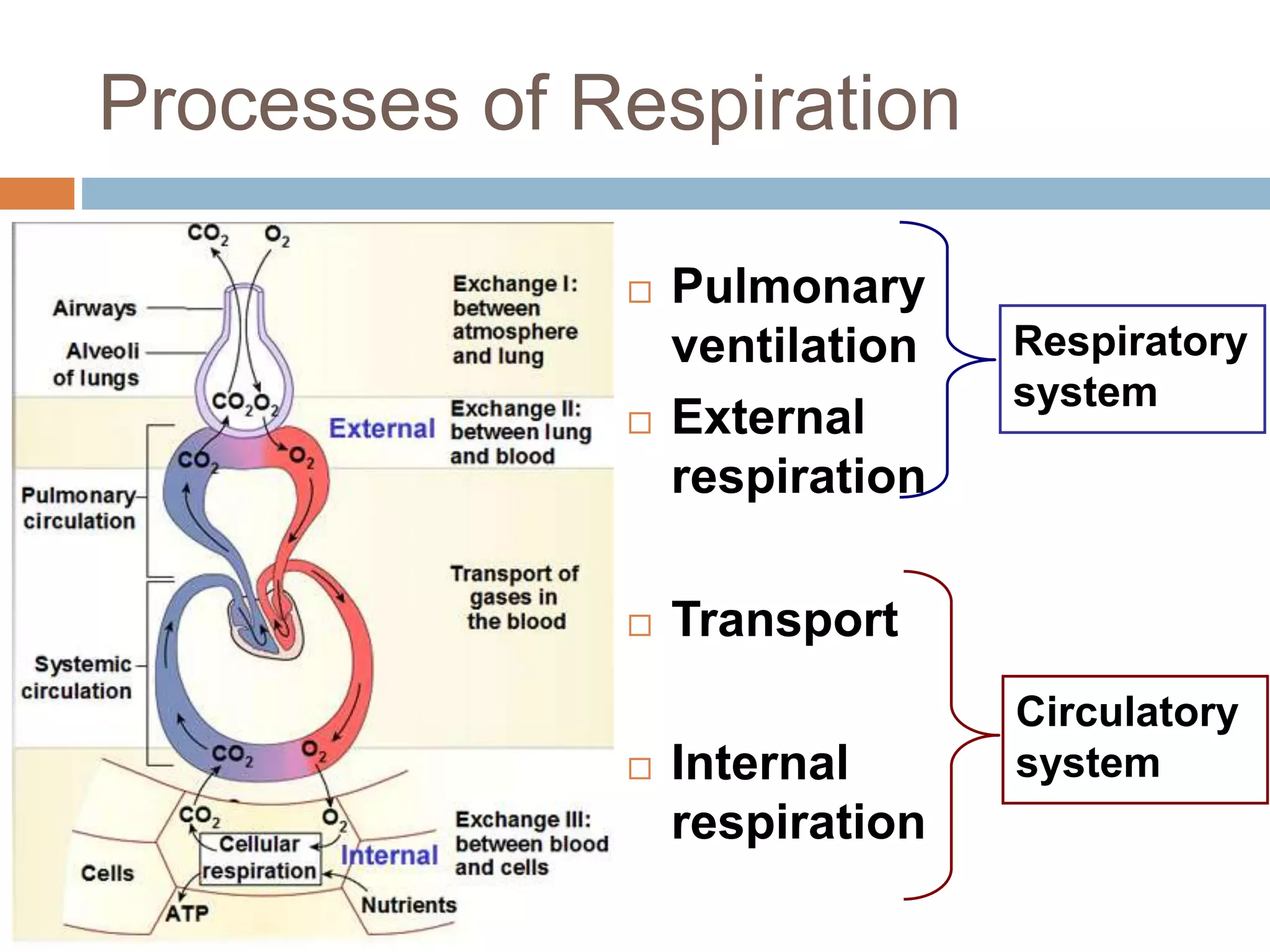
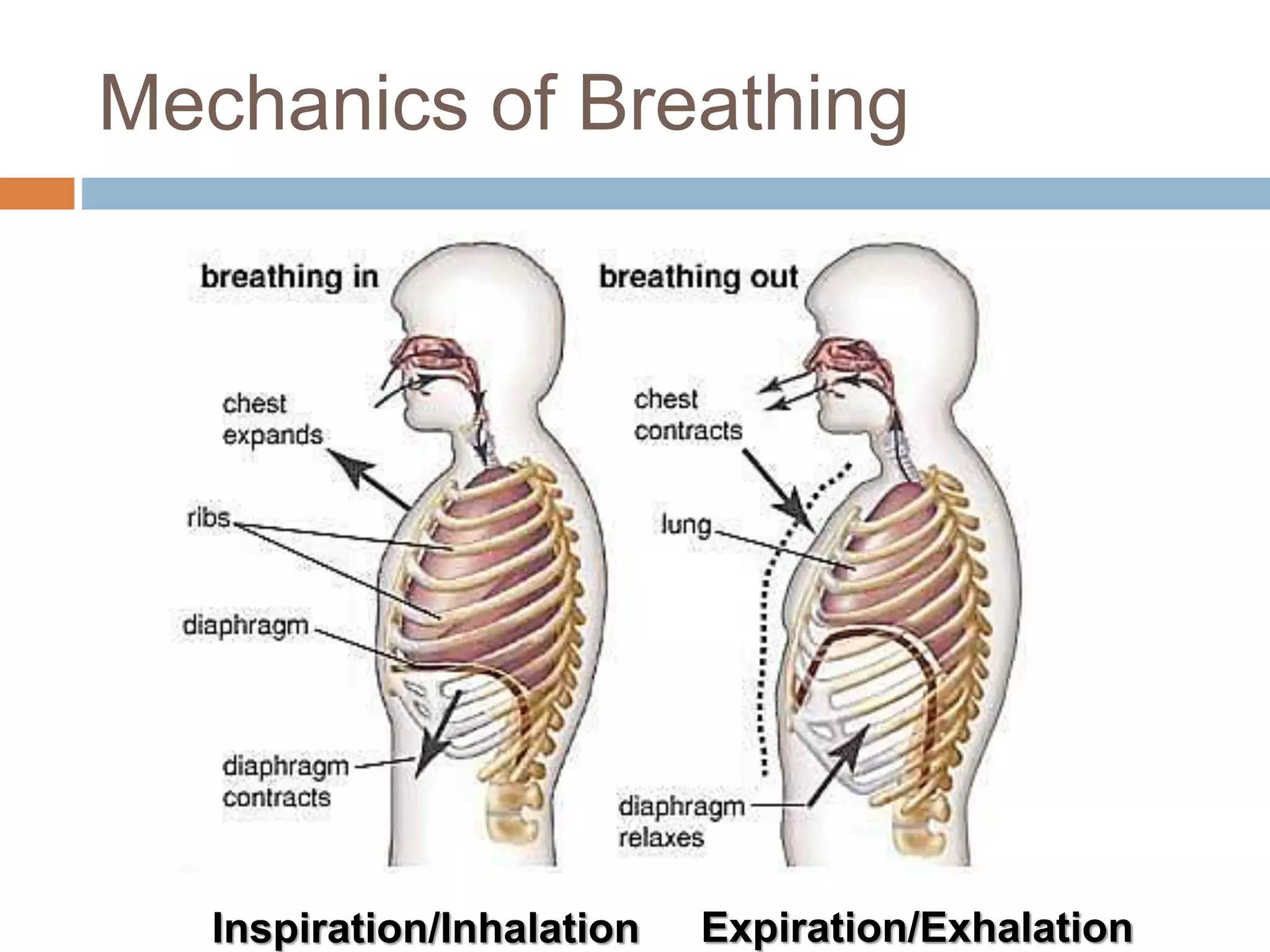
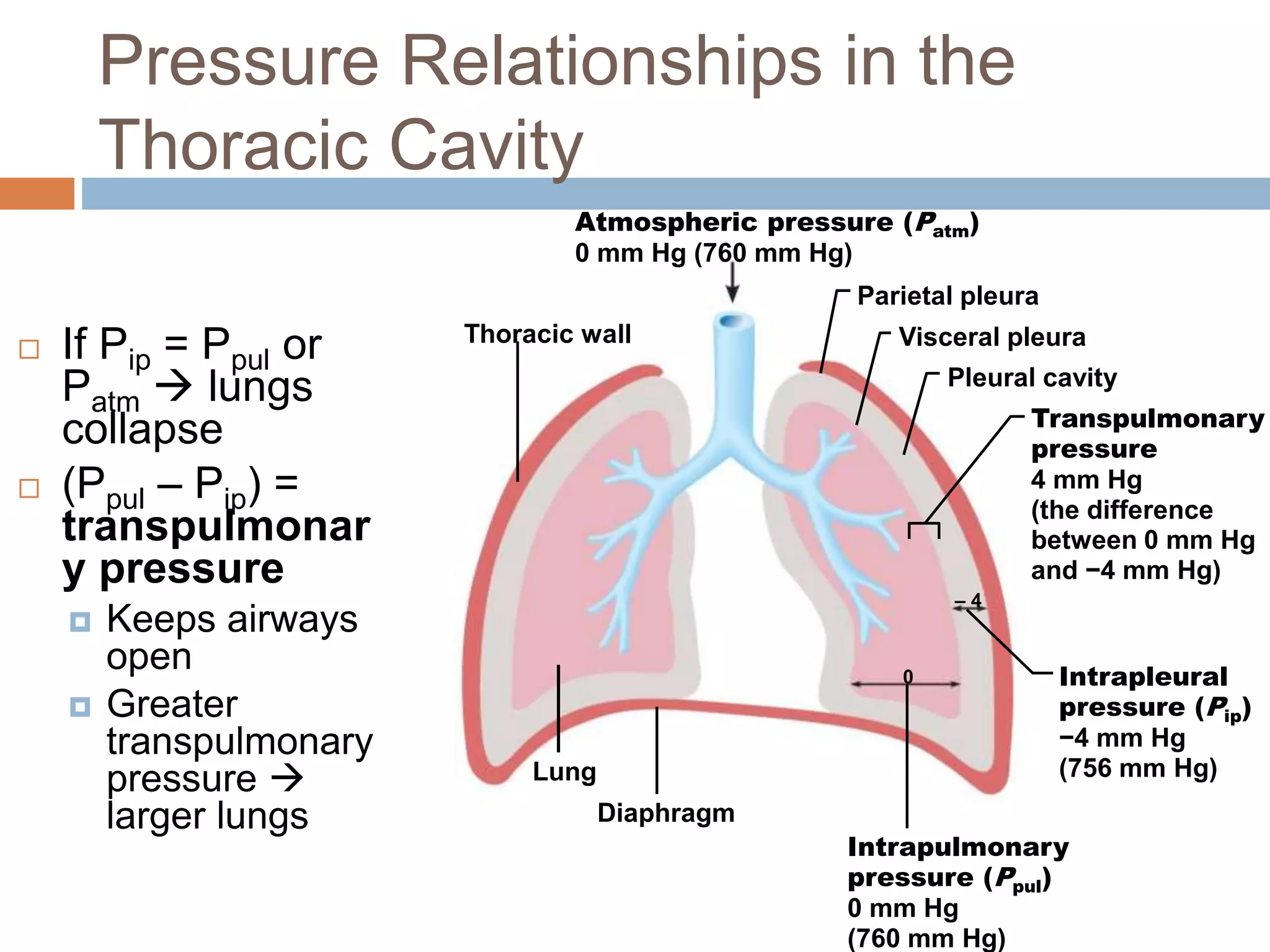
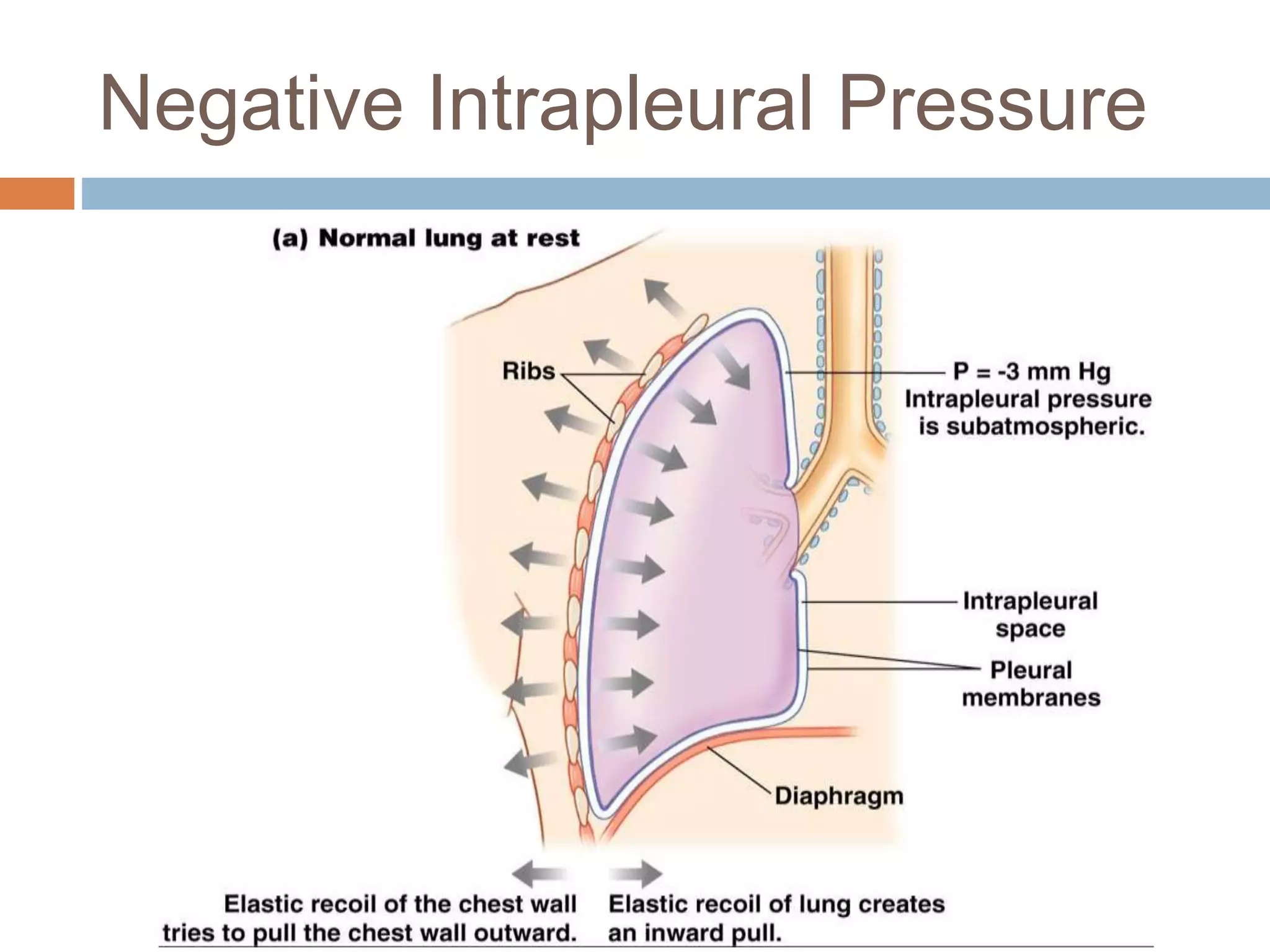
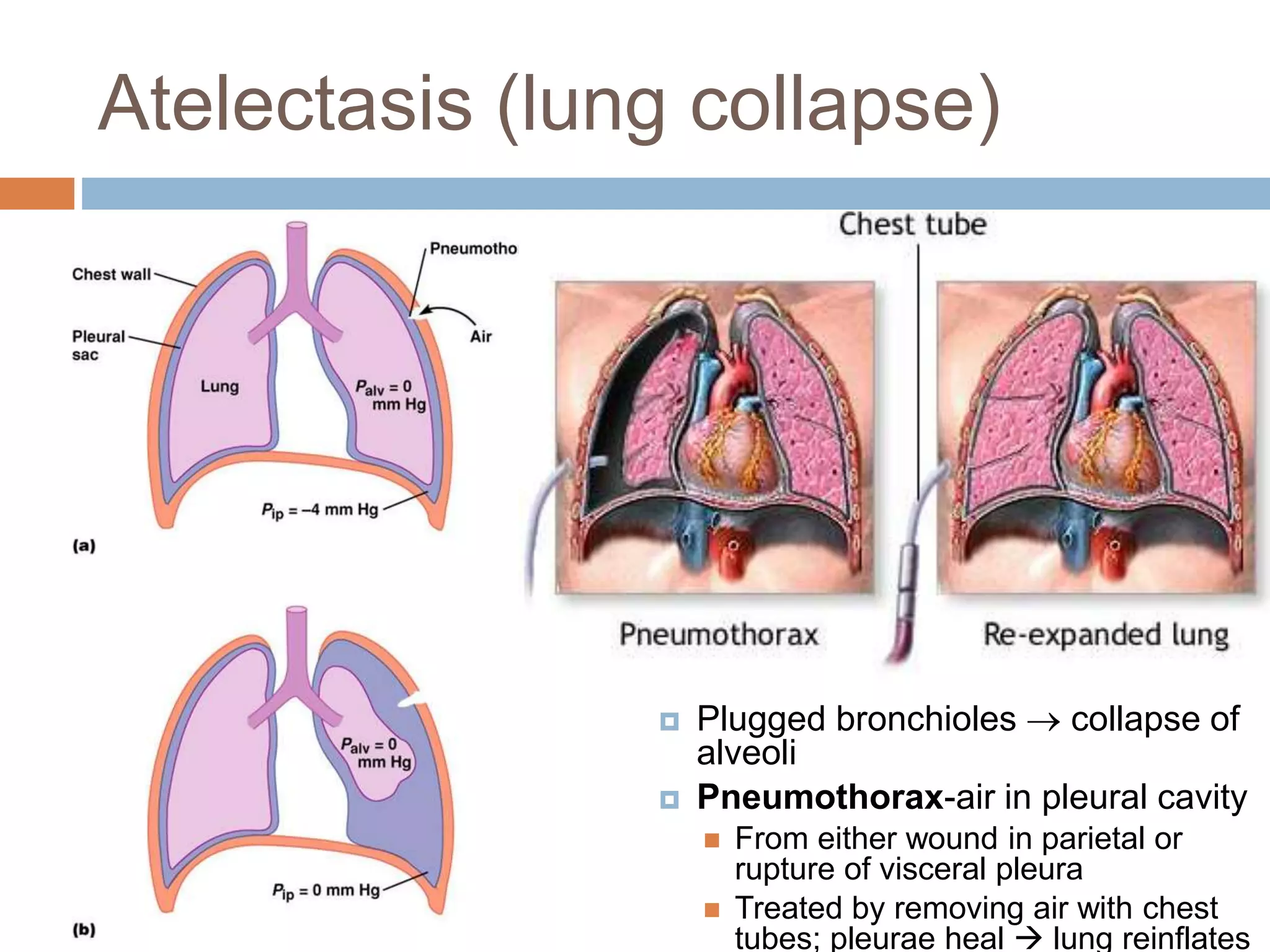
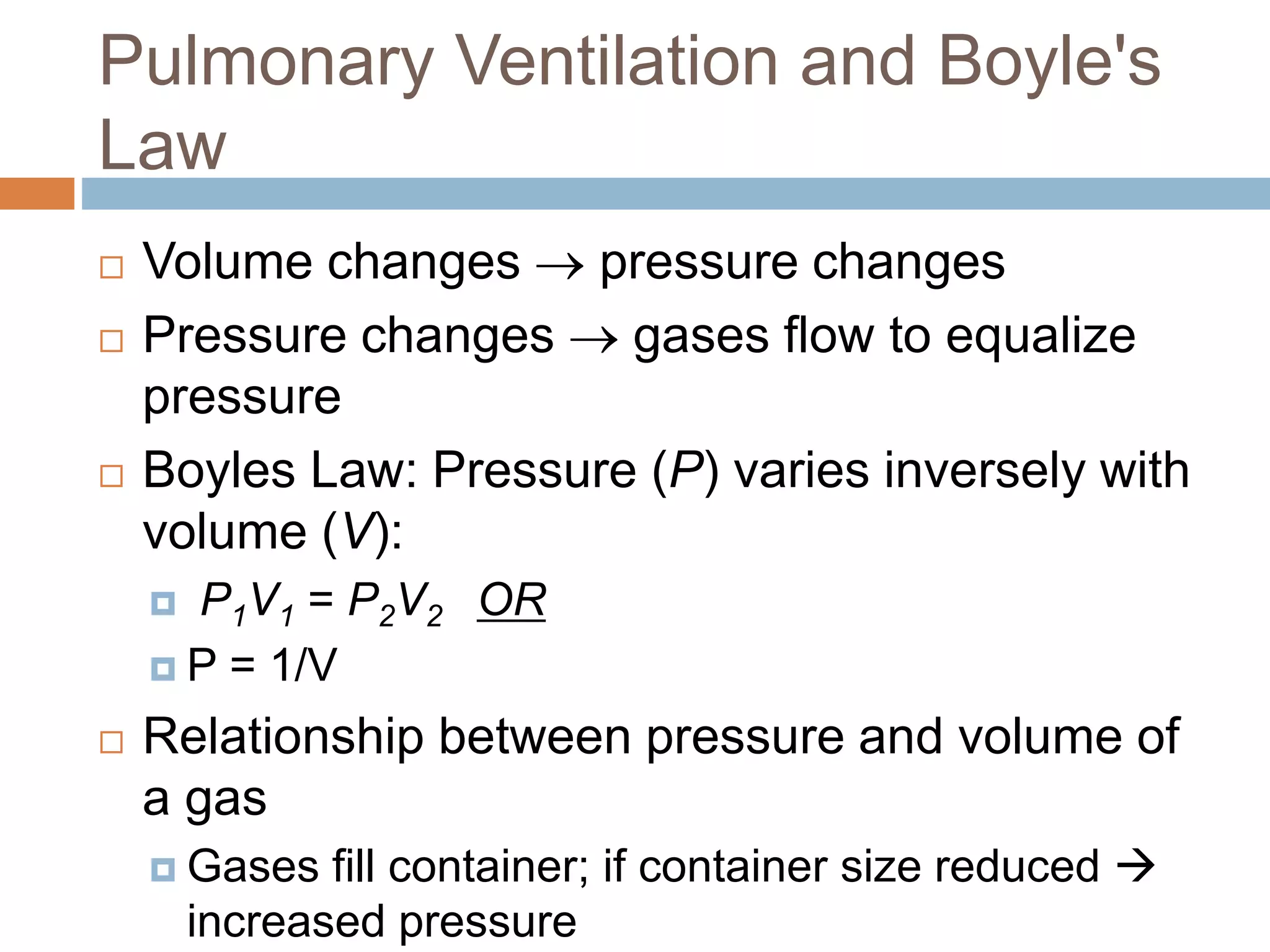
