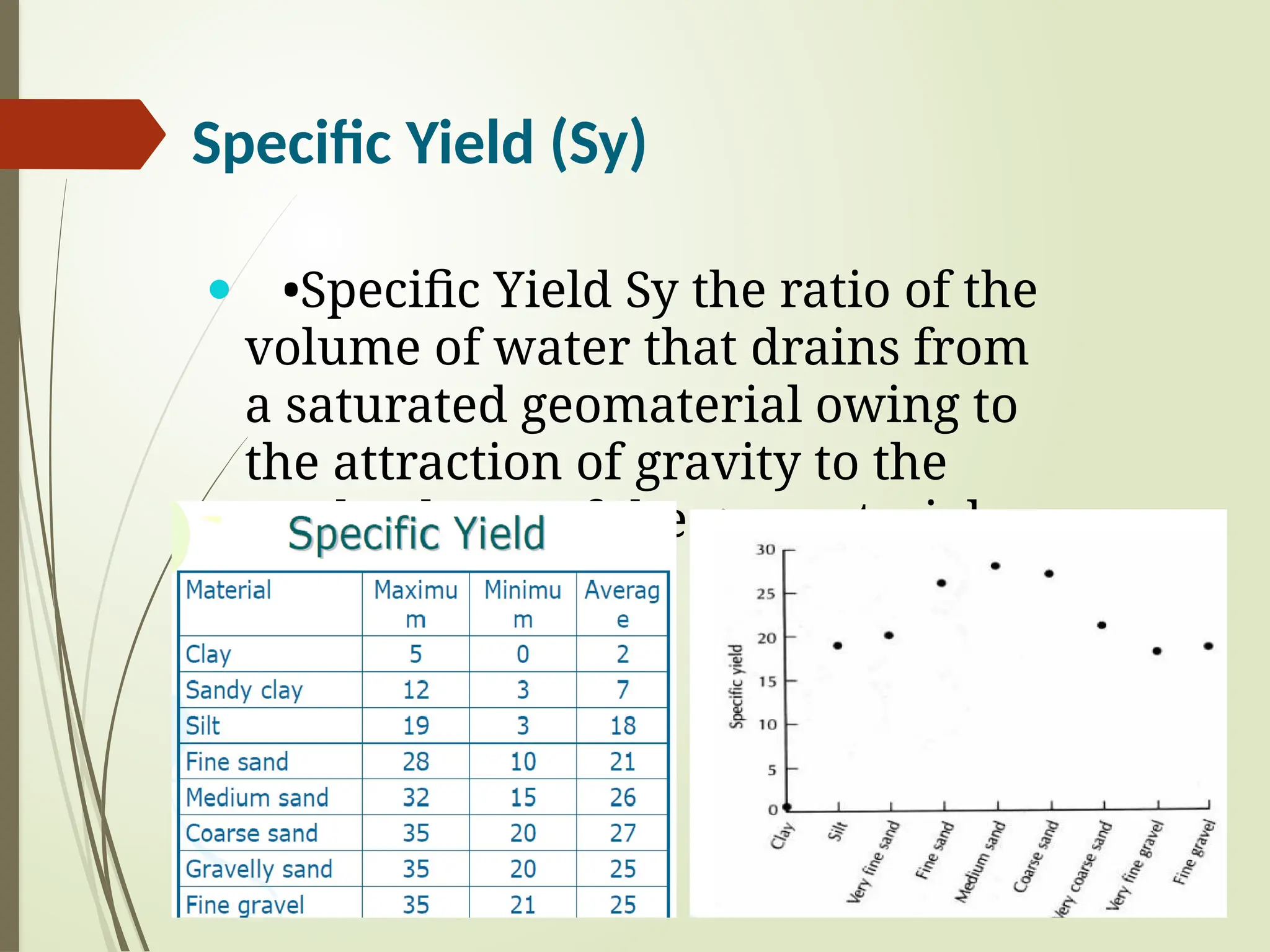
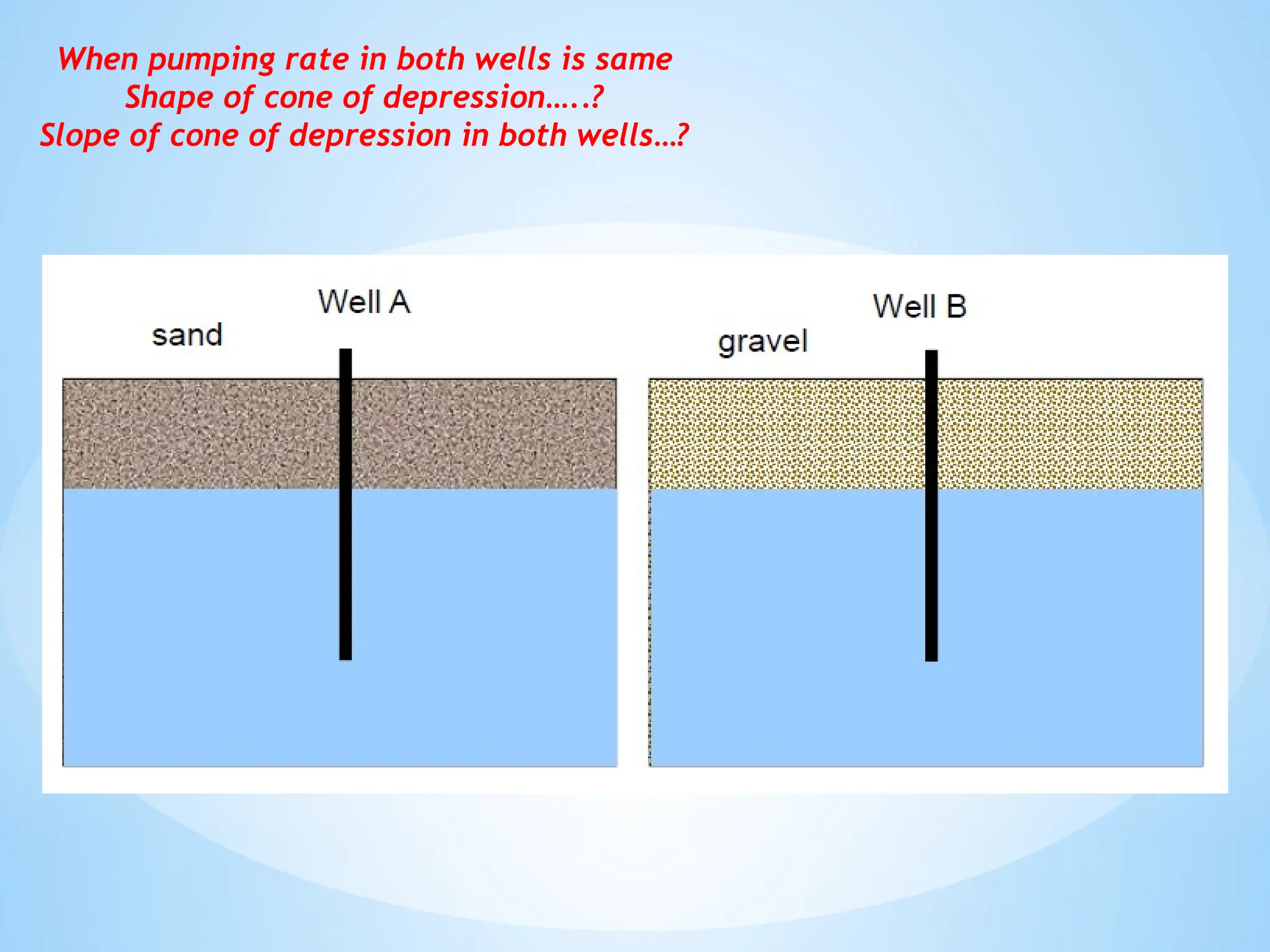
