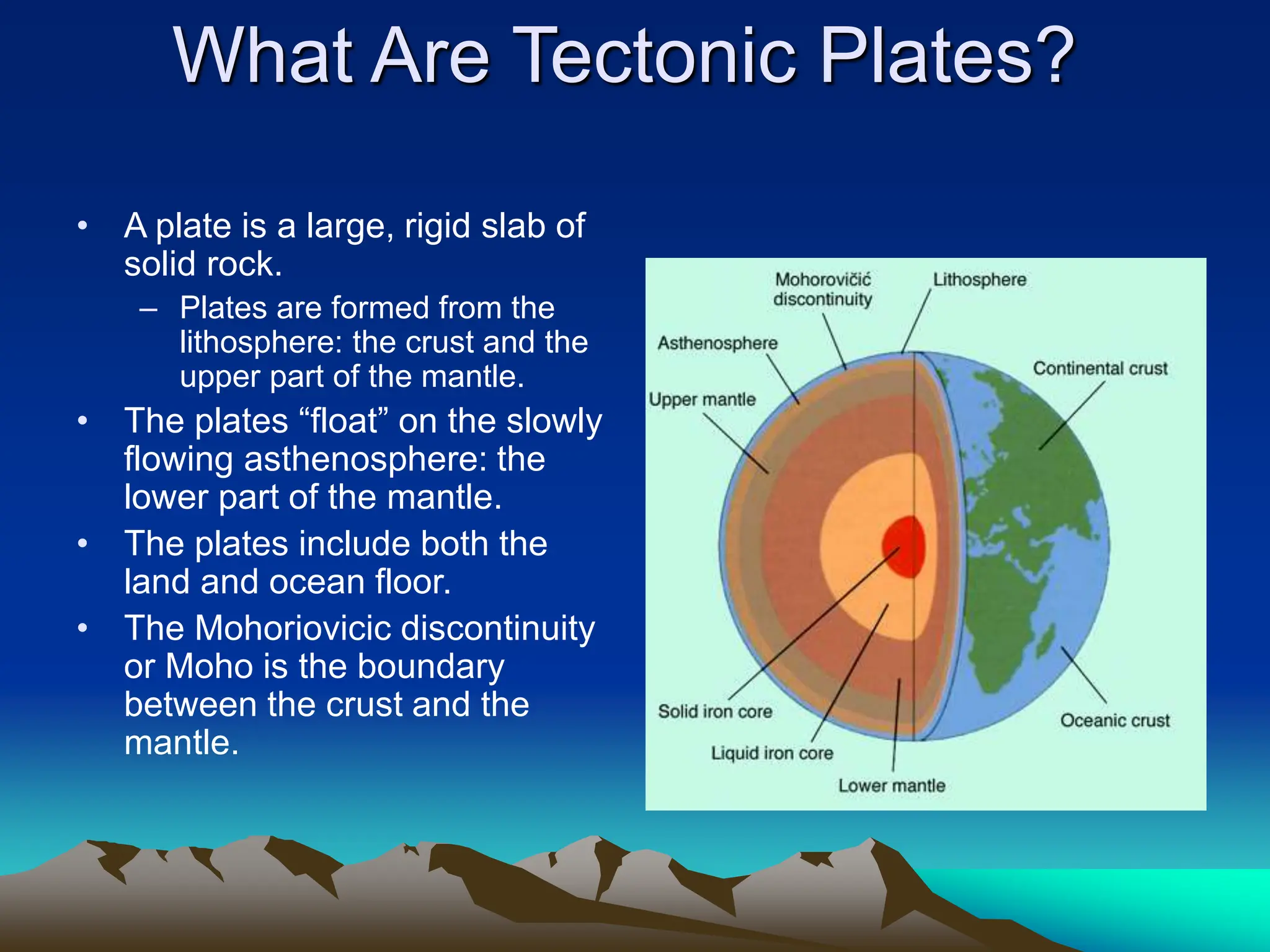
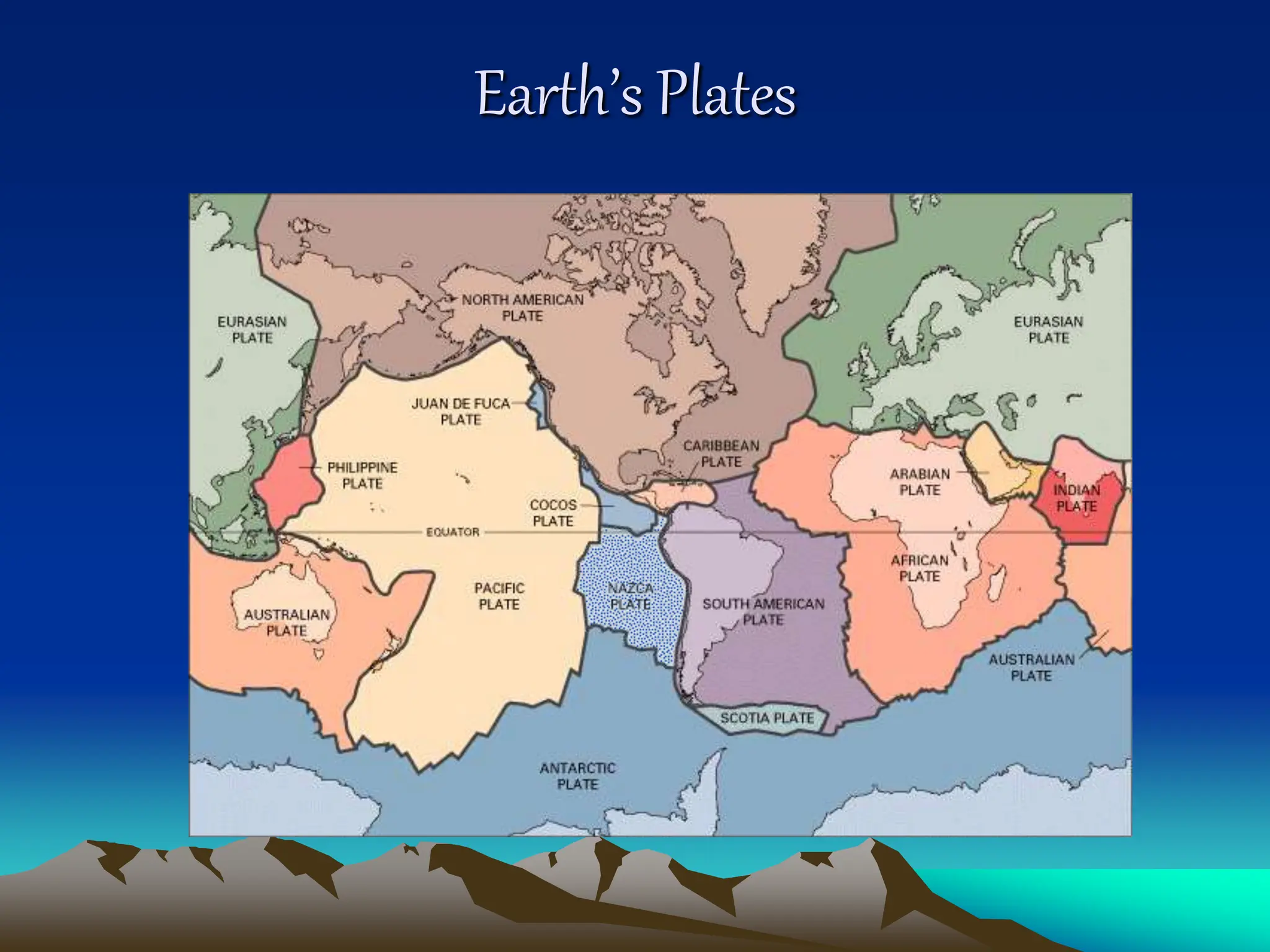
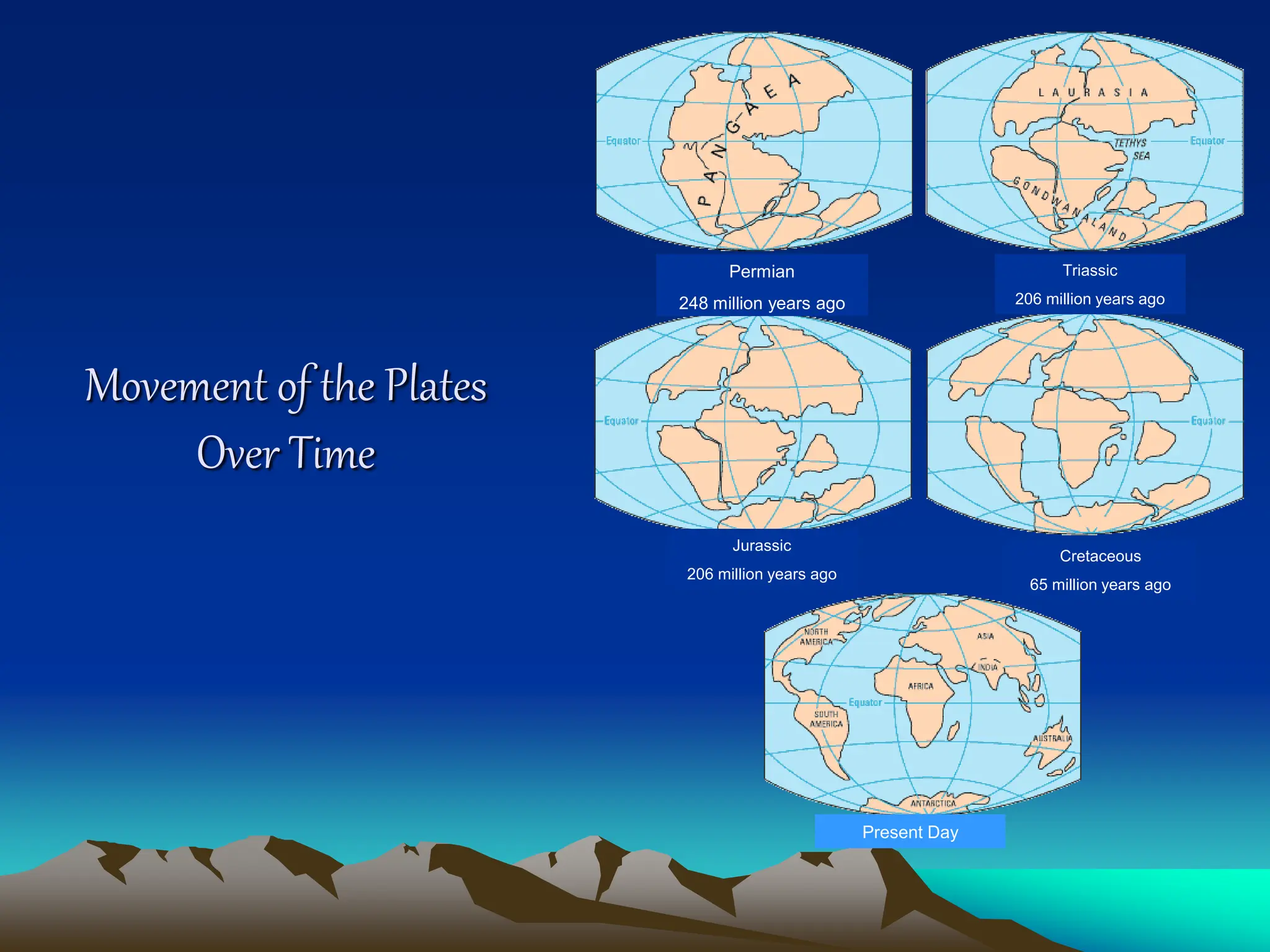
