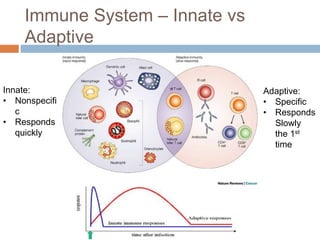
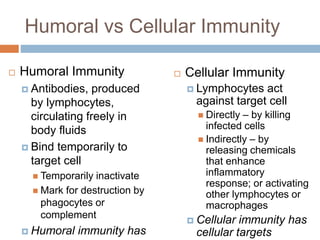
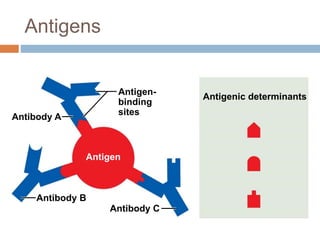
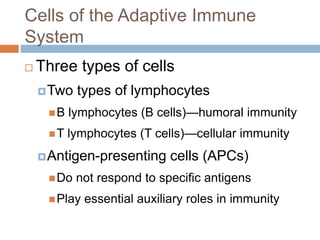
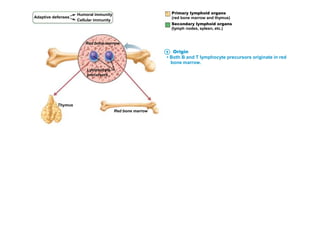
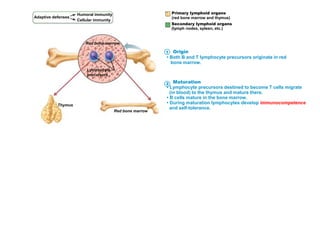
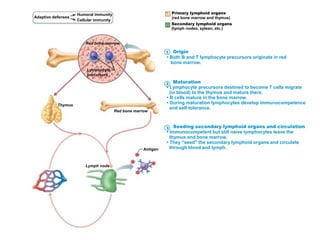
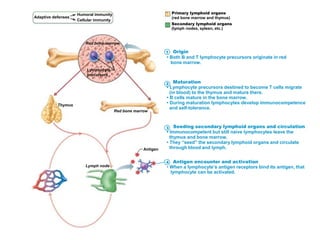
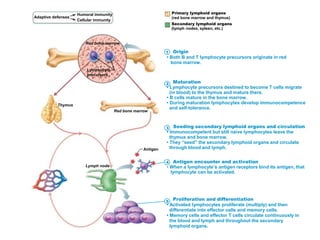
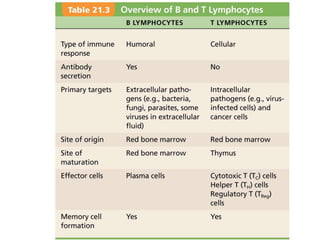
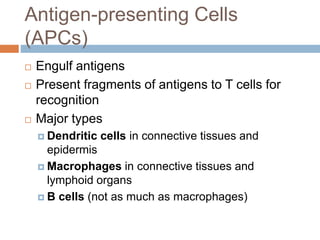
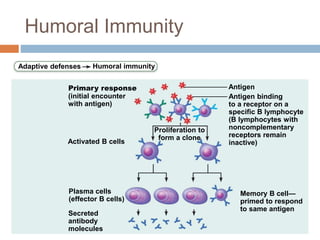
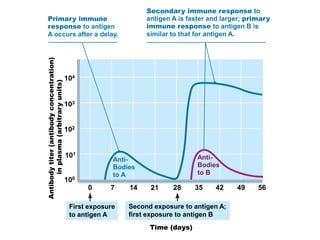
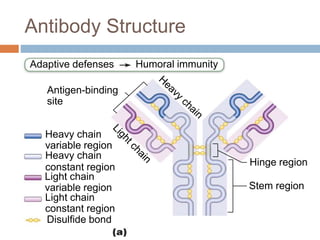
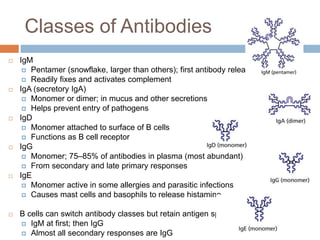
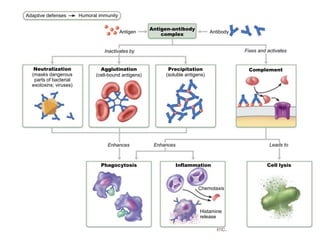
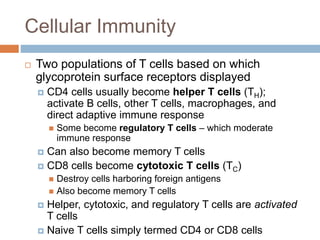
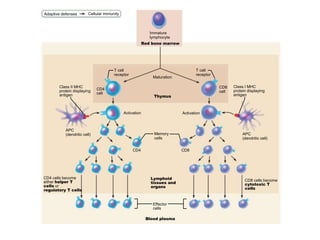
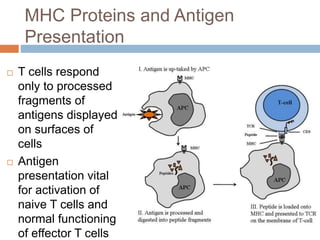
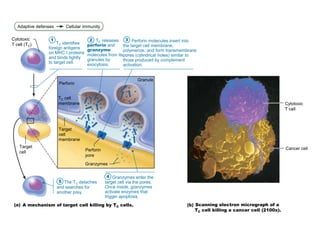
The document summarizes adaptive immunity and compares humoral and cellular responses. It describes the origin of B and T lymphocytes in bone marrow and thymus, their maturation processes, and roles in immunity. B cells mediate humoral immunity through antibody production while T cells direct cellular immunity, including cytotoxic T cells that directly kill infected cells. Memory B and T cells provide faster responses upon reexposure to pathogens. Antigen-presenting cells also play key roles in activating lymphocytes.