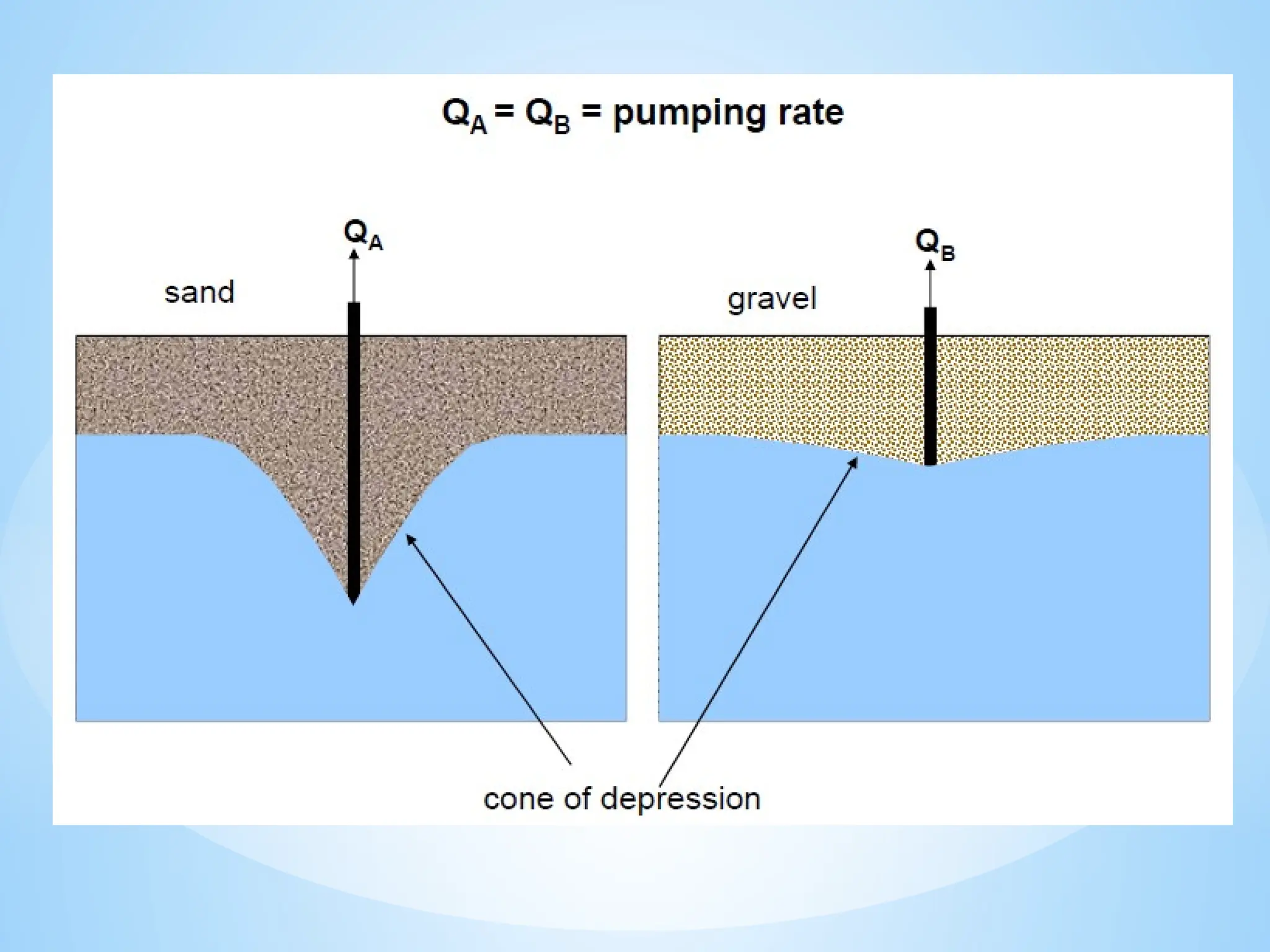
3. Porosity: The percentage of void space in a rock or soil