The document discusses key marketing concepts including:
- The definition of marketing as a social and managerial process to satisfy needs through product creation and exchange.
- The objectives of marketing which include increasing sales, creating goodwill, profit through customer satisfaction, and more.
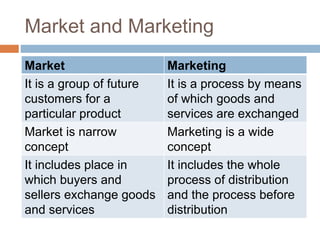
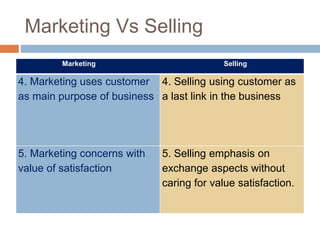
- The distinction between marketing and selling, where marketing focuses on customer needs and selling focuses on product sales.
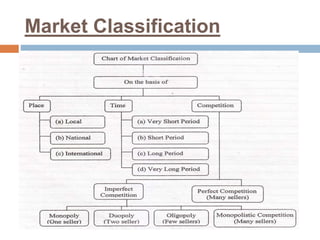
- Marketing classifications based on place, time, and competition.
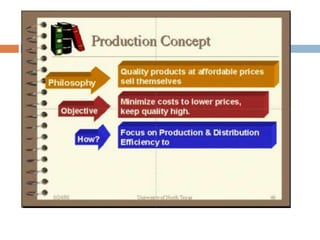
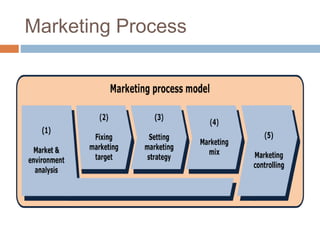
- An overview of marketing management and the production, product, selling, marketing, and societal concepts in marketing.