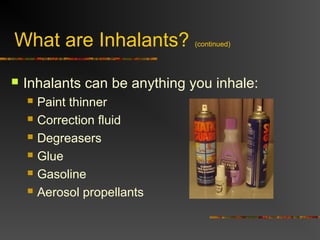
This document discusses different types of drugs, their effects, dangers of abuse, and treatment options. It defines drugs as substances that alter physical or mental state. It categorizes major drug types as stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants, narcotics, and inhalants. For each drug type, specific examples are provided along with how they work in the body and associated health risks like overdose, organ damage, and addiction. The final sections discuss how addiction develops through tolerance, dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Treating addiction involves talking to others, medical help, and rehabilitation programs.