that can hold water.
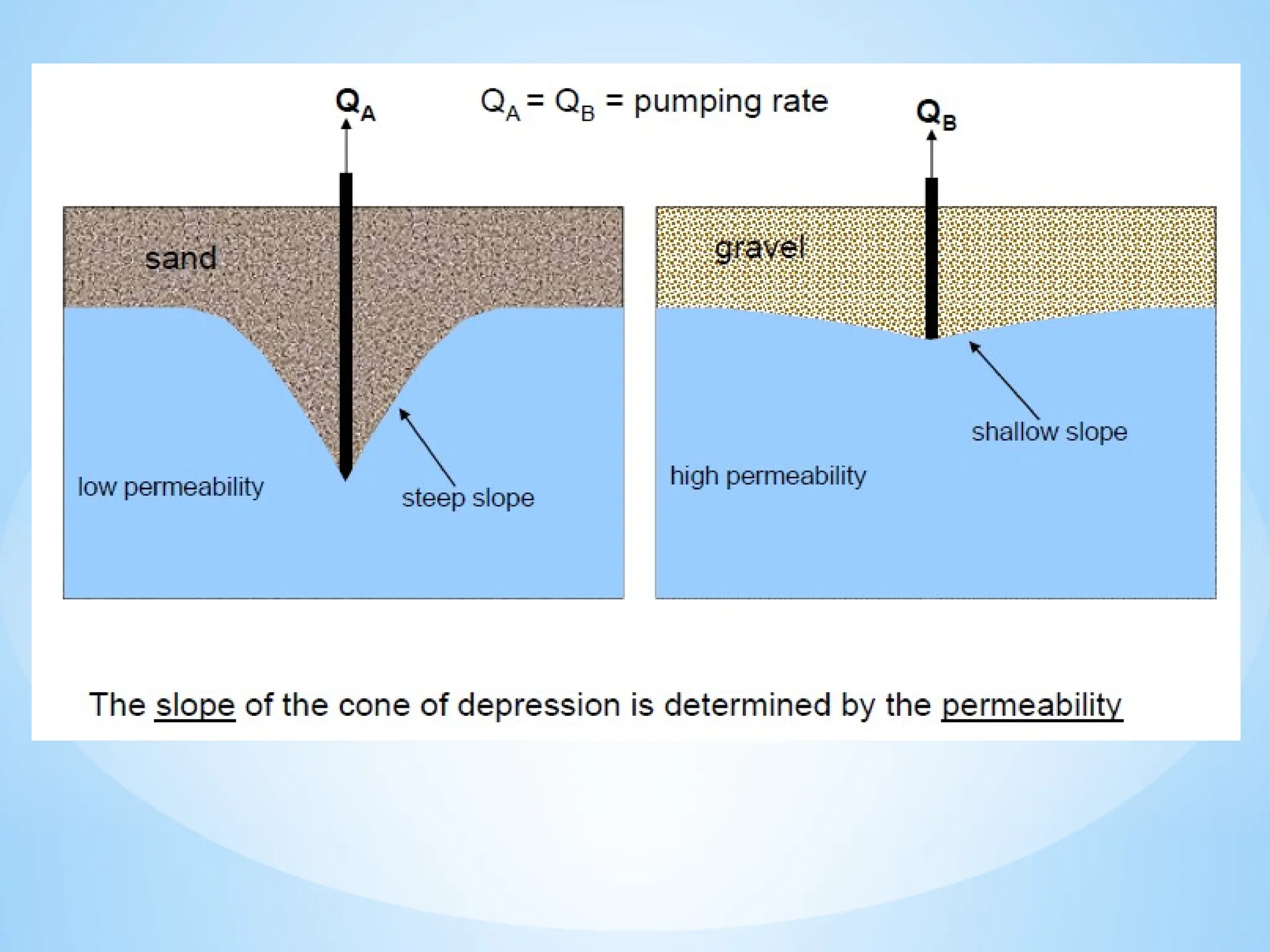
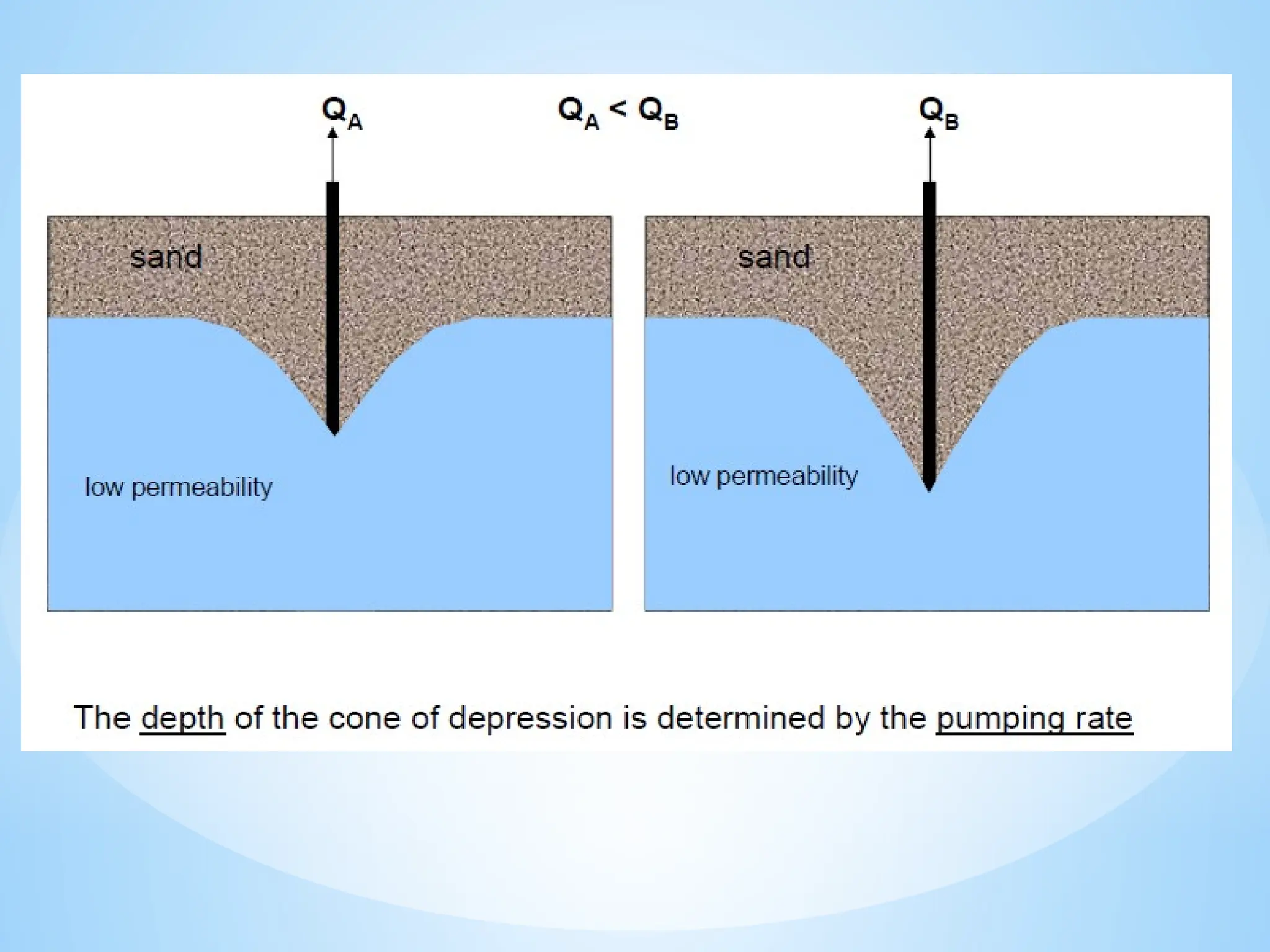
