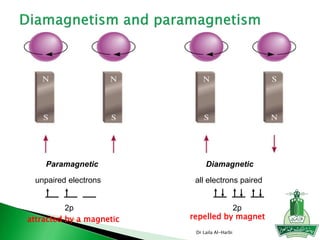
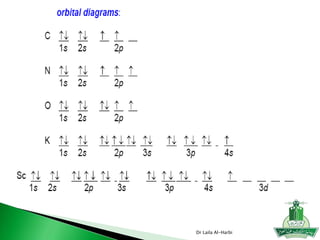
1. N has an unpaired electron in its 2p orbital, so it is paramagnetic.
2. Mg, Na, and N all have their electrons paired, so they are diamagnetic.
3. Mn2+ has the electron configuration [Ar] 3d5, so it has 5 unpaired electrons.
4. Mn has the electron configuration [Ar] 3d5 4s2, so it has 3 unpaired electrons.
5. Fe2+ has the electron configuration [Ar] 3d6, so it has 4 unpaired electrons.
6. Fe3+ has the electron configuration [Ar] 3d5, so it has 5 unpaired electrons.













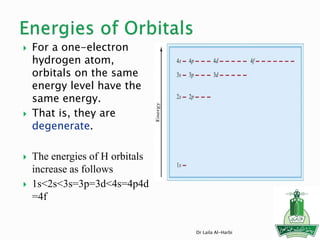
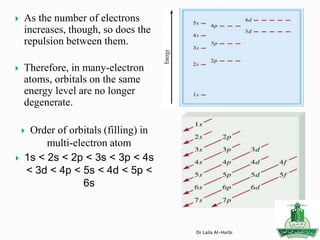
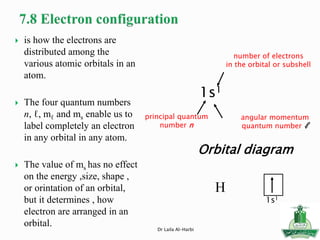

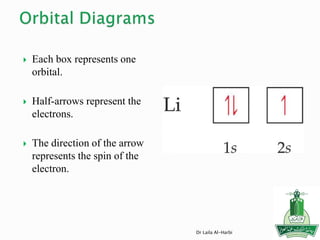


![Short-hand notation -- show preceding inert gas configuration
plus the additional electrons
Some irregularities occur when there are enough electrons to
half-fill s and d orbitals on a given row.
For instance, the electron configuration for copper 29Cu is
[Ar] 4s1 3d 10 rather than the expected [Ar] 4s2 3d 9.
the electron configuration for 24Cr is
[Ar] 4s1 3d 5 rather than the expected [Ar] 4s2 3d 4.
Dr Laila Al-Harbi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-141230112610-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-7-37-320.jpg)