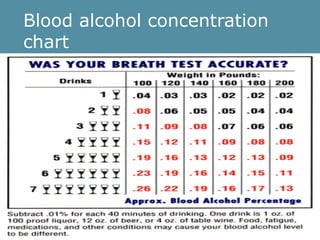
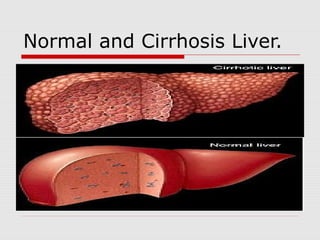
Alcohol is considered a drug because it causes intoxication and changes a person's physical and mental state. The short-term effects of alcohol include irritating the digestive system, increasing heart rate, causing dehydration and making the liver work harder. It also acts as a depressant on the nervous system, impairing judgment, coordination and mood. Long-term alcohol abuse can cause permanent damage to organs like the liver, resulting in conditions like cirrhosis, and the brain, potentially leading to dementia. Binge drinking or drinking above the legal limit puts one at risk for these long-term health consequences.