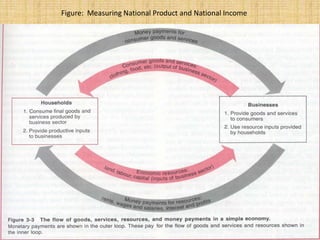
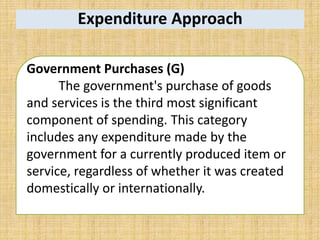
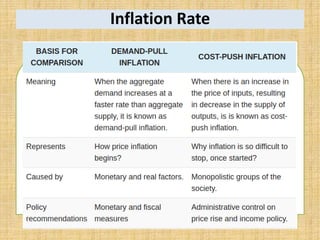
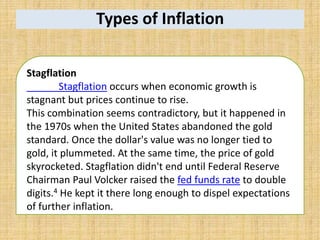
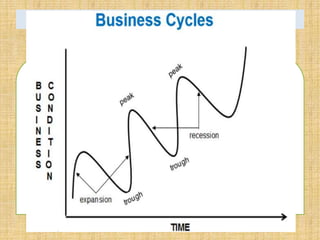
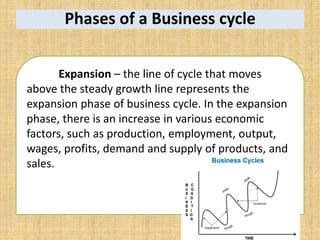
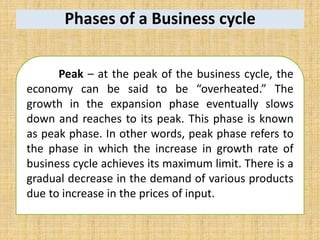
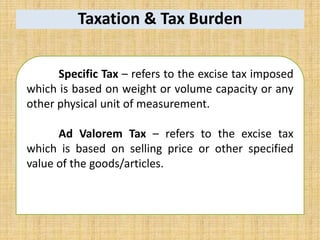
National income measures the total value of goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time. It is important for economists to measure national income to assess economic growth, changes in living standards, and income inequality. National income can be measured using the expenditure approach, income approach, and value-added approach. The expenditure approach defines GDP as the total final expenditures by consumers, investors, the government, and net exports. The income approach defines GDP as the sum of all incomes received by producing factors. The value-added approach defines GDP as the sum of the value added from all sectors of the economy.