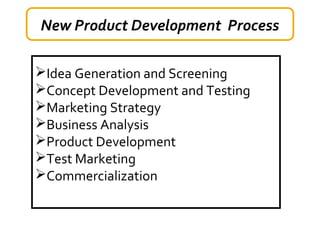
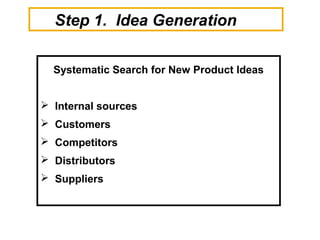
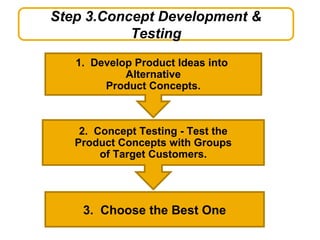
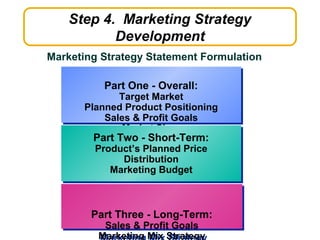
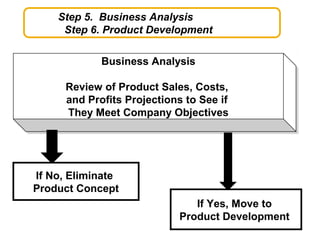
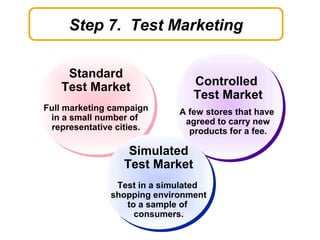
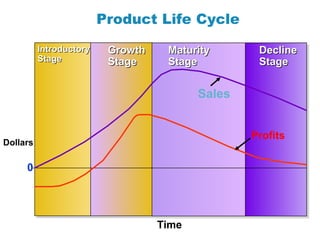
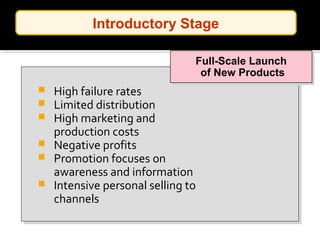
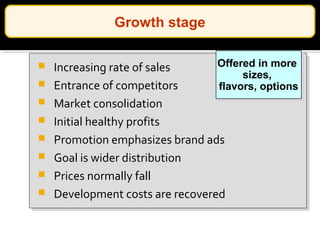
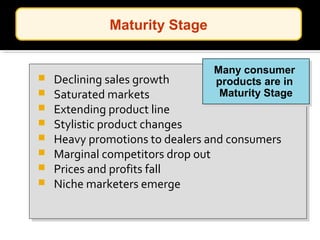
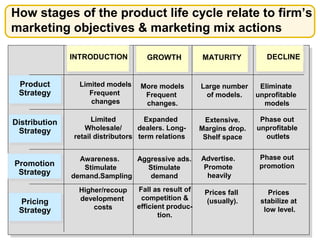
The document discusses new product development and the product lifecycle. It outlines the 7 steps of new product development as idea generation, screening, concept development and testing, marketing strategy development, business analysis, product development, and test marketing. It then describes the 4 stages of the product lifecycle as introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Finally, it shows how a firm's marketing objectives and mix should relate to the different product lifecycle stages.