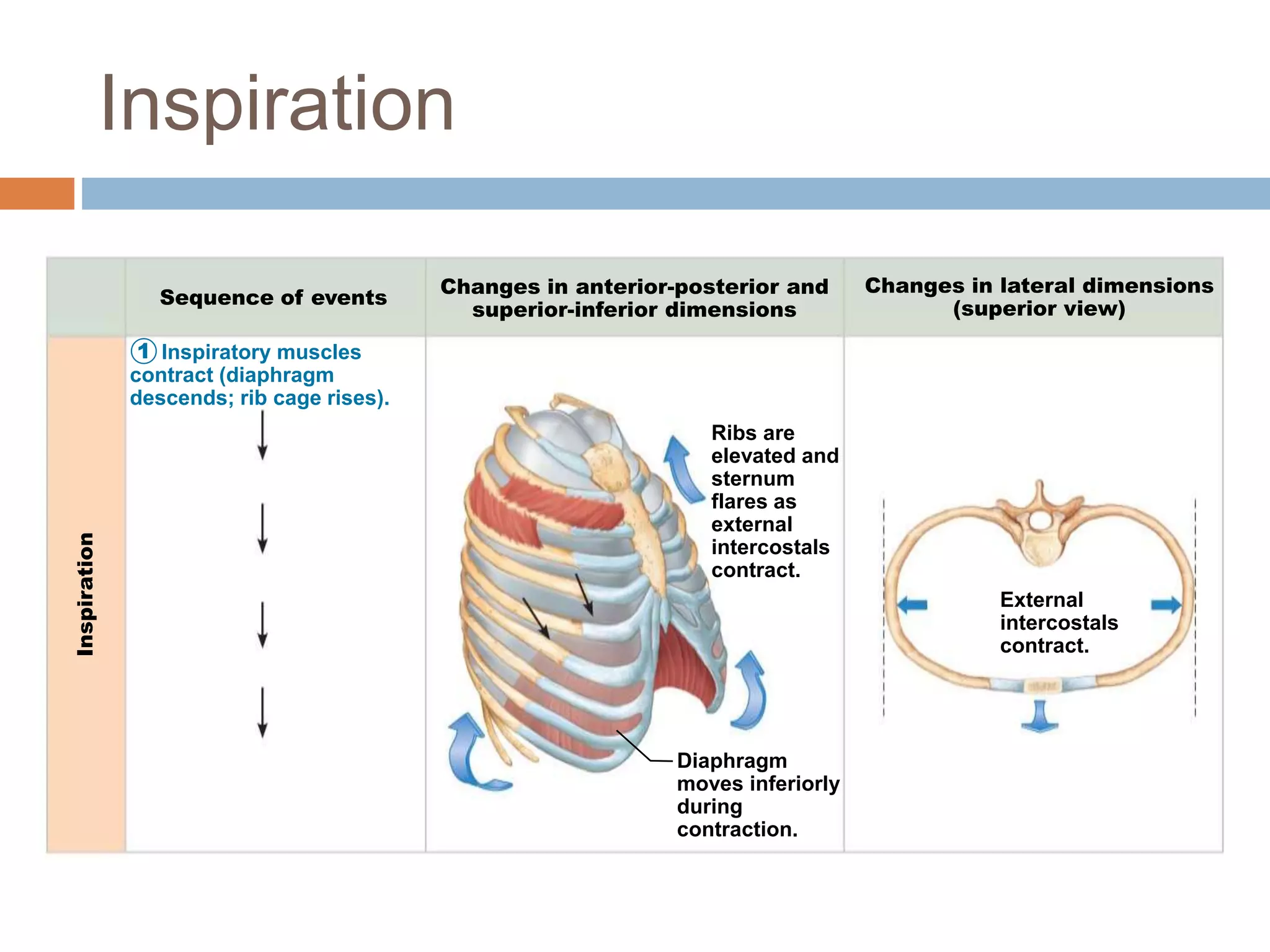
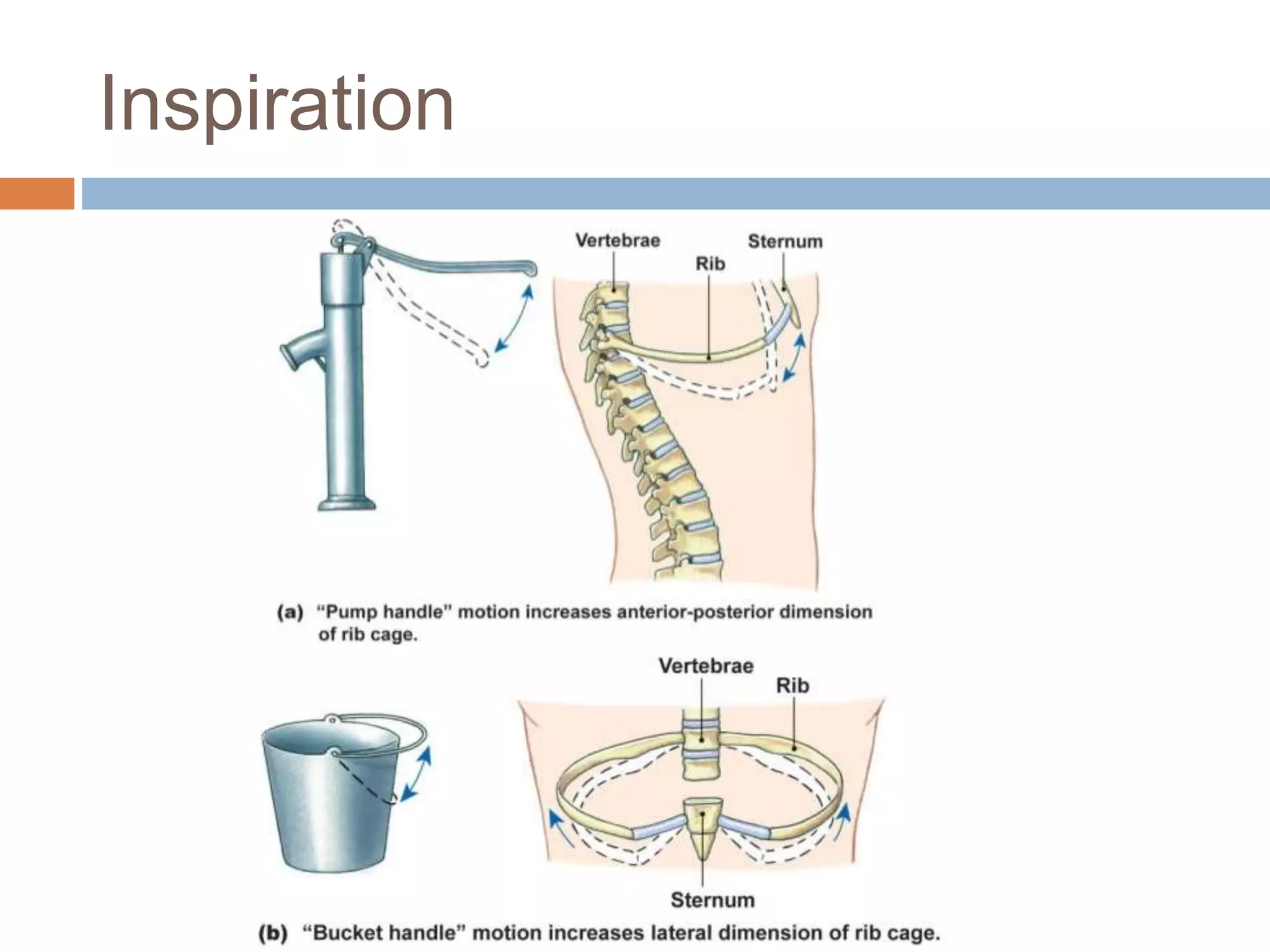
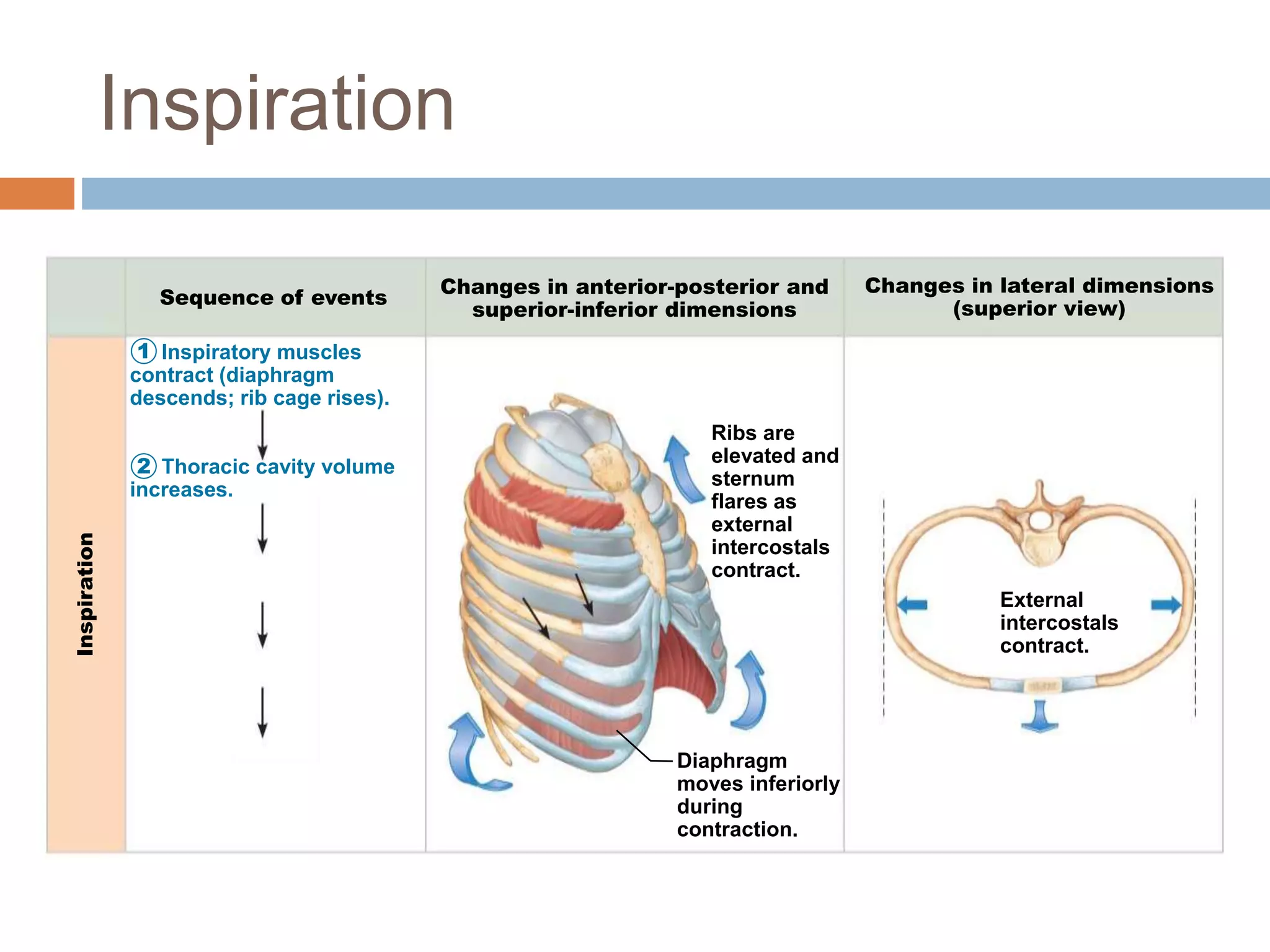
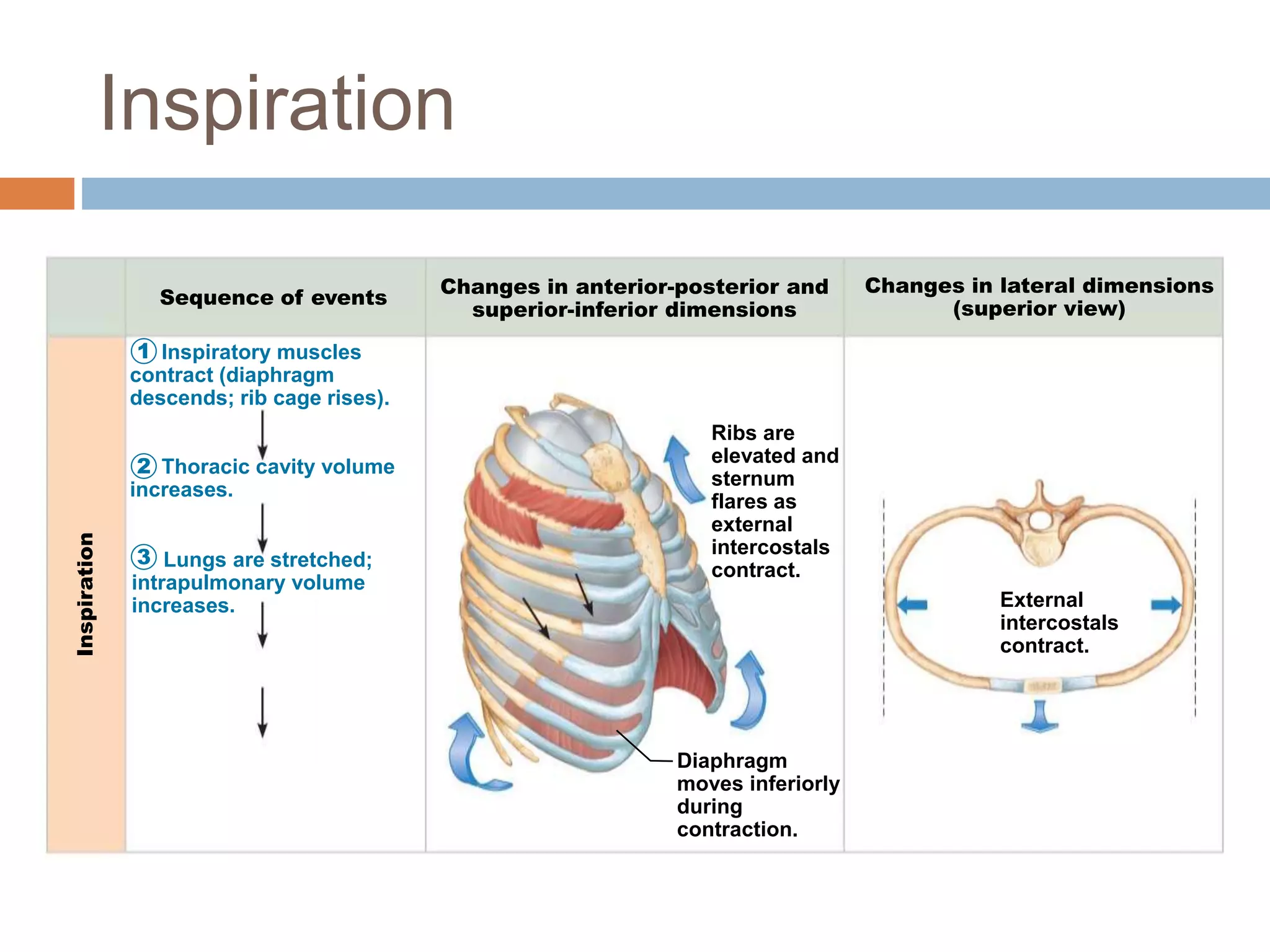
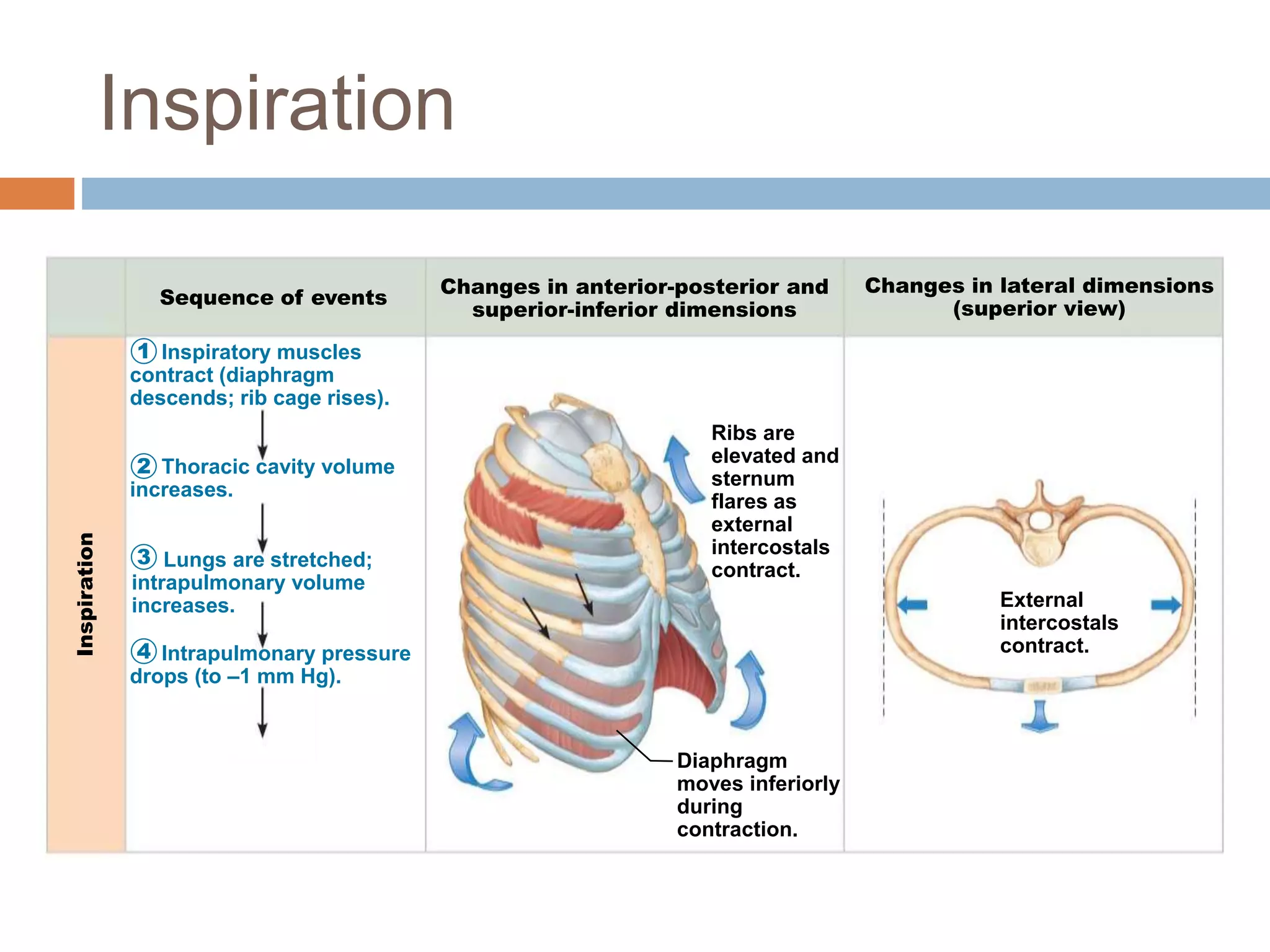