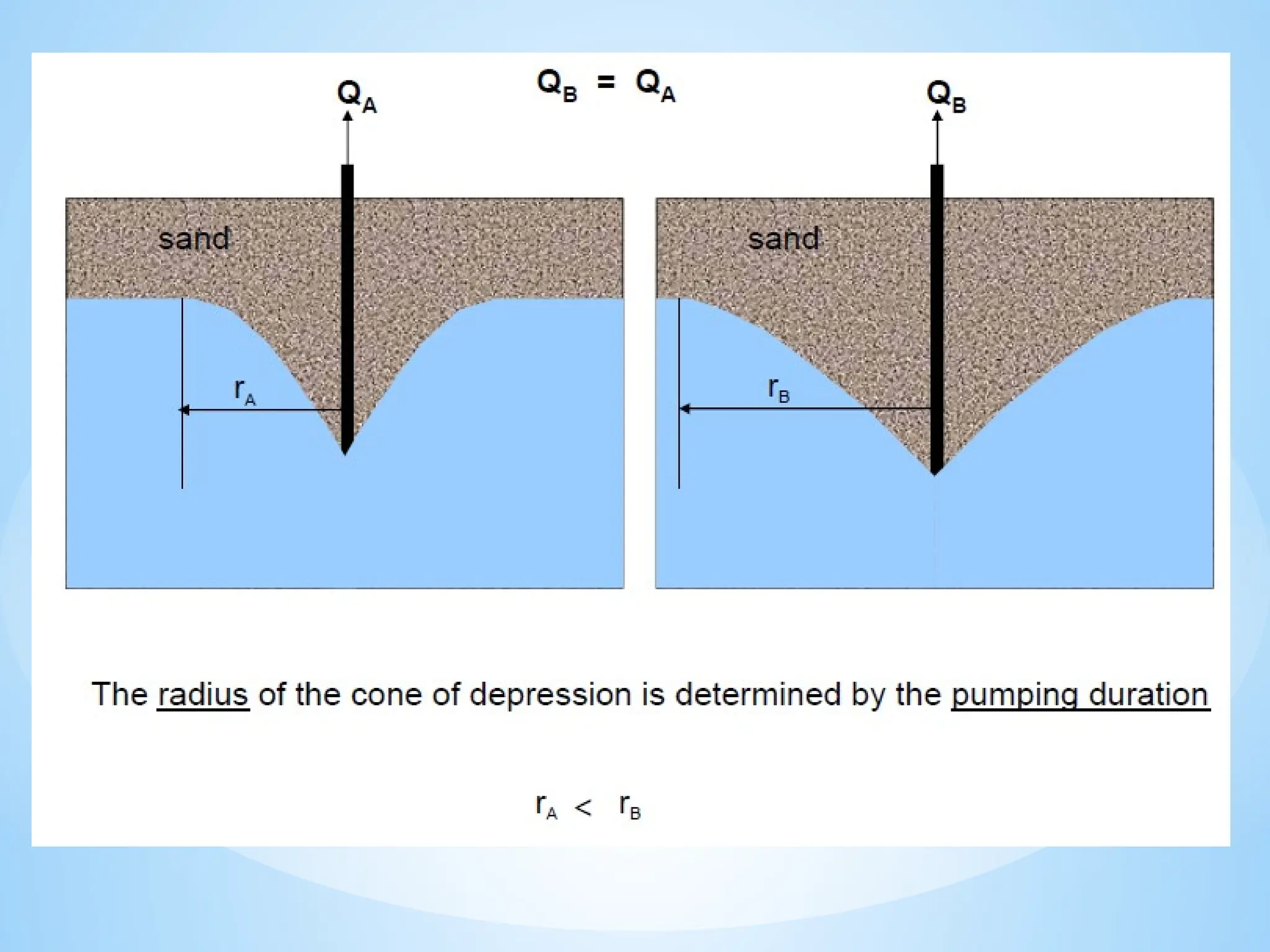
4. Permeability: The ability of a material to transmit water.
5. Recharge and Discharge:
Recharge: Water added to the aquifer, usually from rainfall.
Discharge: Water leaving the aquifer, like through springs or wells.