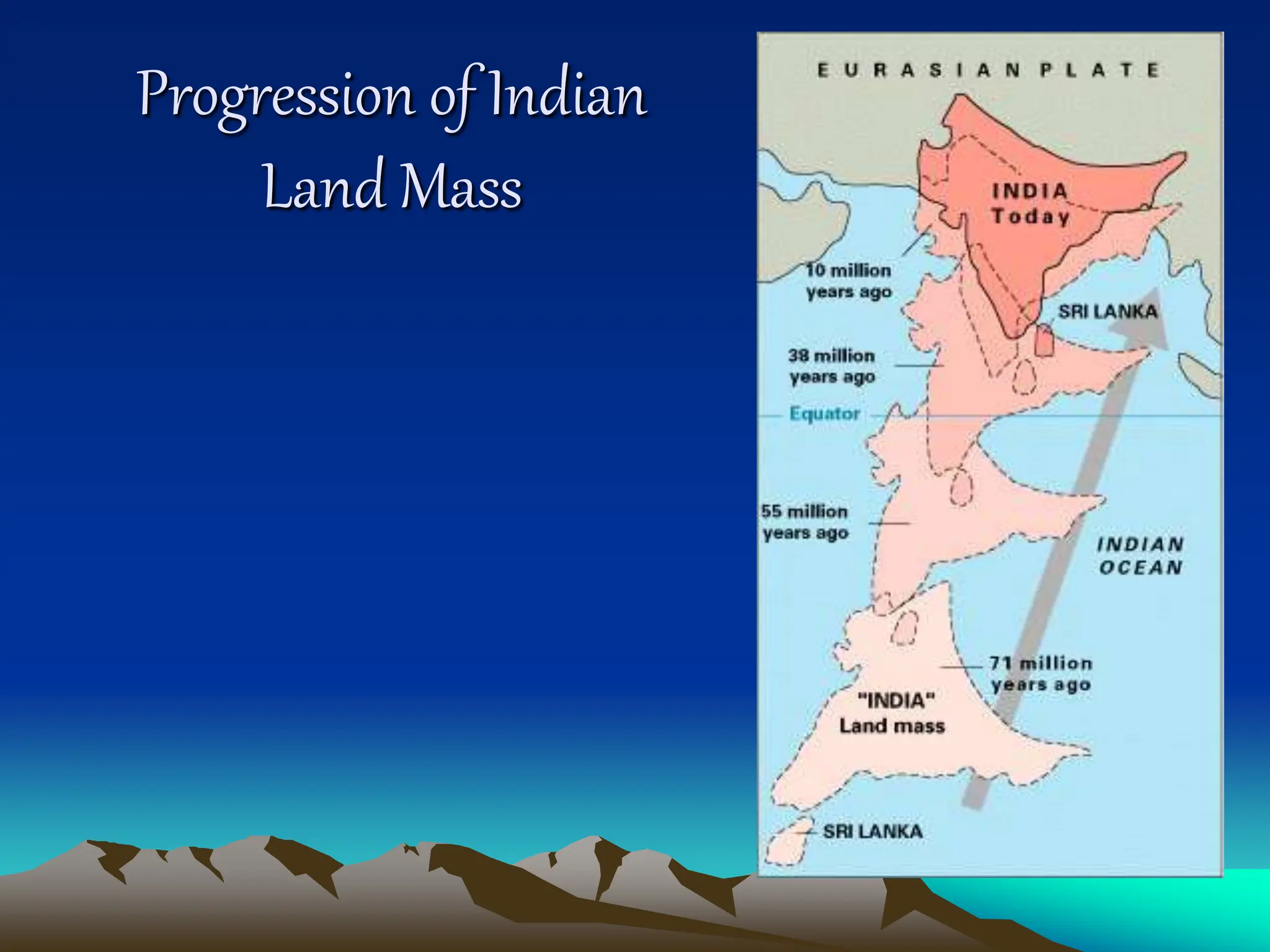
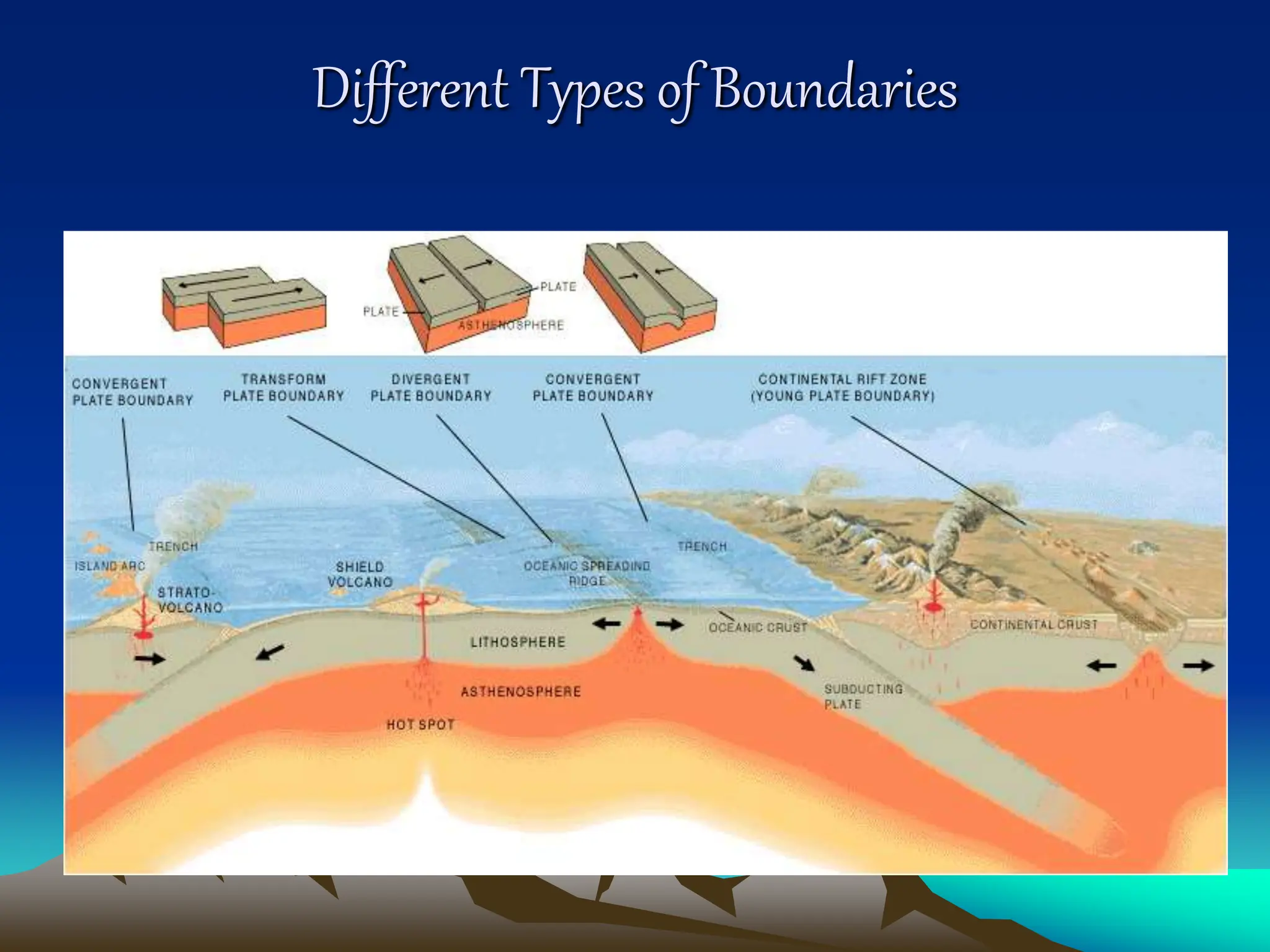
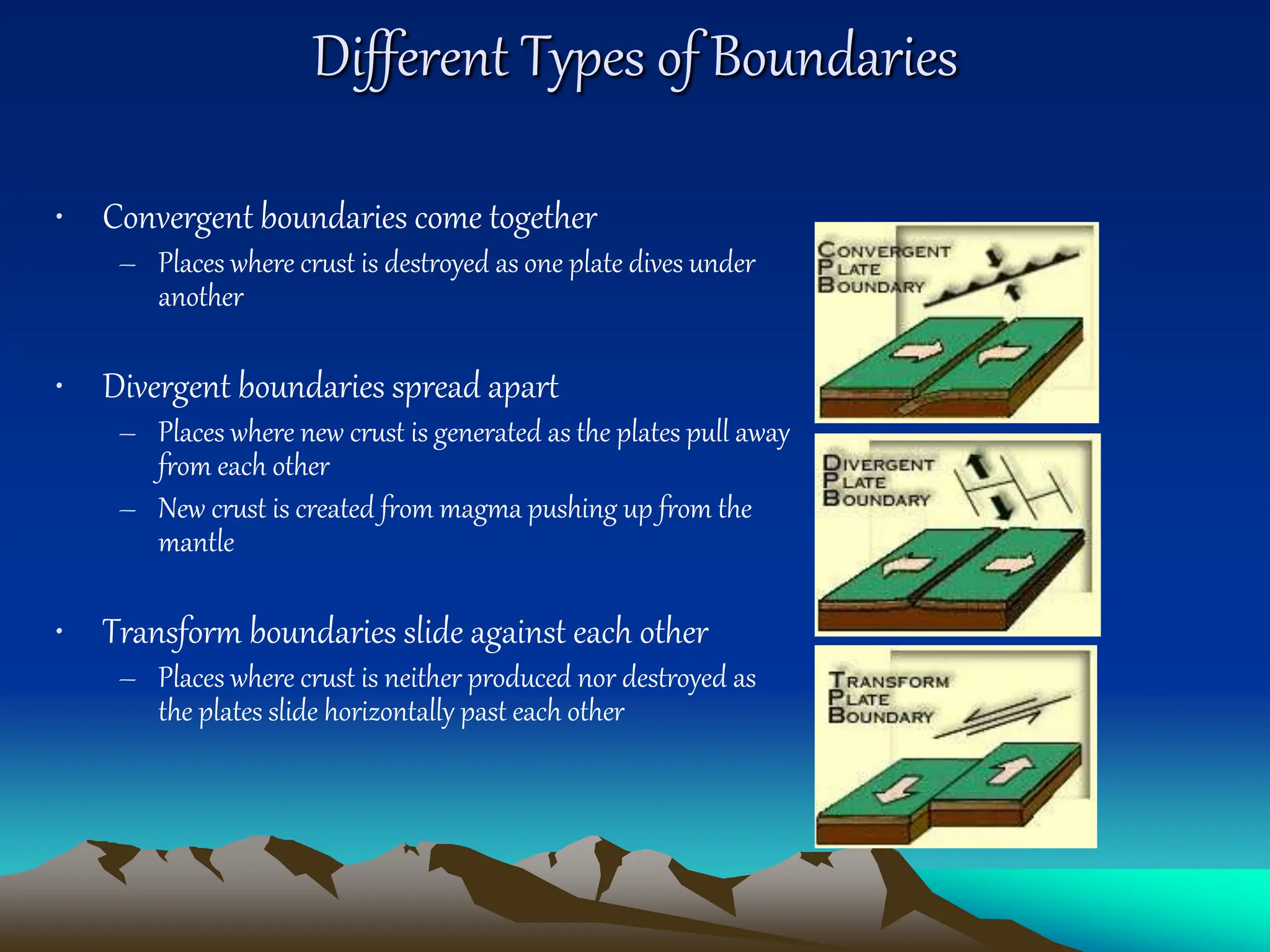