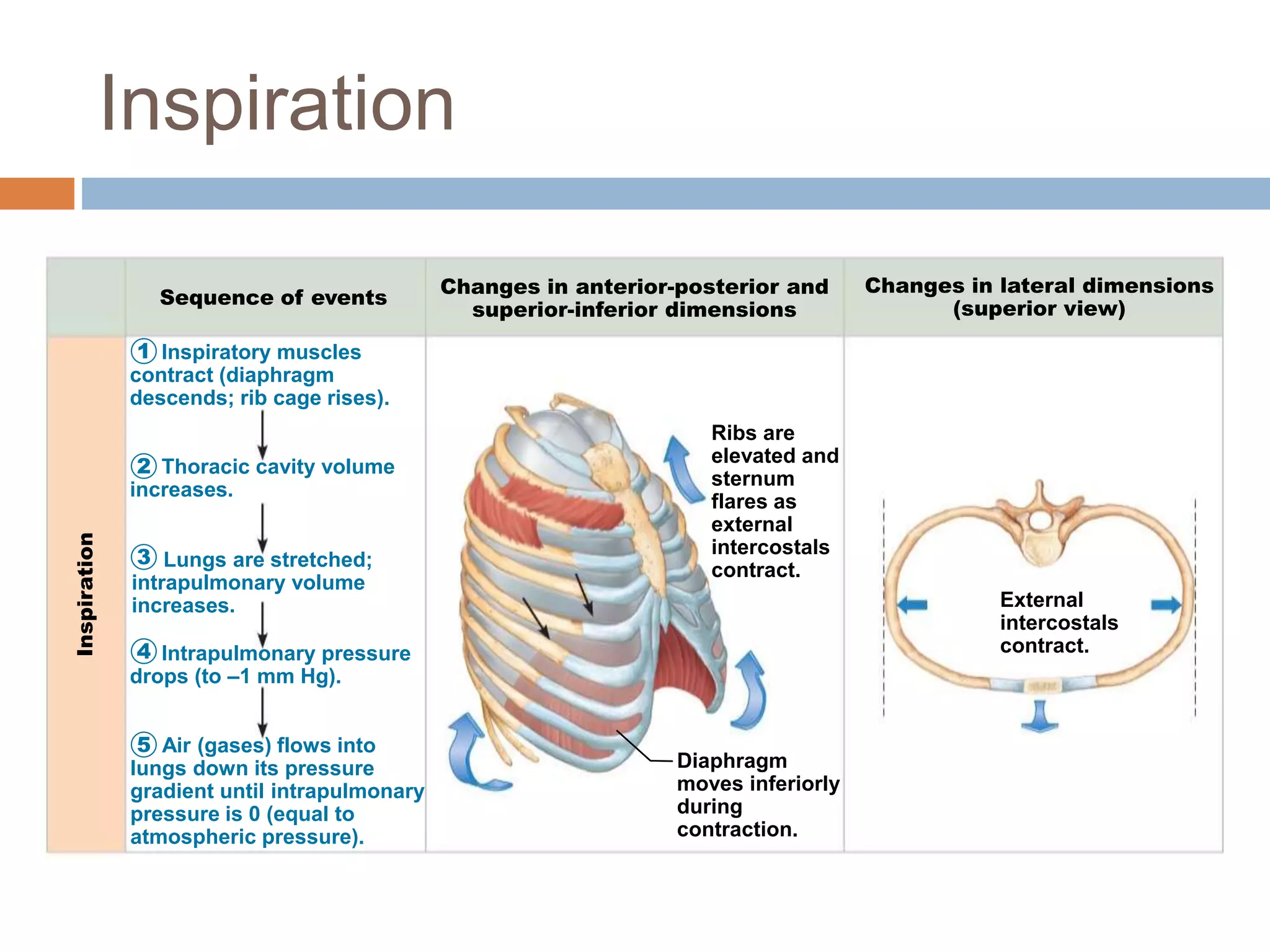
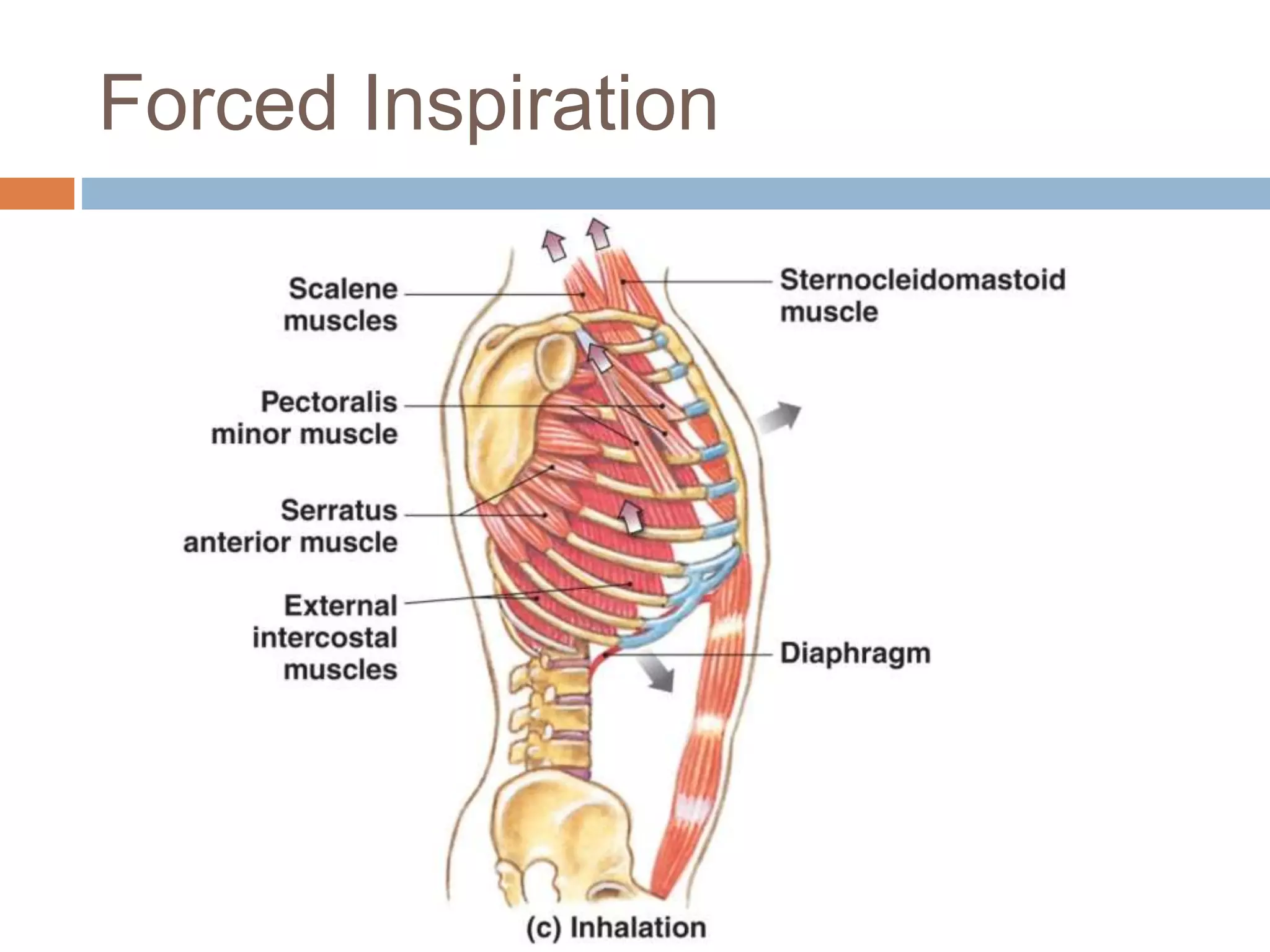
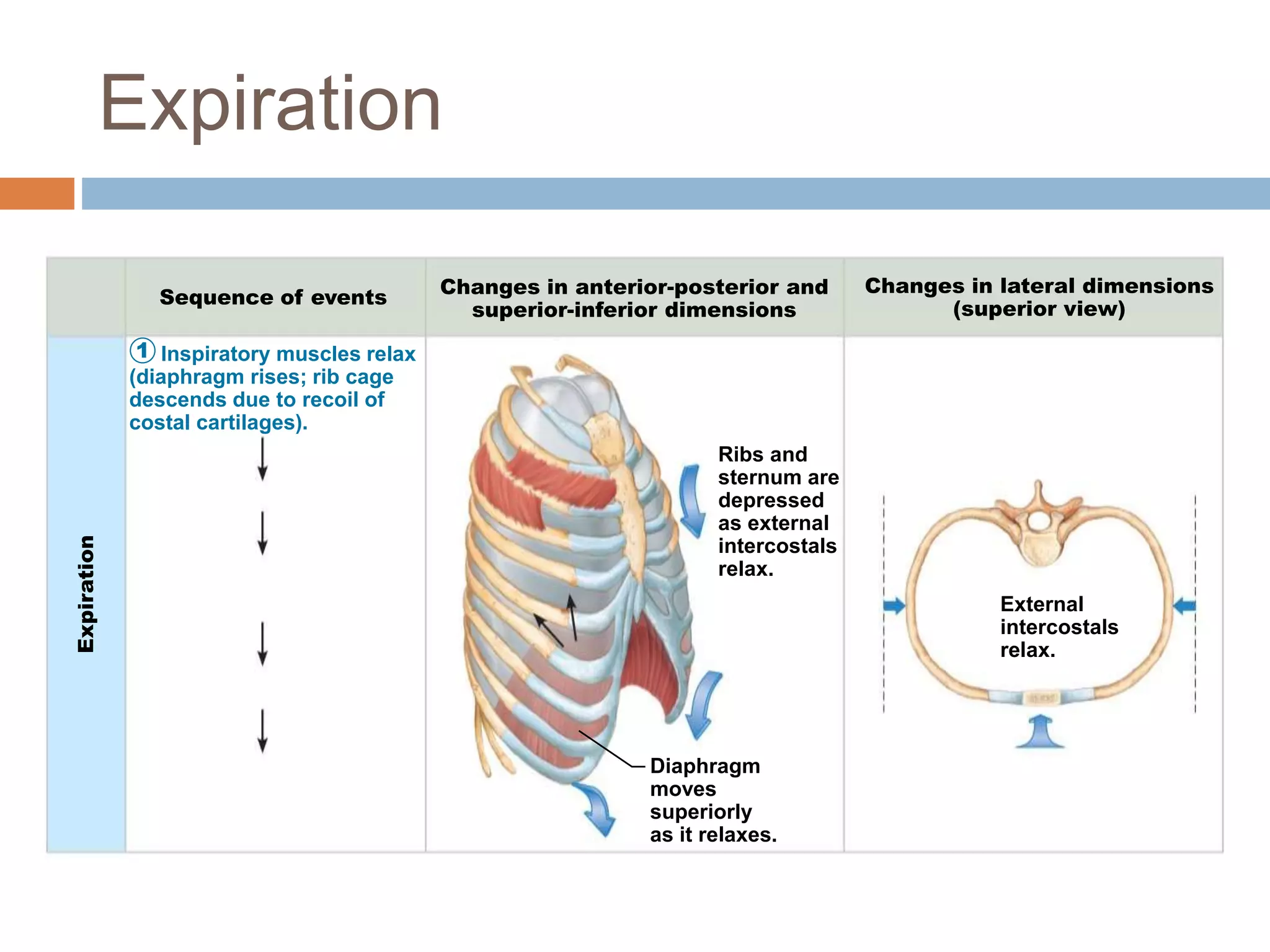
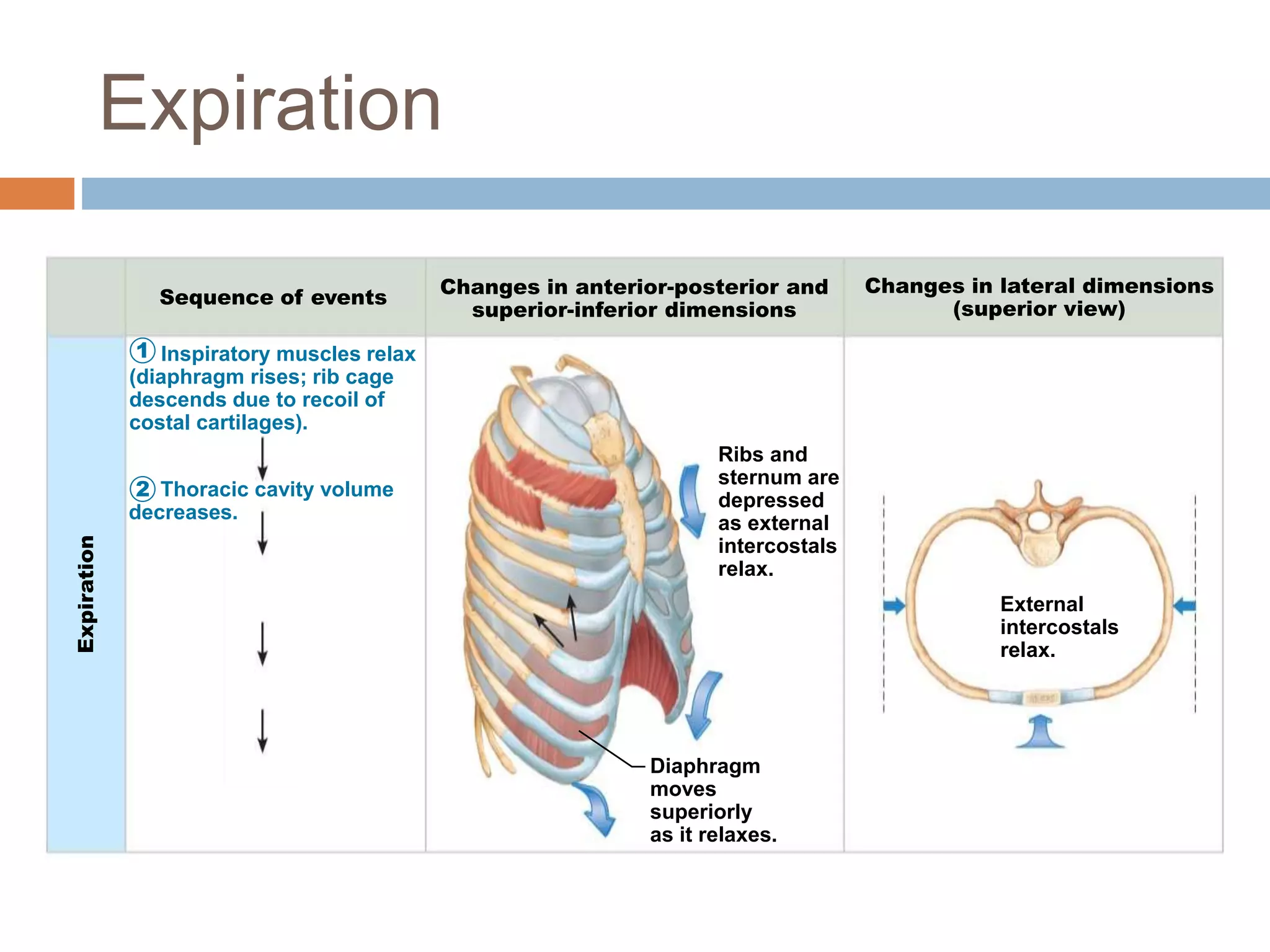
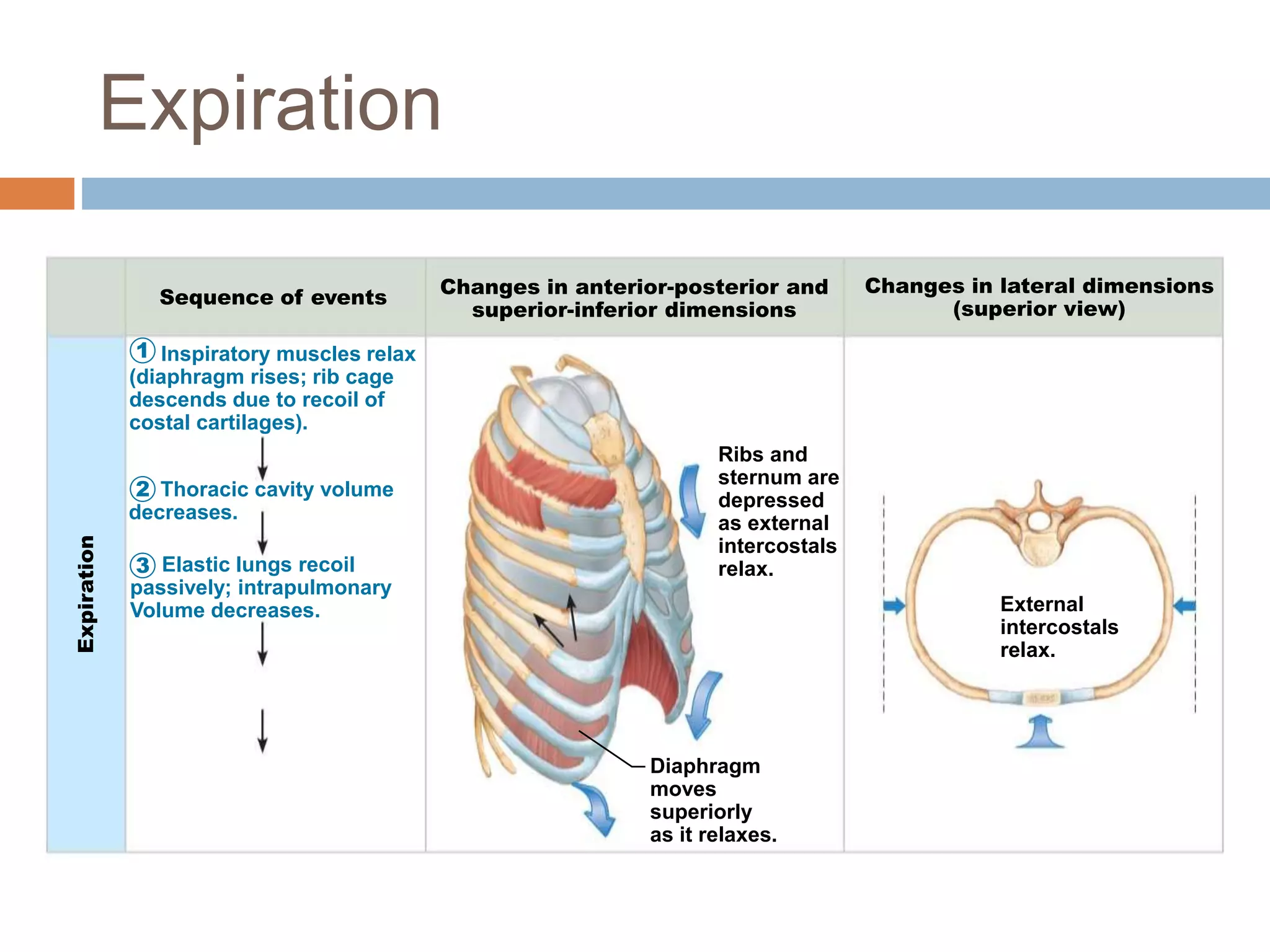
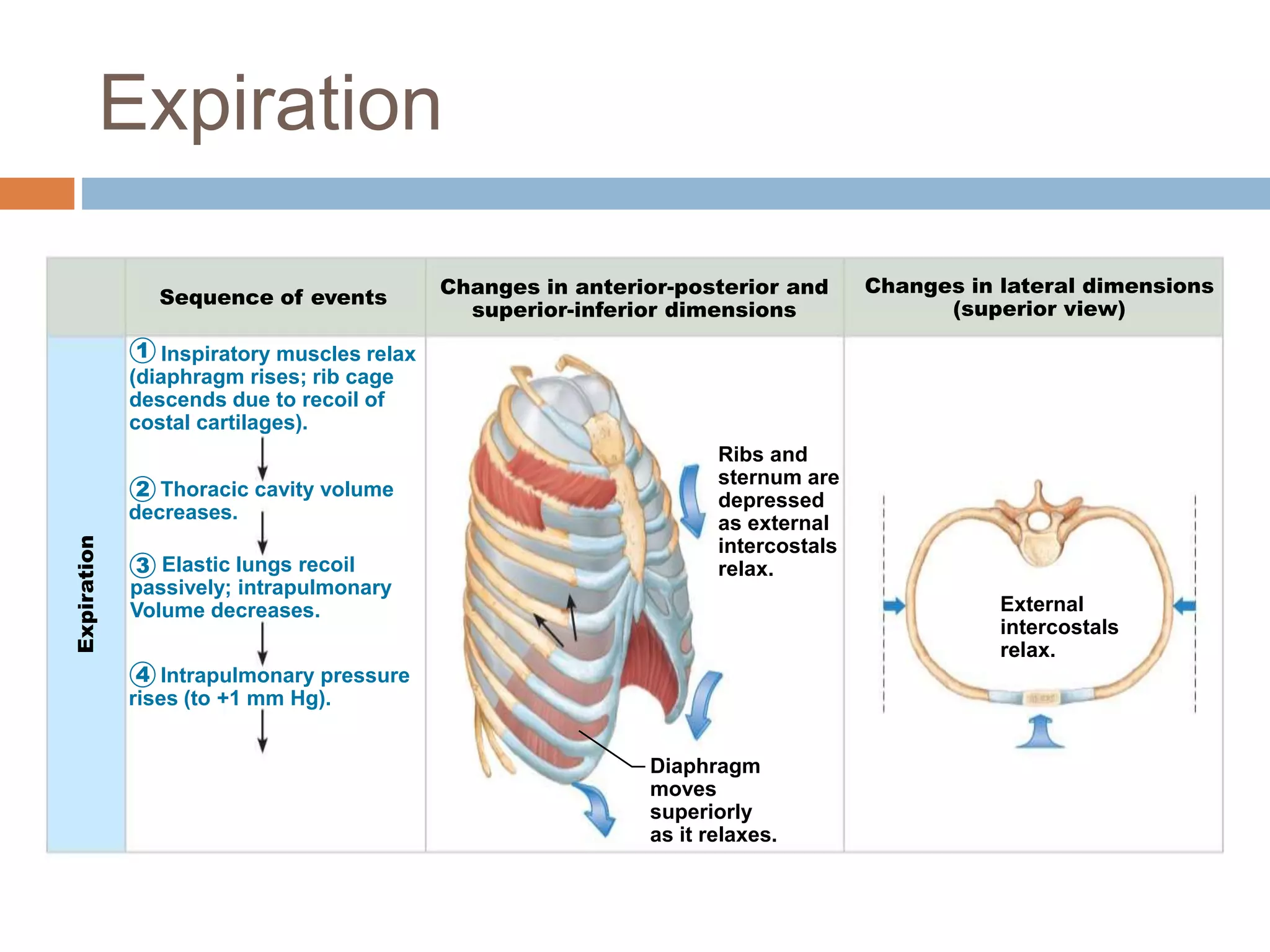