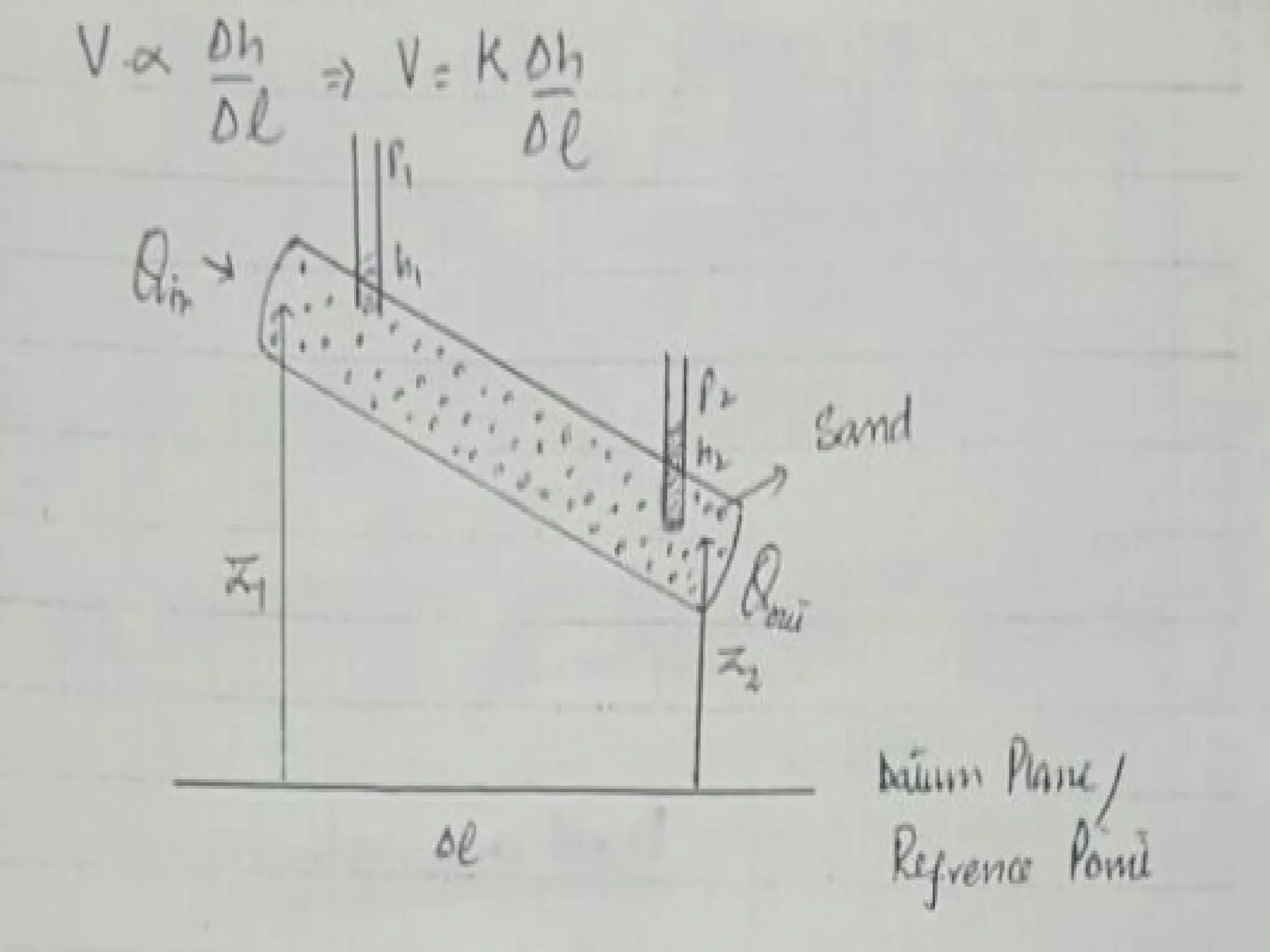
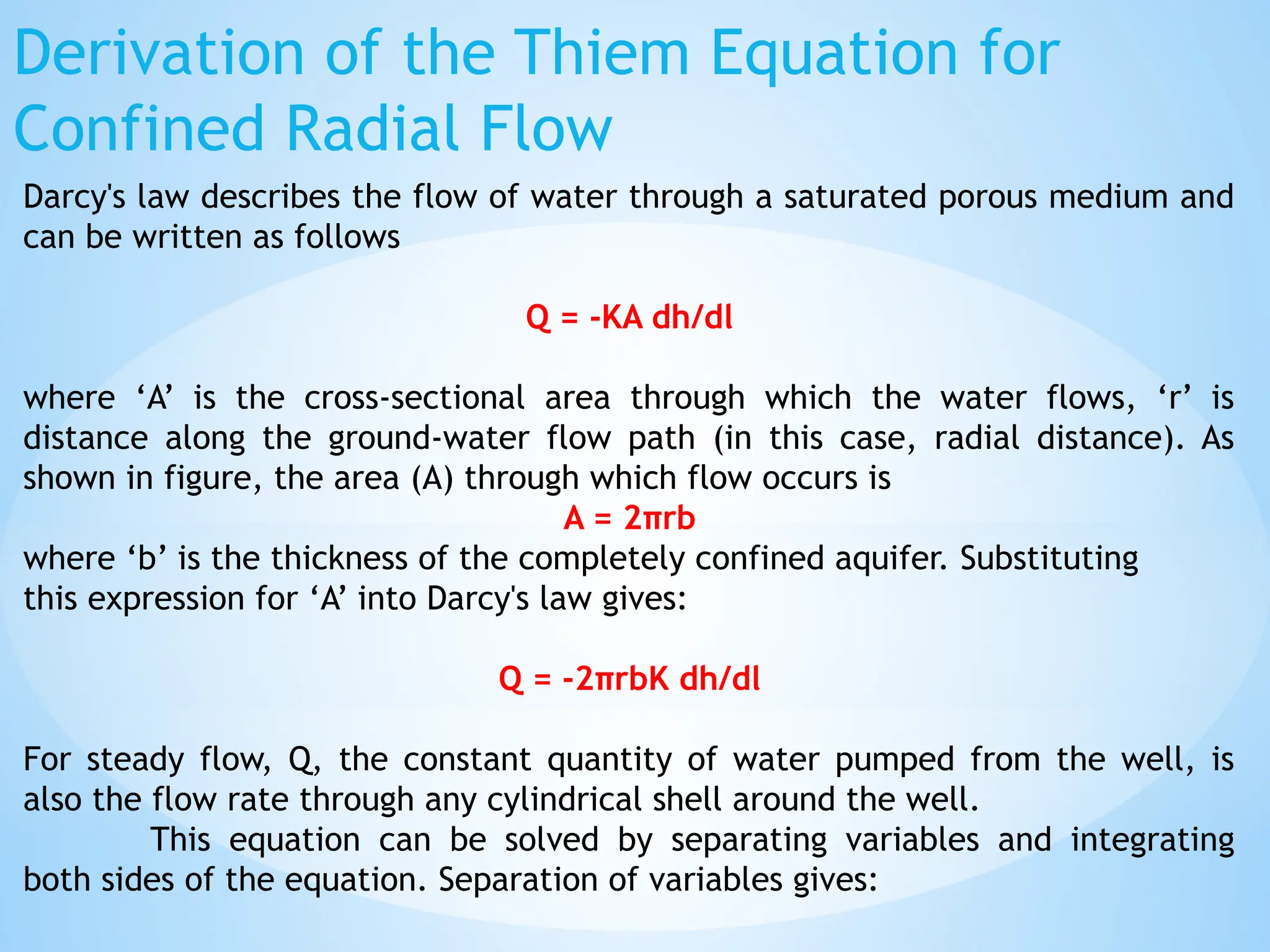
6. Groundwater Flow: Governed by Darcy's Law, which describes the flow of fluid through porous media.