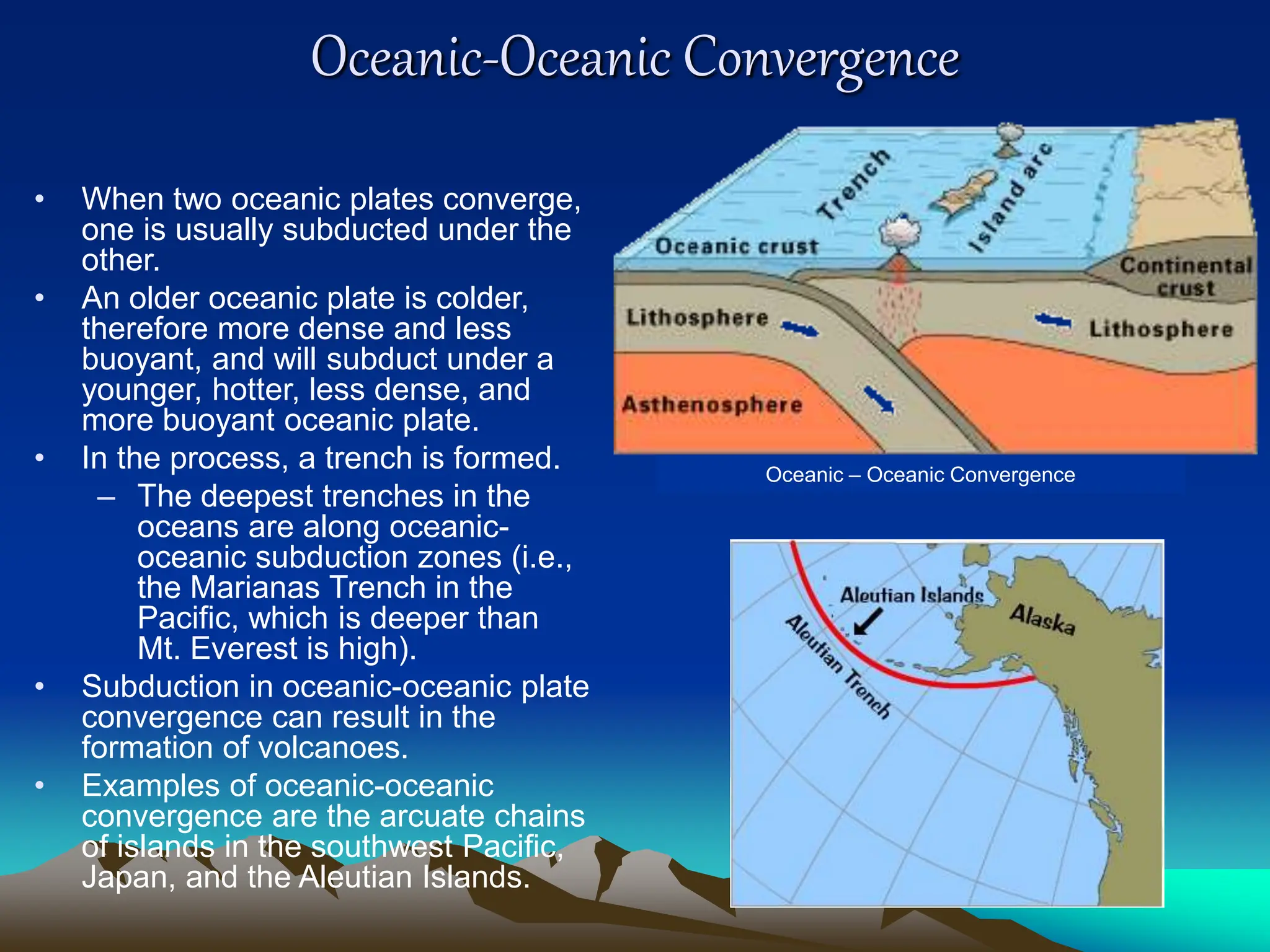
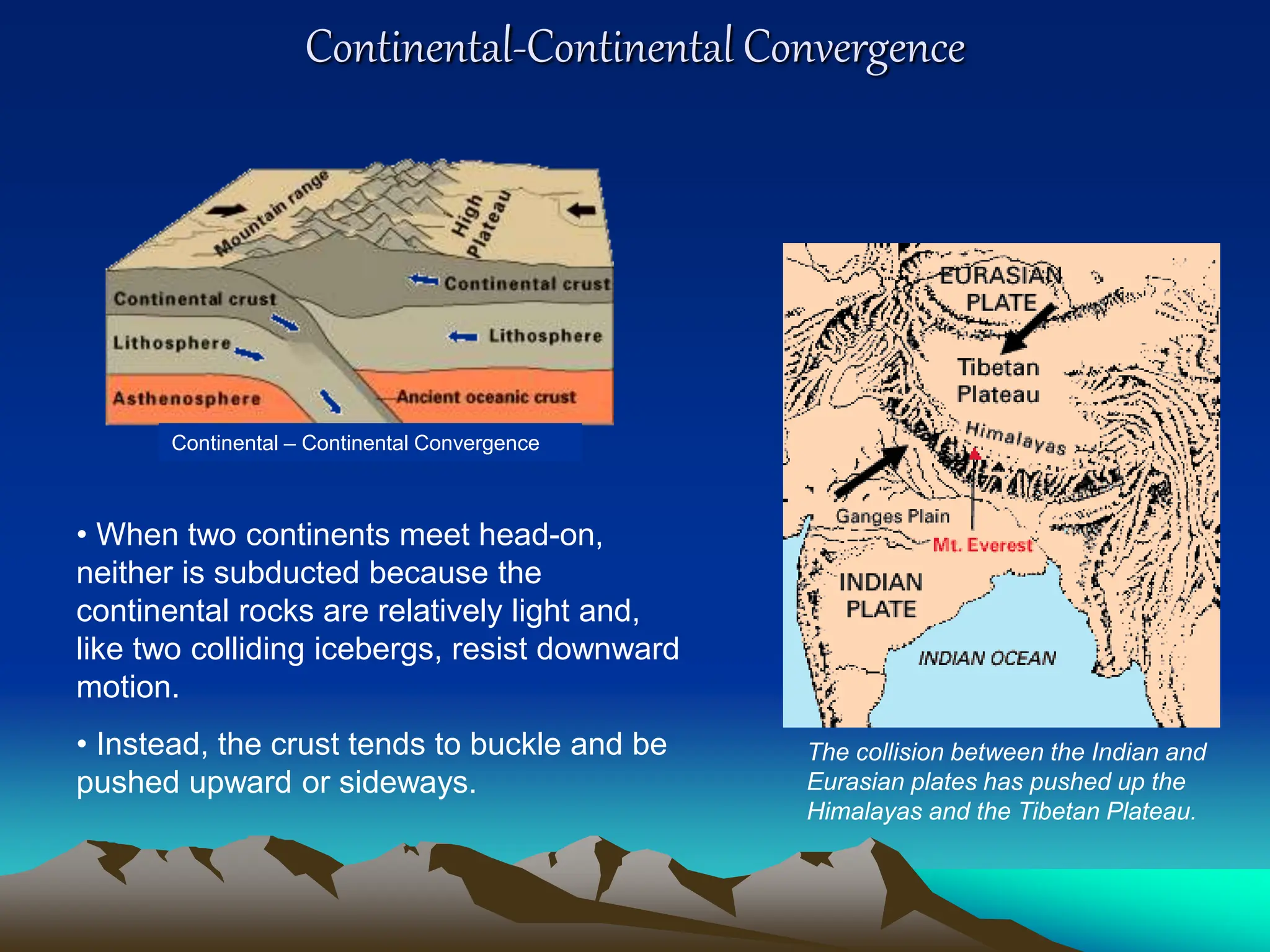
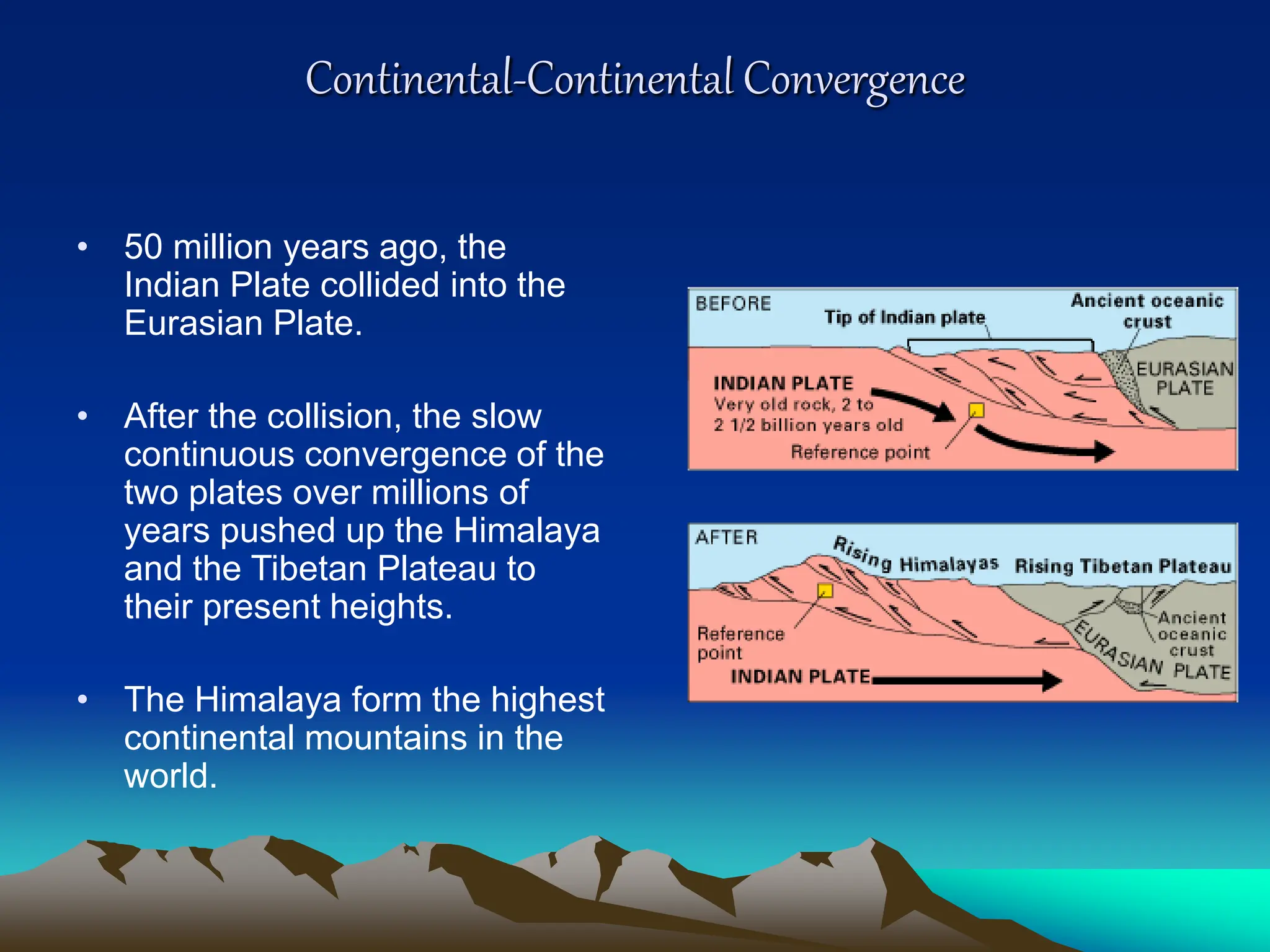
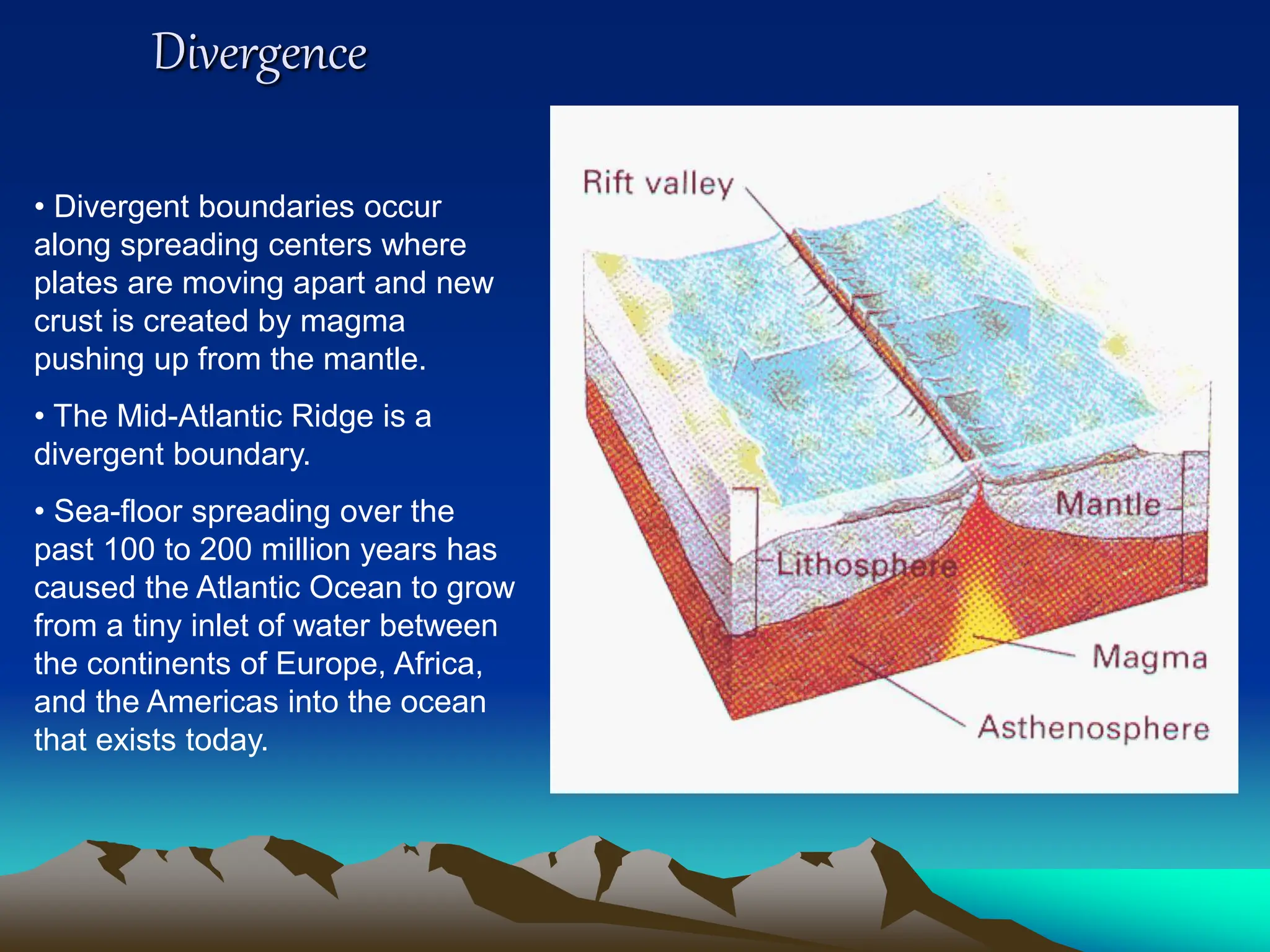