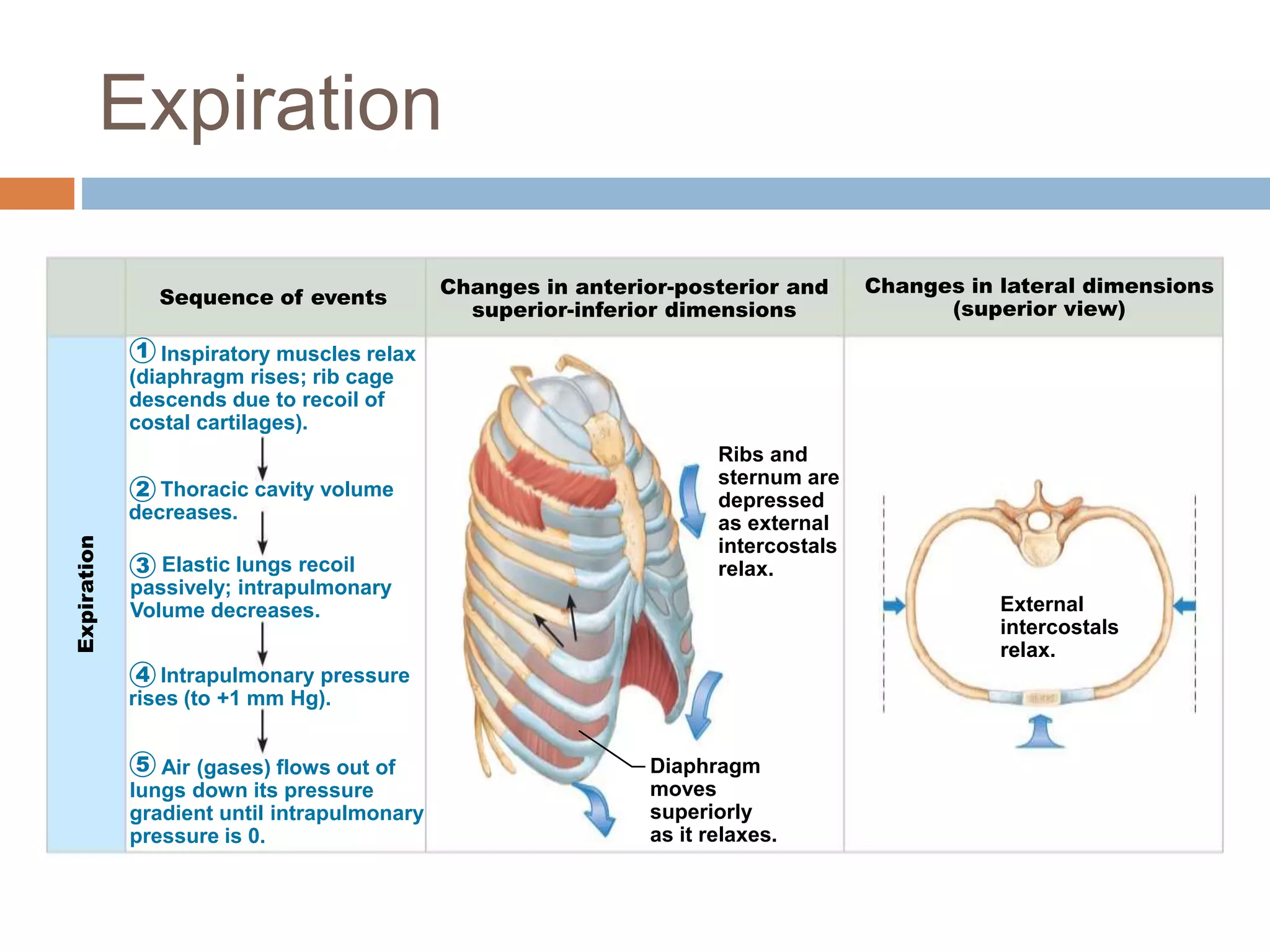
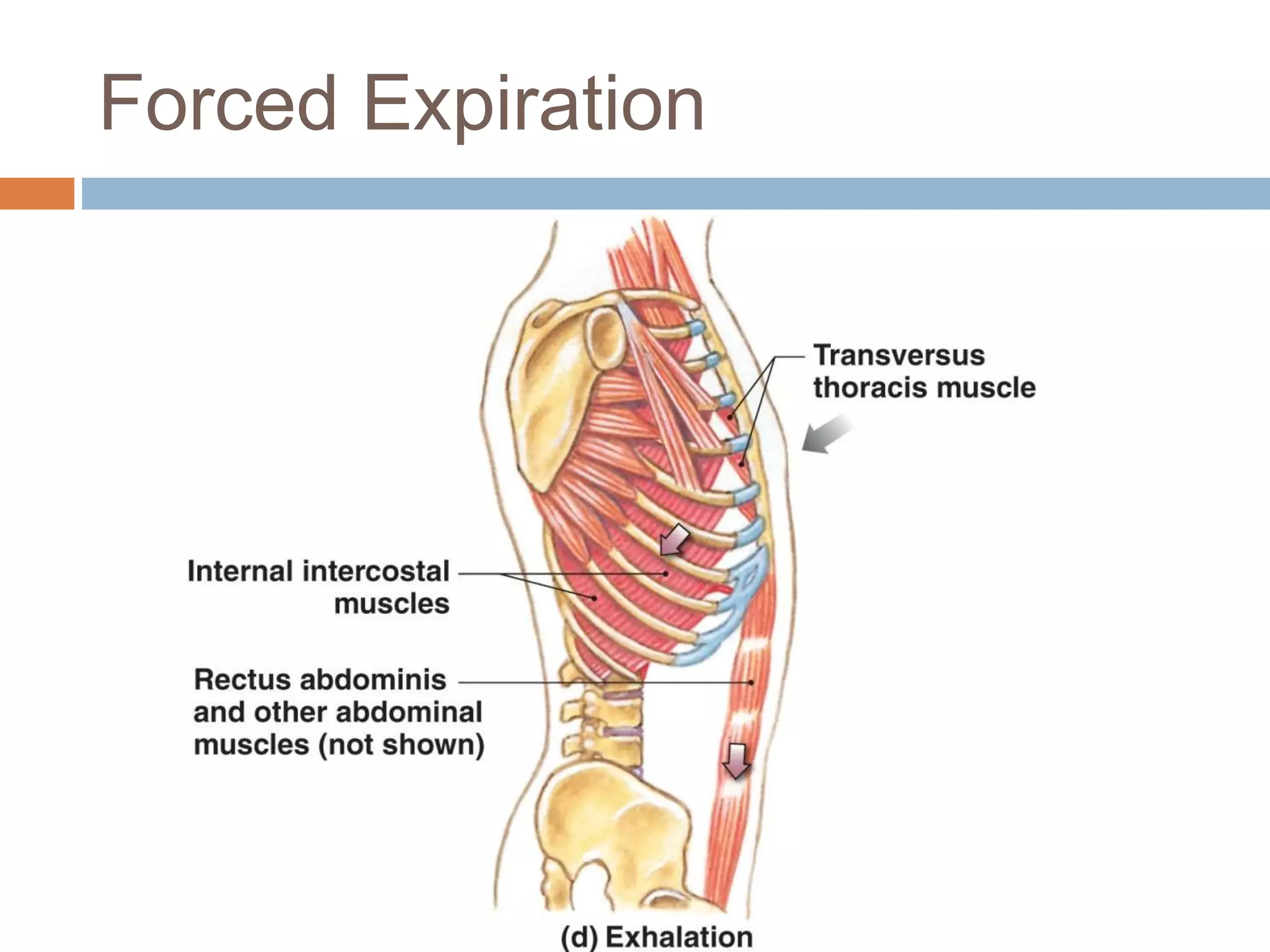
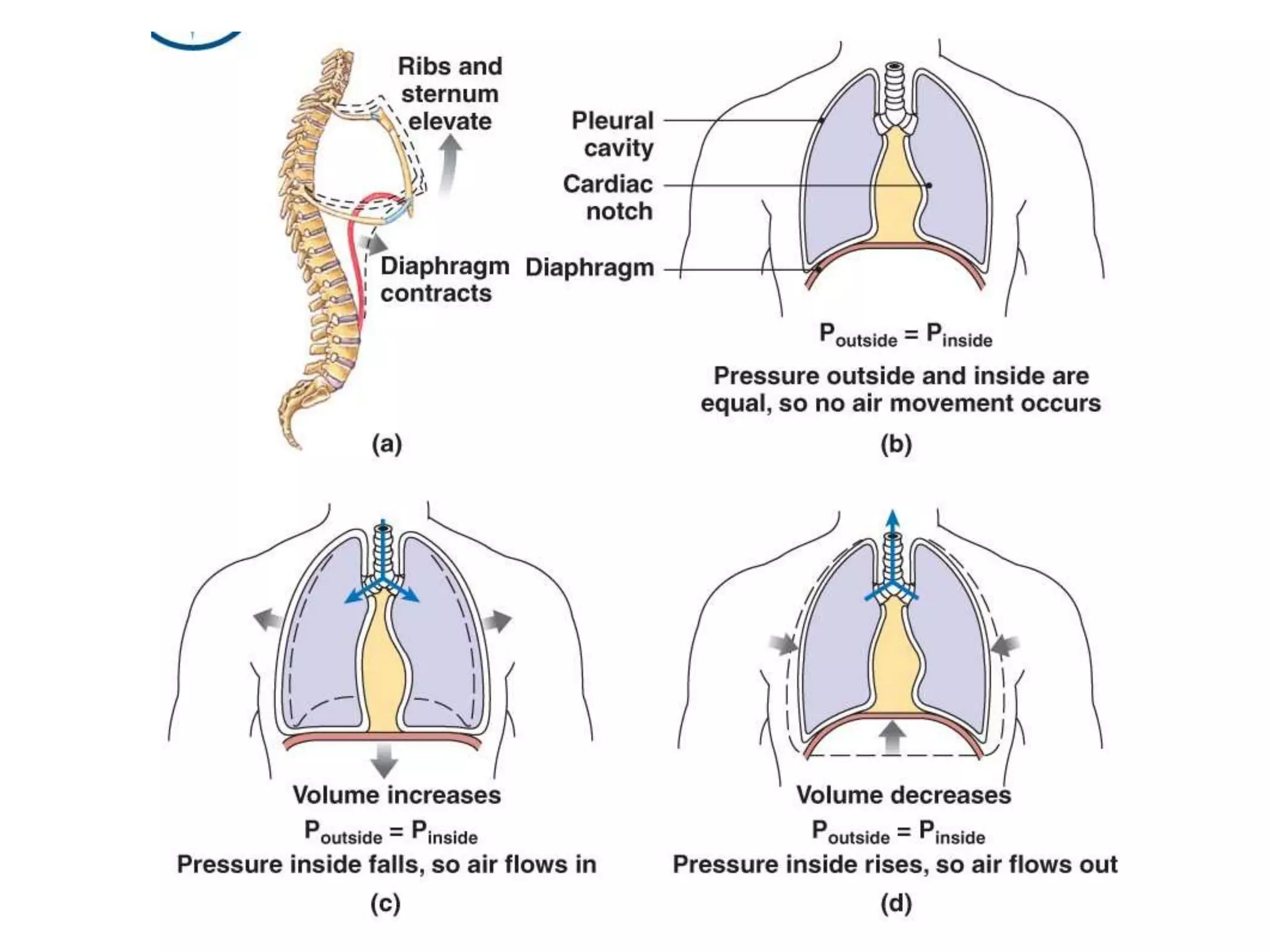
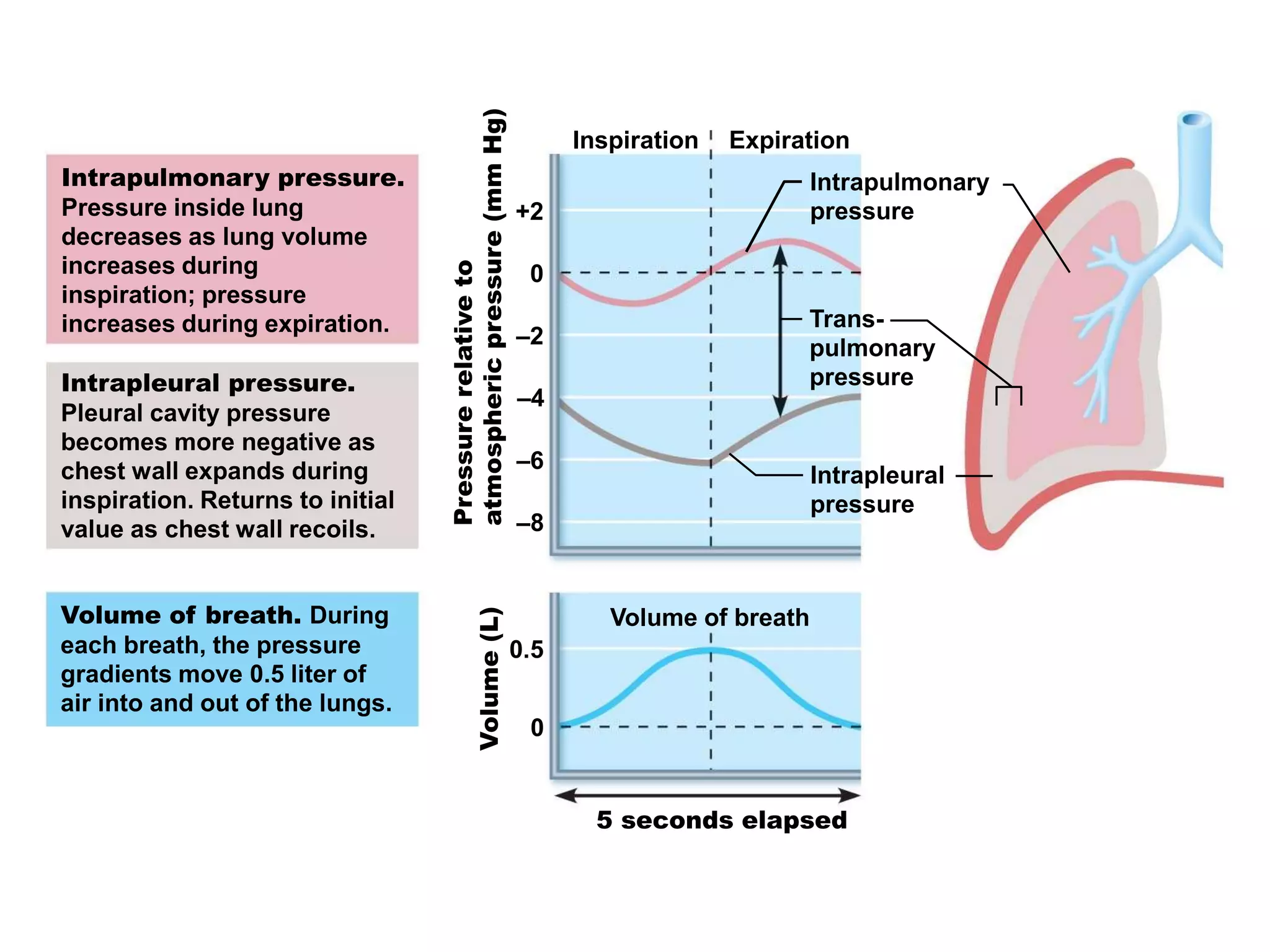
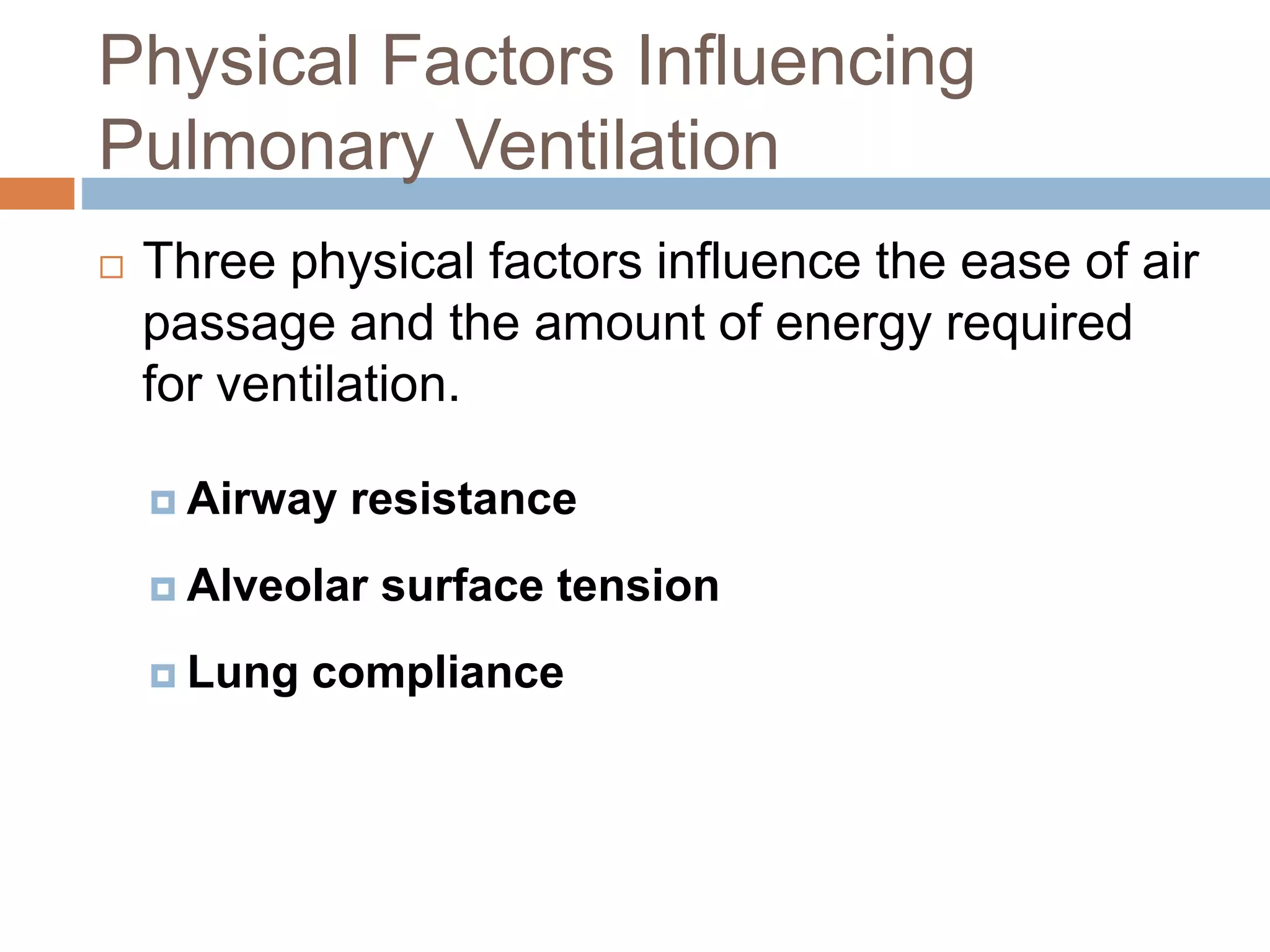
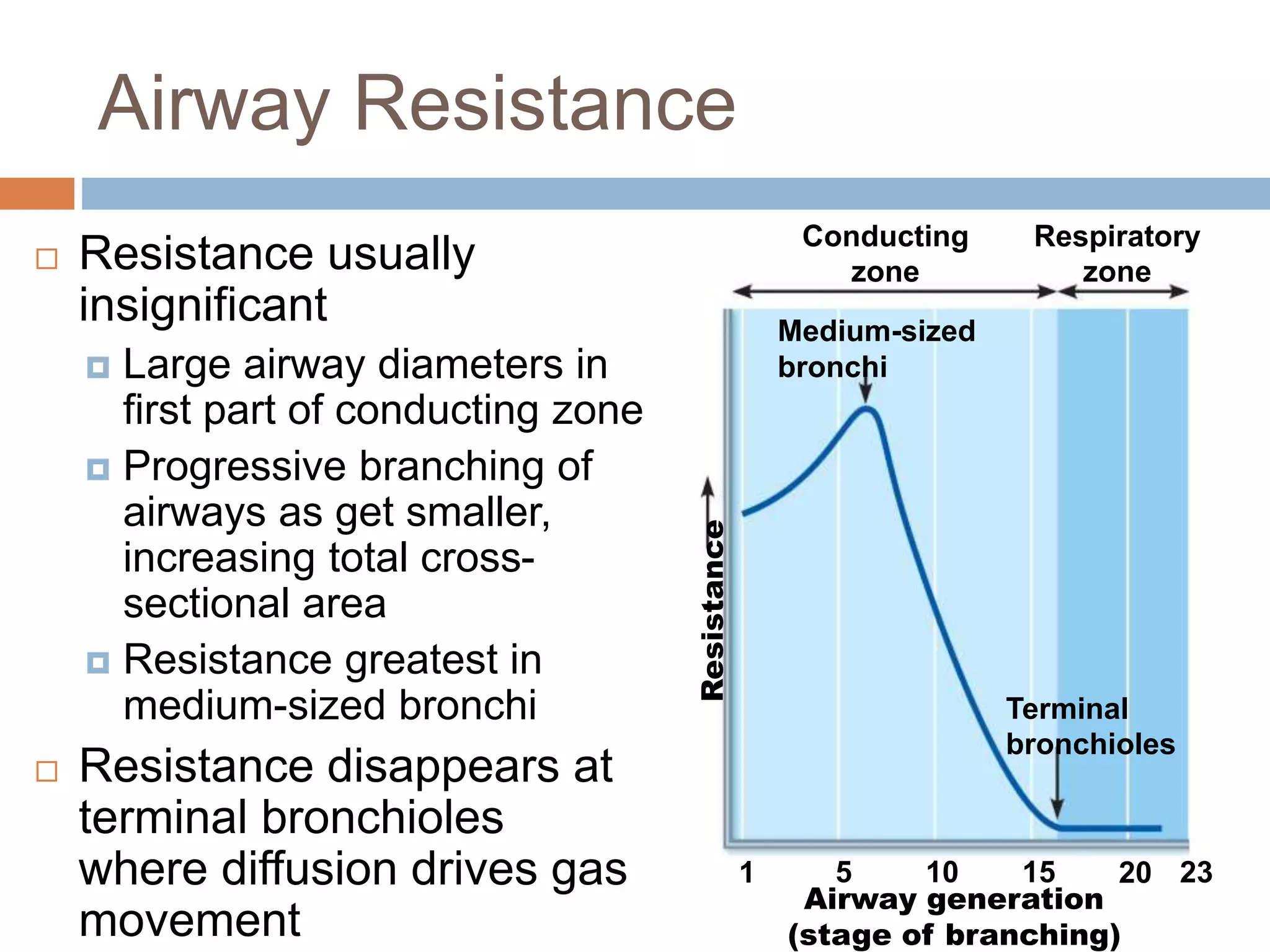
