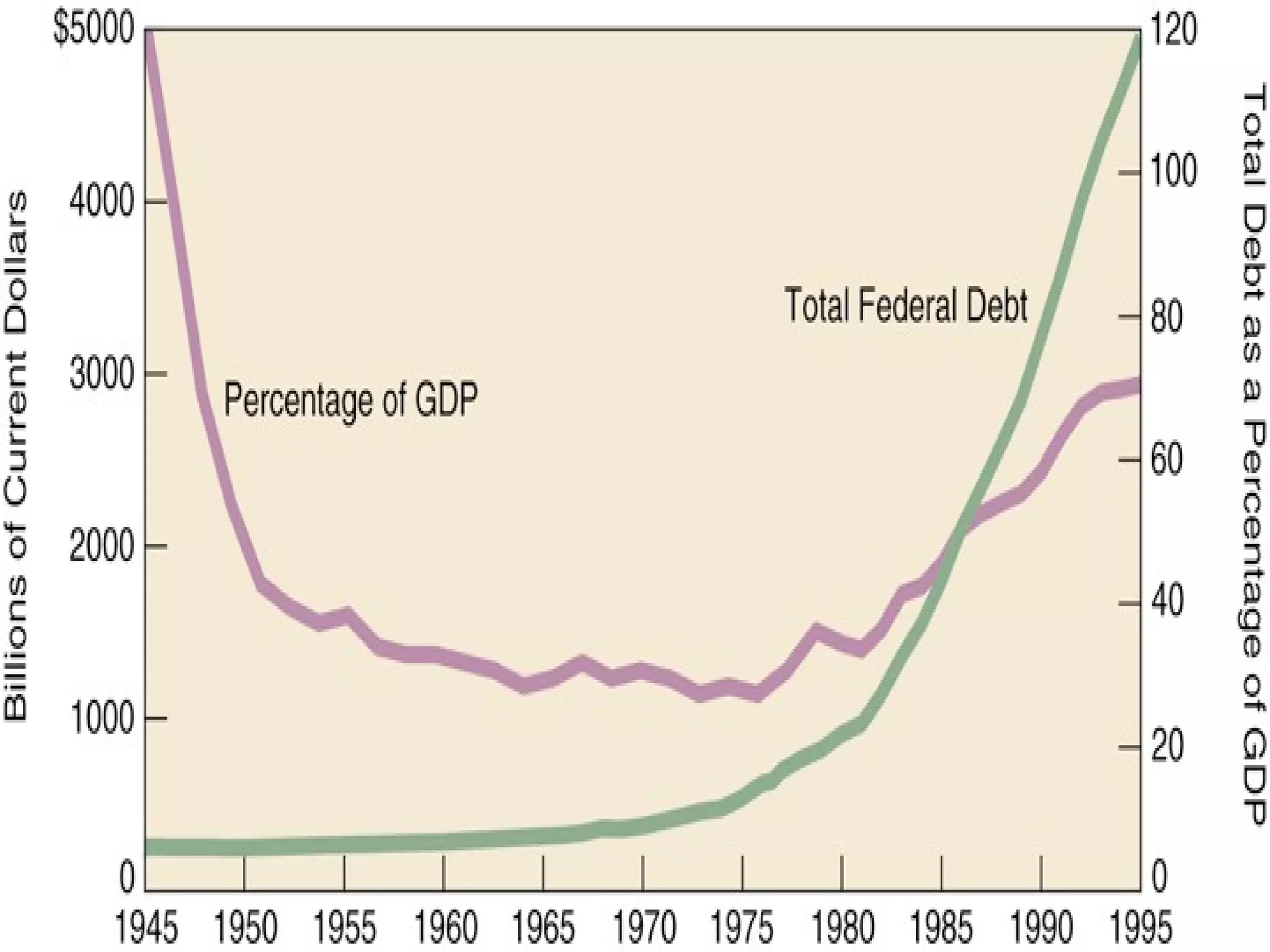
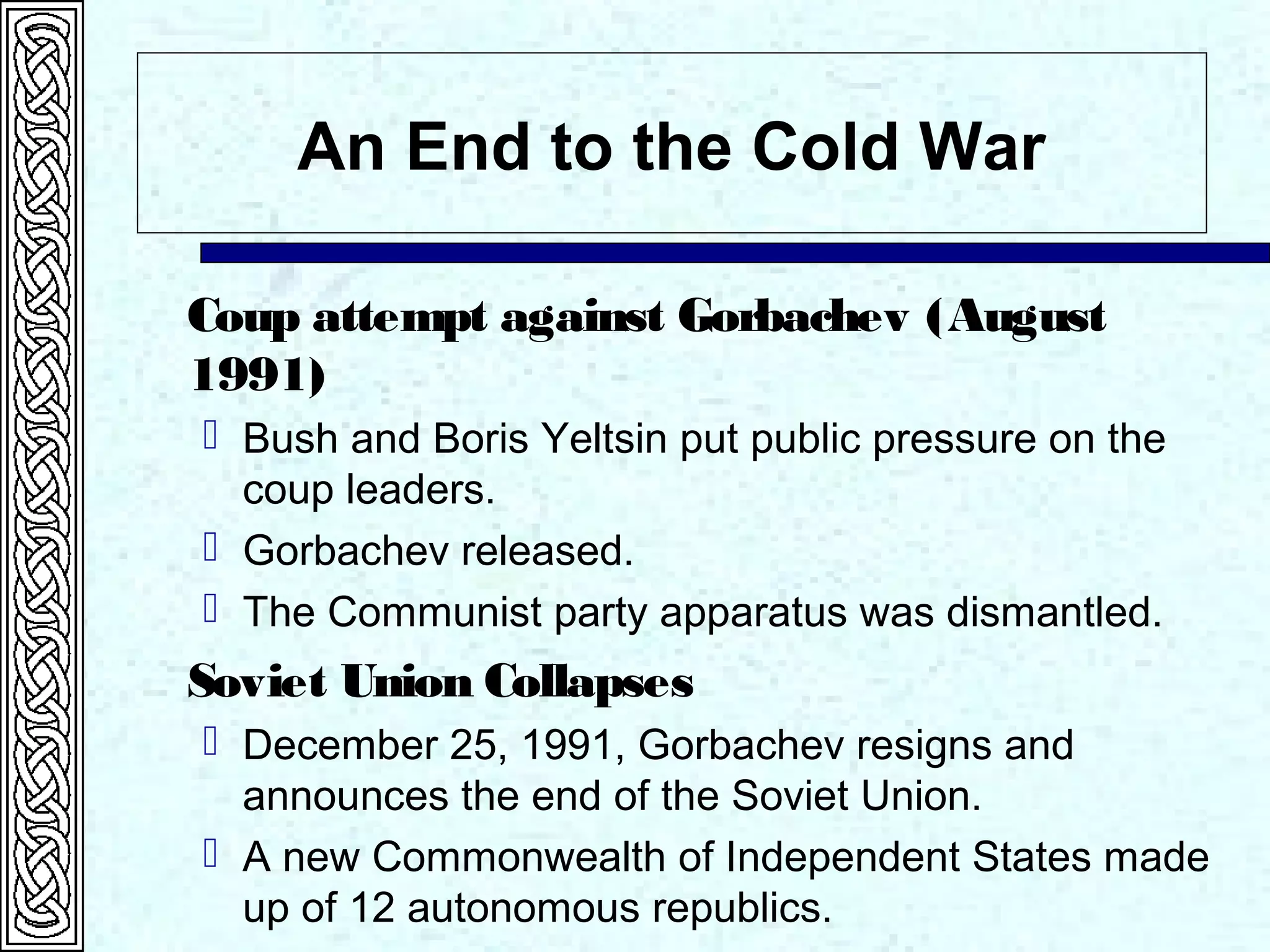
Ronald Reagan served as president from 1981 to 1989. His presidency saw significant tax cuts and increased military spending. This led to large budget deficits. Reagan pursued a policy of peace through military strength against the Soviet Union during the Cold War. This military buildup contributed to the eventual collapse of the Soviet Union under Gorbachev in 1991, ending the Cold War. Reagan's vice president, George H.W. Bush, was elected president in 1988 and continued Reagan's foreign policy while also seeking to reduce the national debt through tax increases and spending cuts.