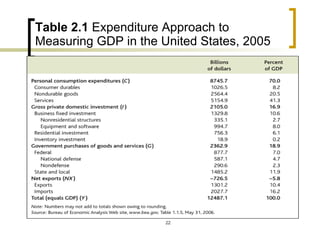
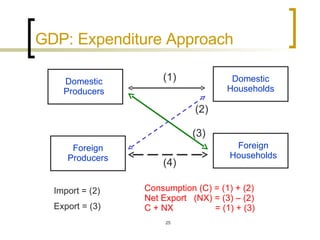
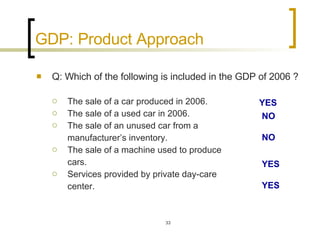
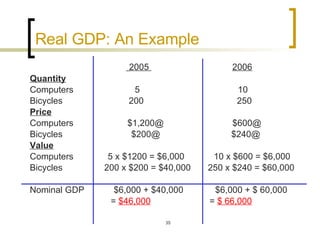
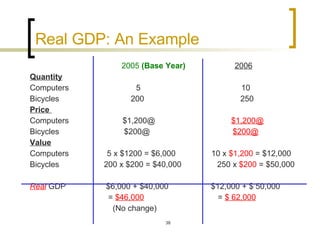
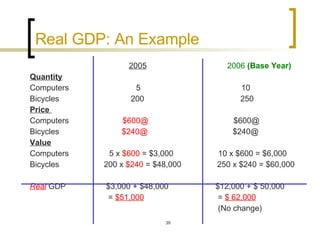
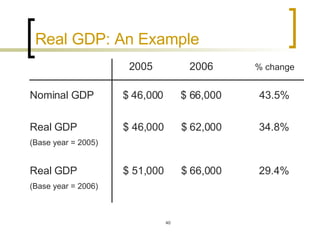
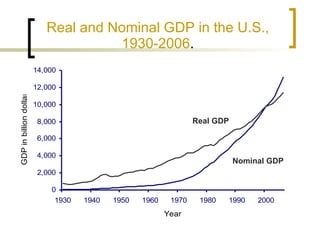
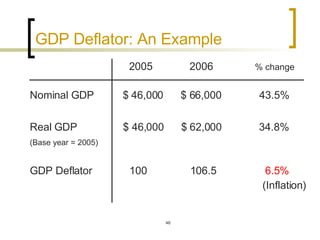
This chapter discusses how economic activity is measured at the national level. It introduces the basic framework of national income accounting and the three approaches to measuring GDP: the product, income, and expenditure approaches. It provides an example to illustrate how the three approaches should yield the same result. The chapter also distinguishes between nominal and real GDP and explains how price indexes like the GDP deflator and CPI are used to measure inflation.












![GDP: Income Approach Compensation of employees is the before-tax income of workers (excluding the self-employed). [57% of GDP in 2005.] Corporate Profits represent the remainder of the corporate revenue after wages, interest, rents and other costs have been paid but before taxes have been paid. [10.8% of GDP in 2005.] Proprietor’s income is the income of the non-incorporated self-employed. [7.5% of GDP in 2005.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-1209103493611214-8/85/Chapter-2-19-320.jpg)
![GDP: Income Approach Taxes on production and imports include indirect business taxes (such as sales taxes) as well as custom duties and taxes on residential real estate. [6.8% of GDP in 2005.] Net interest is interest earned by individuals from businesses and foreign sources minus interest paid by individuals. [4.0% of GDP in 2005.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-1209103493611214-8/85/Chapter-2-20-320.jpg)