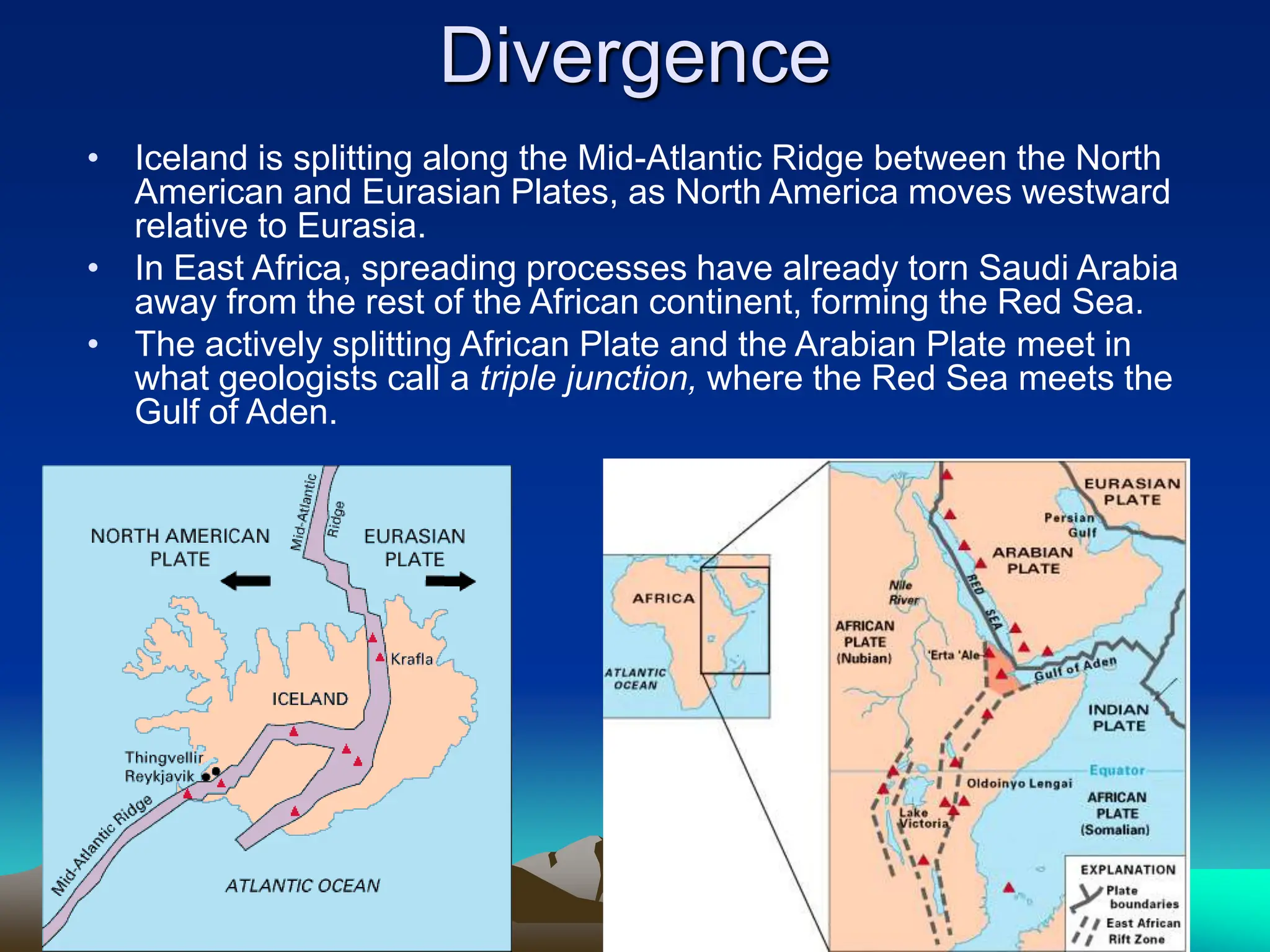
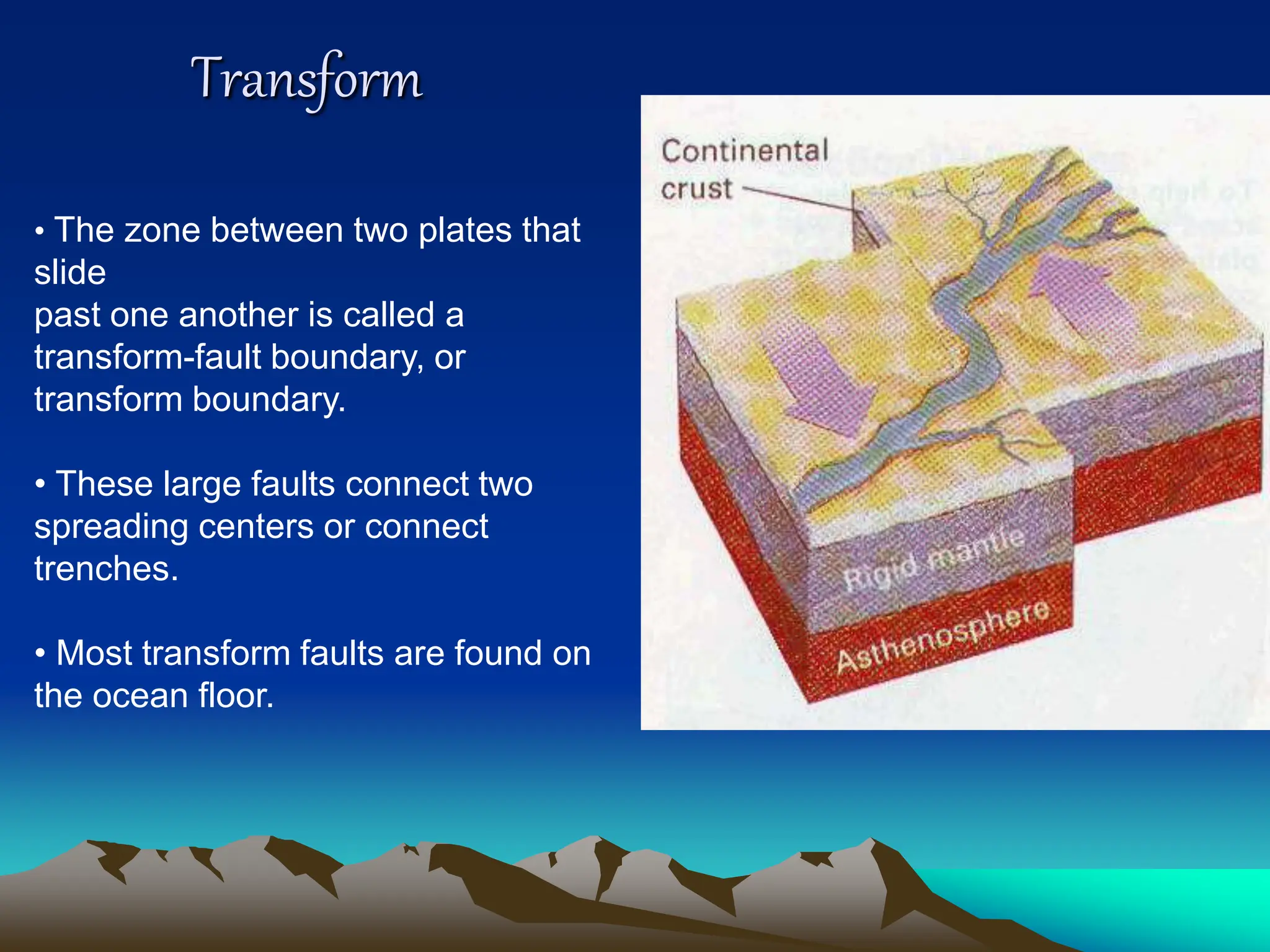
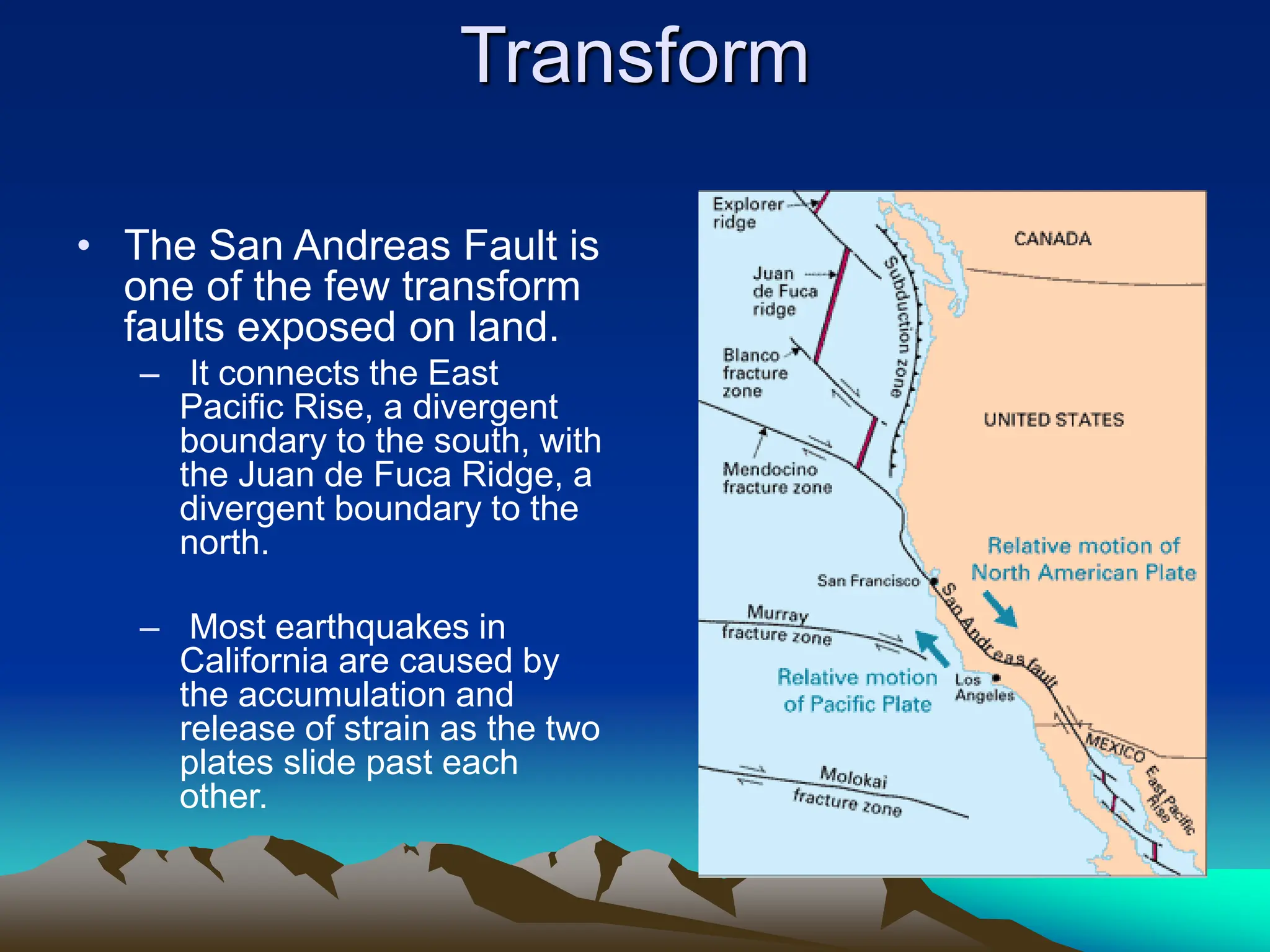
