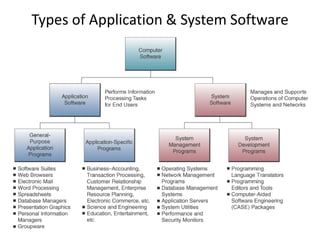
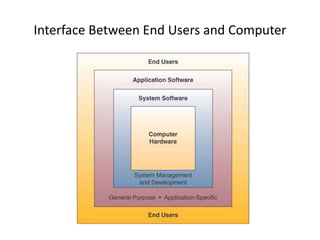
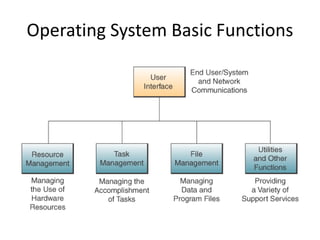
This document discusses different types of computer software, including application software and system software. It provides examples of various application software such as word processing programs, spreadsheets, presentation software, and personal information managers. It also discusses types of system software like operating systems and database management systems. The document outlines the basic functions of operating systems, which include managing resources, files, and tasks to maximize productivity and efficiency.