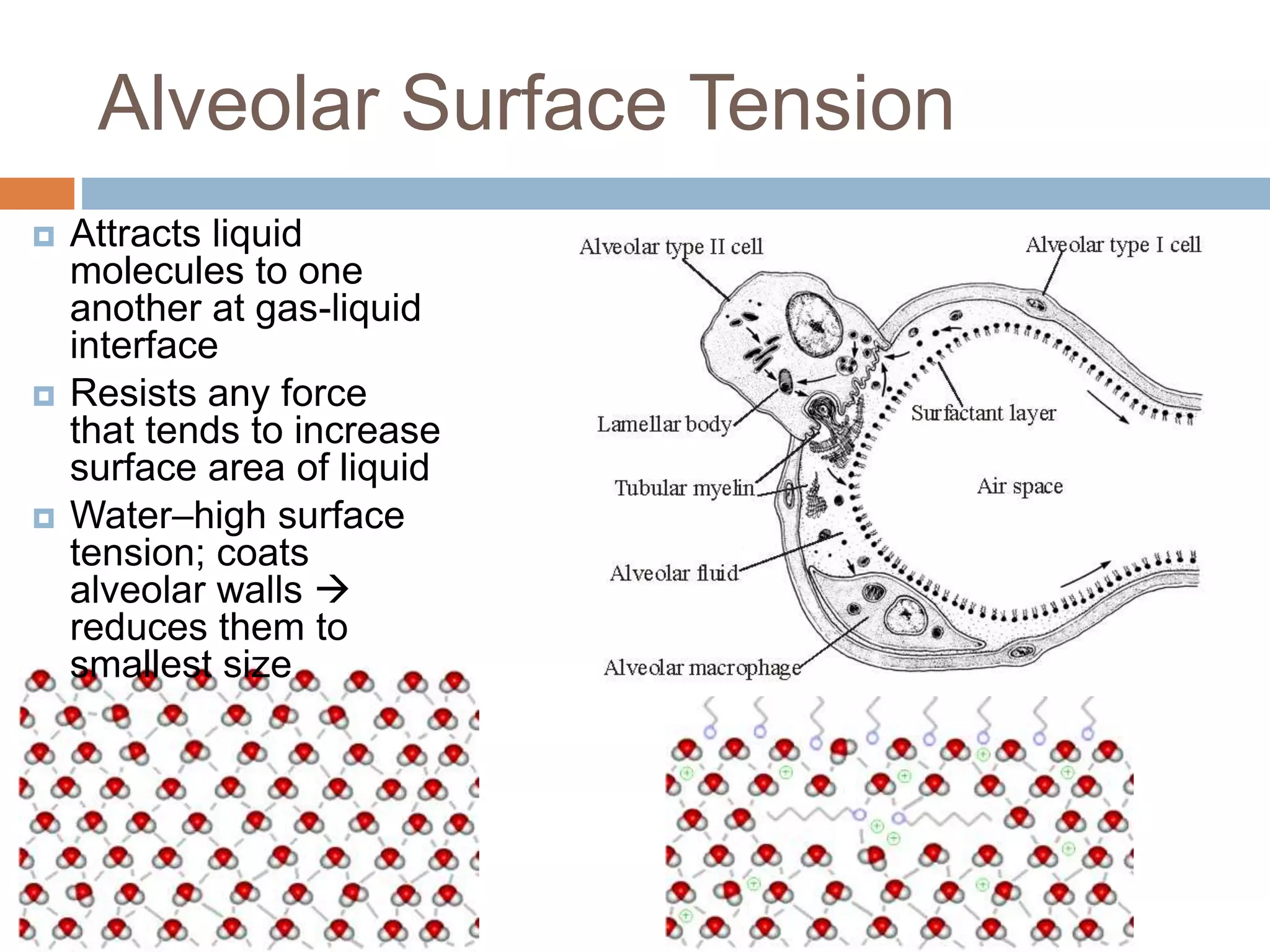
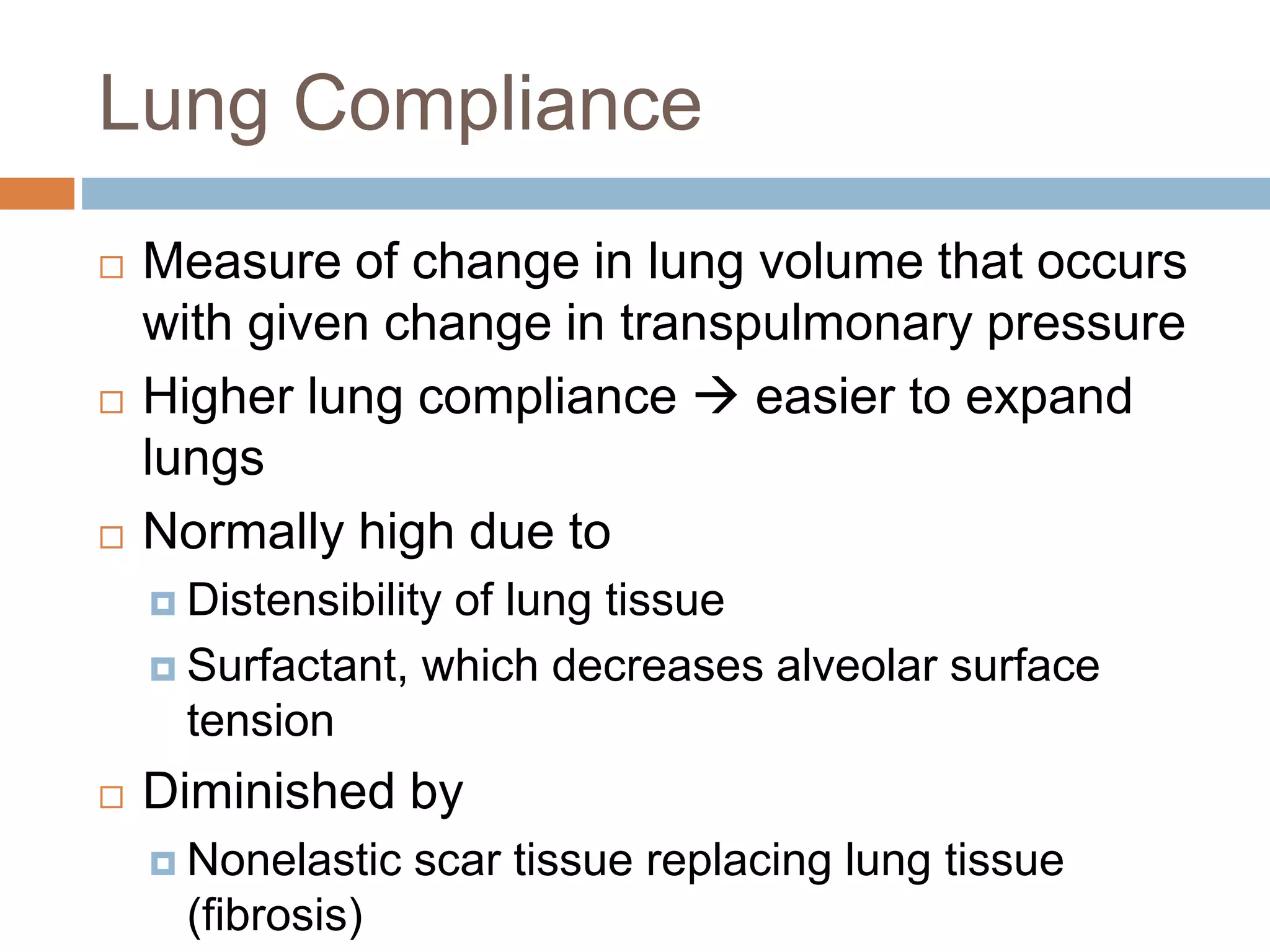
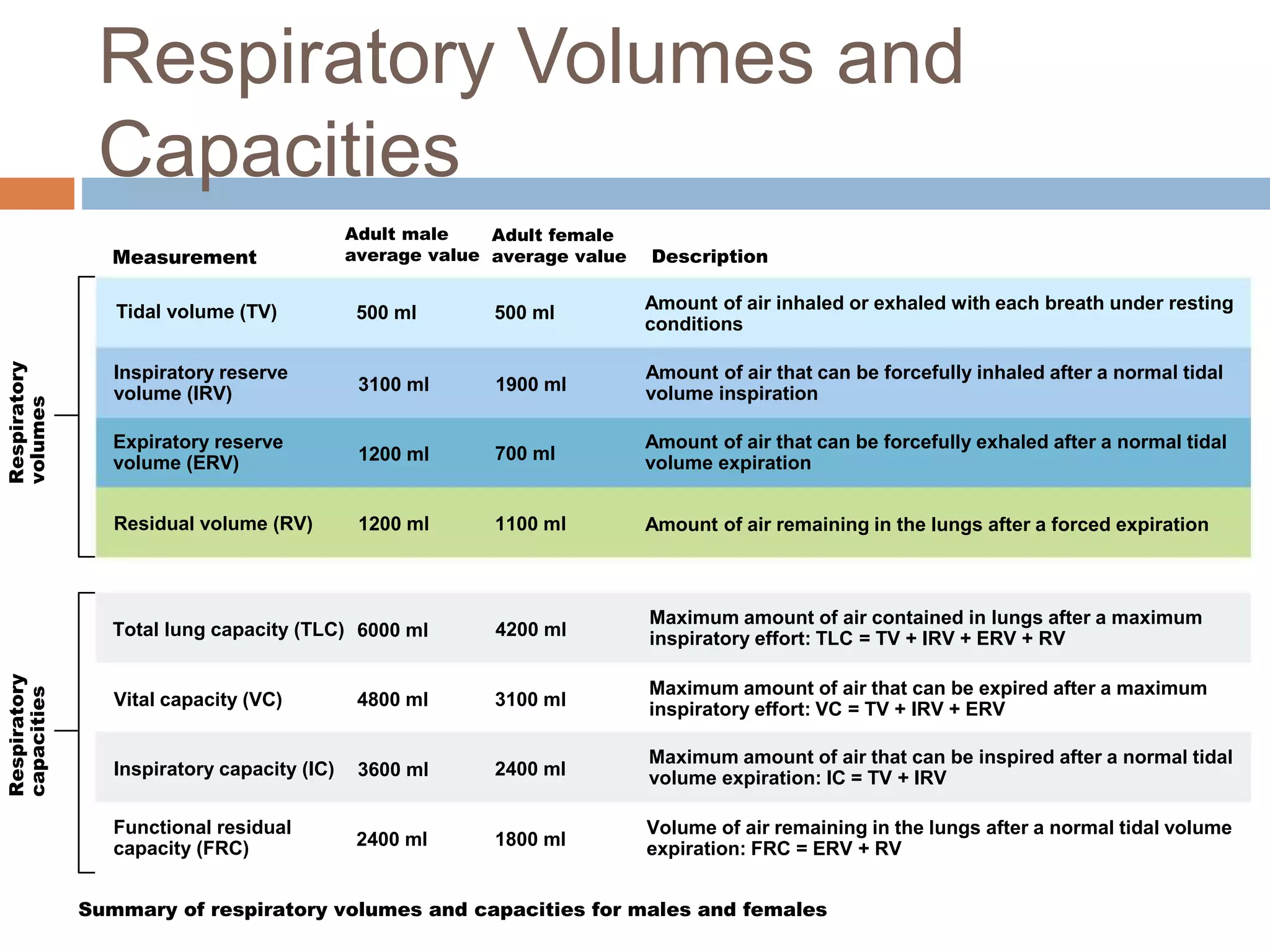
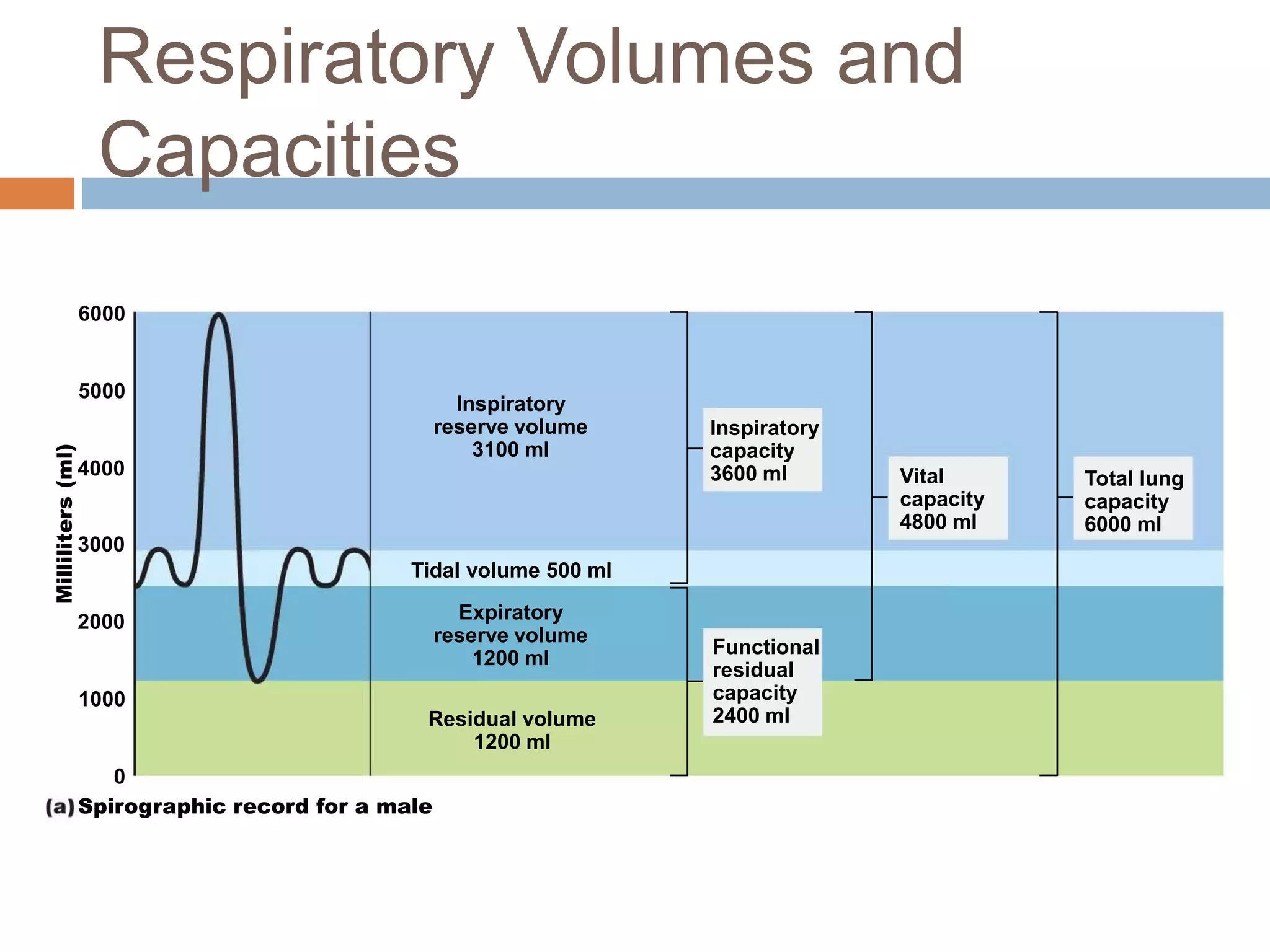
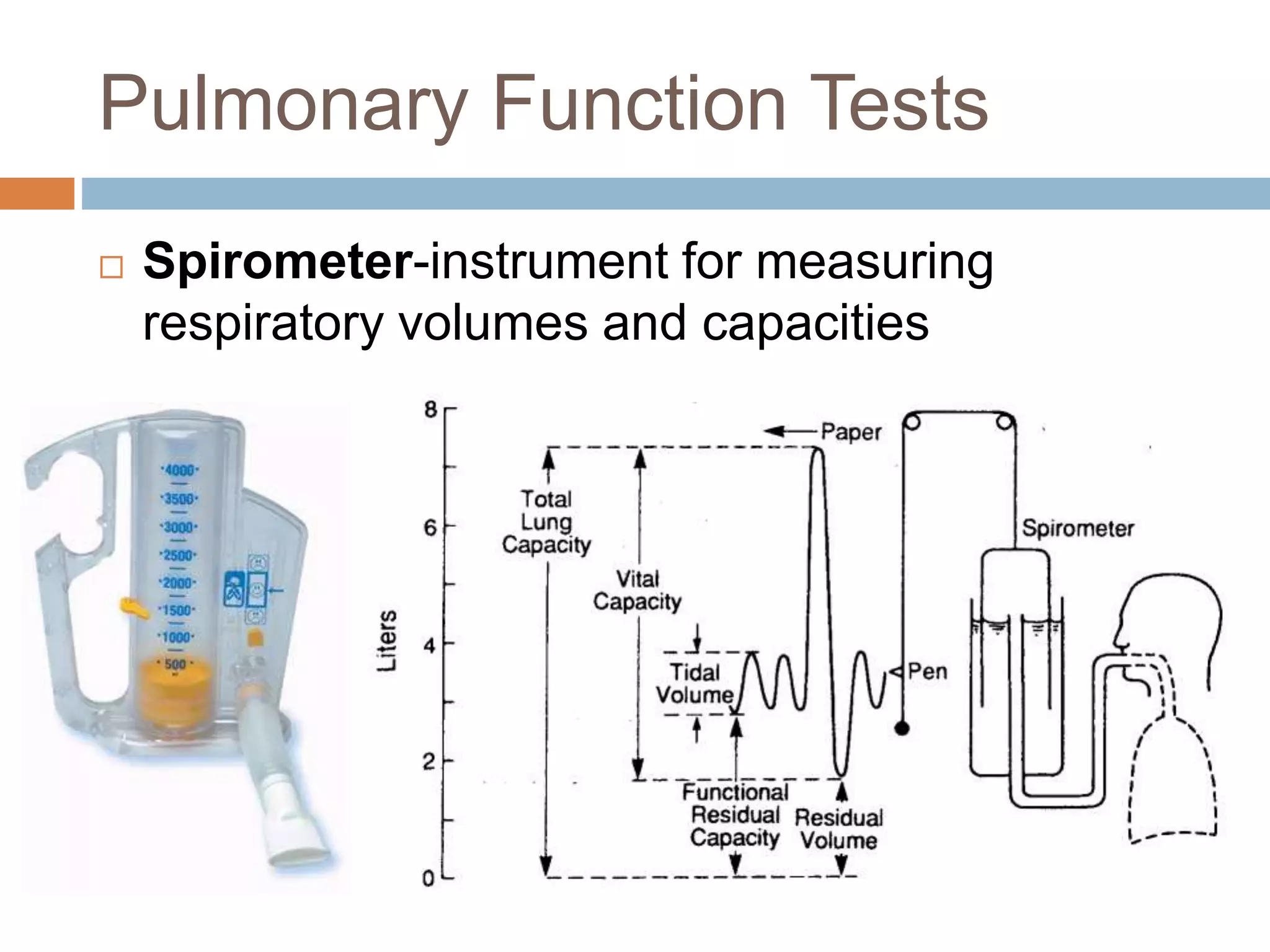
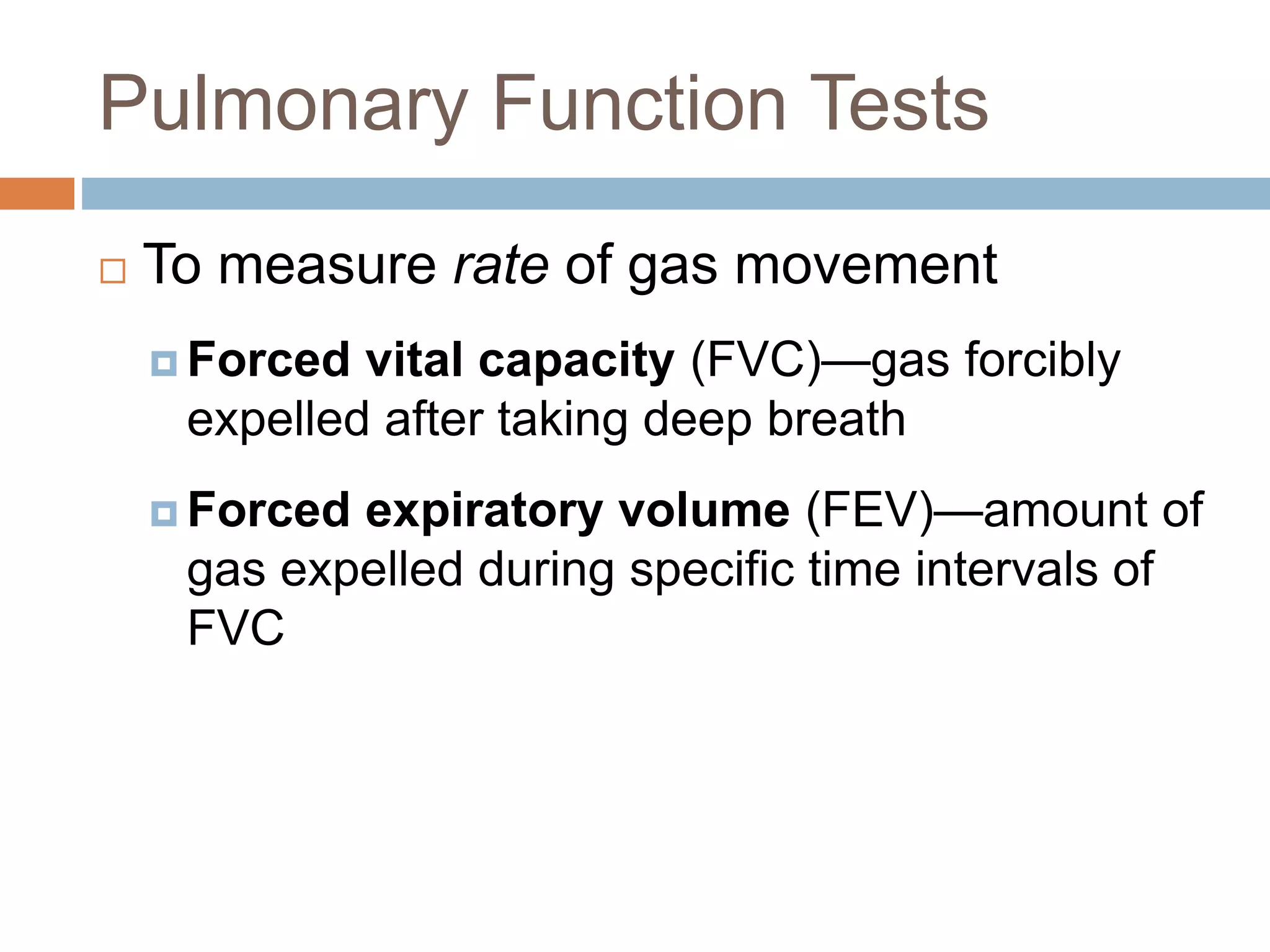
The document summarizes the mechanics of ventilation in the respiratory system. It discusses how inspiration and expiration occur through changes in pressure and volume in the thoracic cavity, lungs, and alveoli. Inspiration is driven by contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles, which increases thoracic cavity volume and causes air to flow into the lungs down the pressure gradient. Expiration occurs passively as the inspiratory muscles relax and the lungs and chest wall recoil, decreasing thoracic volume and causing air to flow out. The document also covers factors influencing ventilation like airway resistance, alveolar surface tension, and lung compliance.