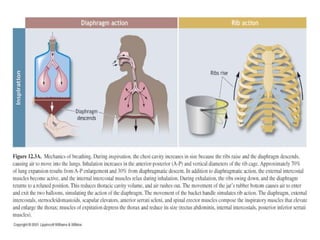
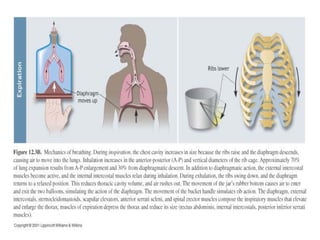
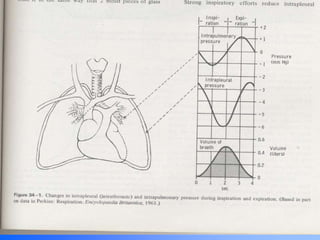
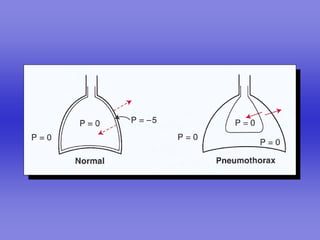
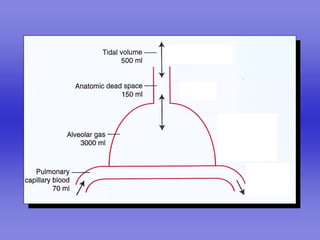
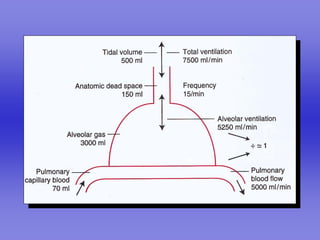
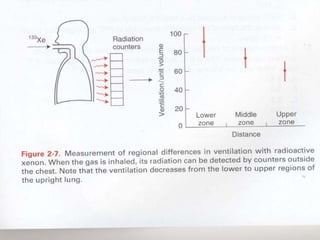
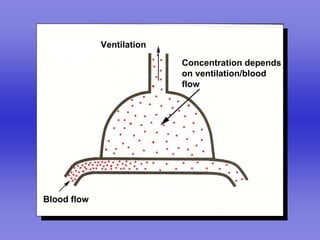
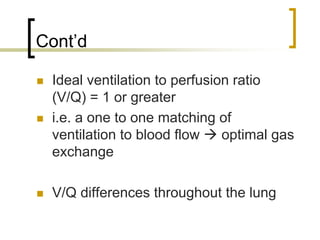
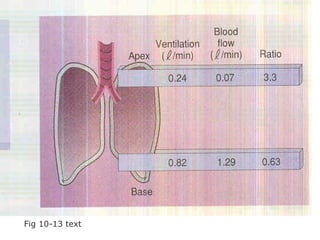
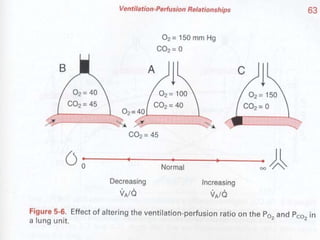
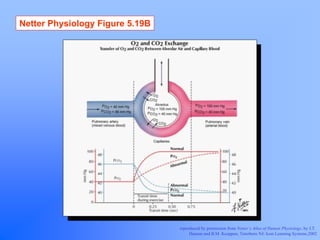
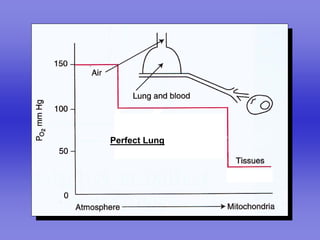
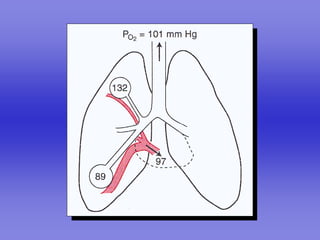
Pulmonary ventilation functions to maintain favorable concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli during rest and exercise. Inspiration occurs when intrapulmonary pressure is reduced below atmospheric pressure through contraction of inspiratory muscles, while expiration is usually a passive process at rest but involves expiratory muscles during exercise. Pulmonary ventilation, measured as minute ventilation, ensures complete gas exchange before blood leaves the lungs for transport throughout the body.




















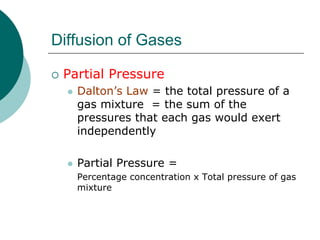




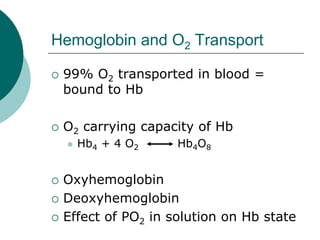
![Cont’d
Amt of O2 that can be transported
per unit volume of blood is
dependent upon [Hb]
Normal [Hb]
Gender differences (m=150g; f=130g)
When completely saturated with O2,
each g of Hb can transport 1.34 ml
O2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respirationpowerpoint-110303080645-phpapp02/85/Respiration-powerpoint-65-320.jpg)