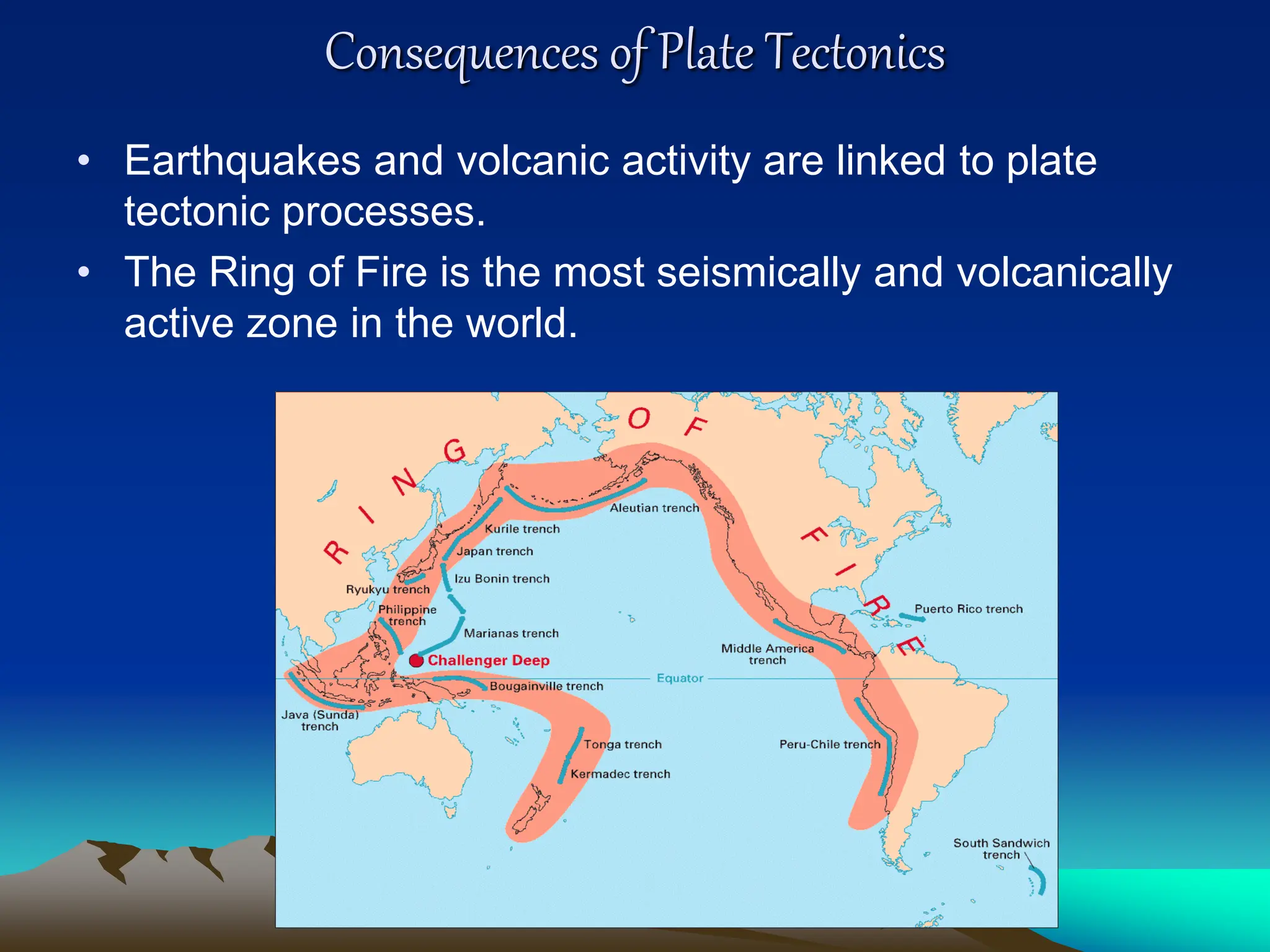
Plate tectonics is the theory that the Earth's outer layer consists of moving slabs called tectonic plates, which are formed from the lithosphere and float on the asthenosphere. These plates interact at different boundaries—convergent, divergent, and transform—leading to geological phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic activity. Significant geological formations, such as mountains and oceanic trenches, arise from these tectonic activities over geological time scales.