This chapter discusses perfect competition and profit maximization in competitive markets. It contains the following key points:
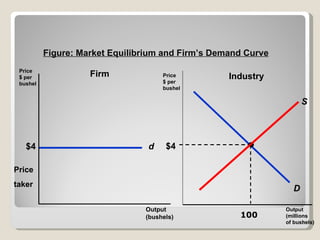
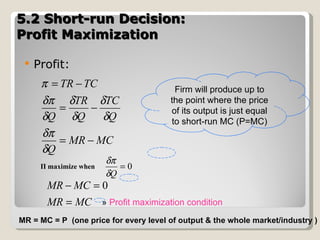
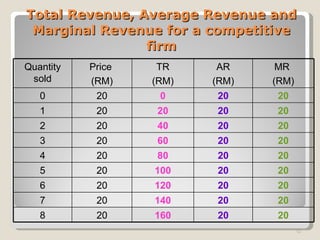
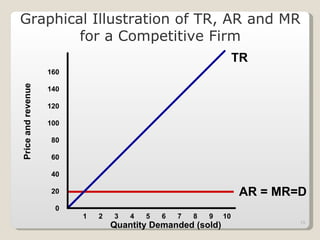
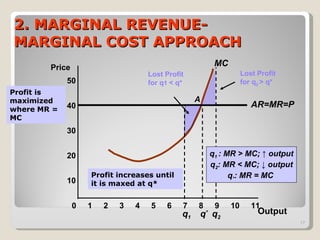
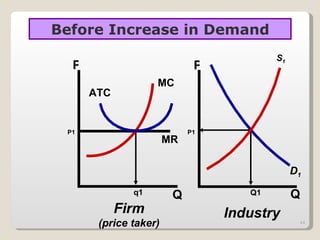
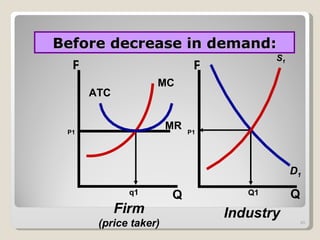
1. Under perfect competition, there are many small firms and buyers/sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and perfect information. Firms are price takers and maximize profits by producing where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
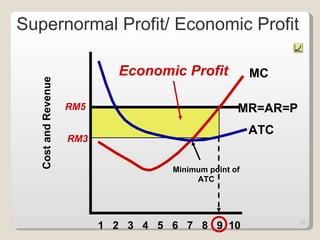
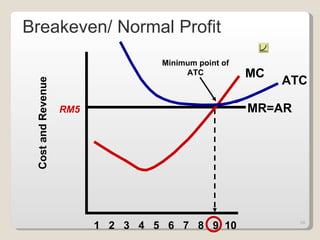
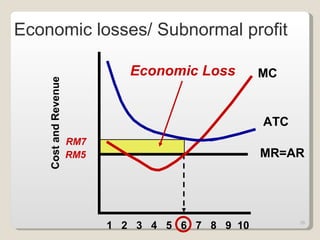
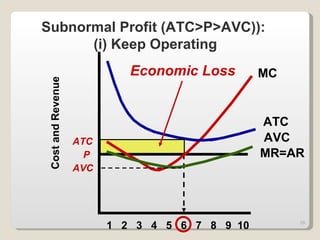
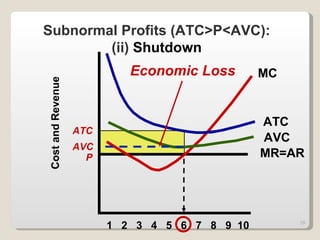
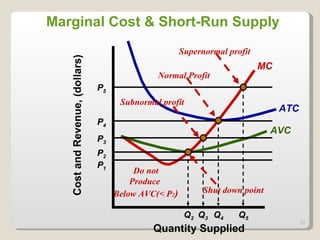
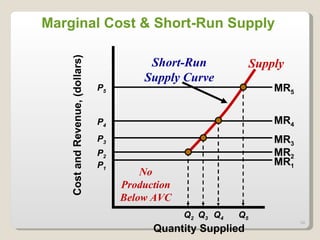
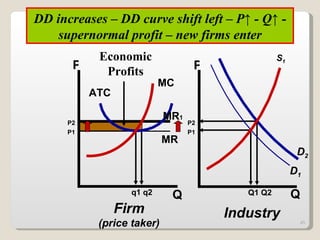
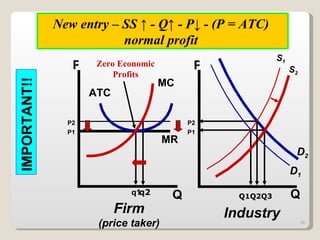
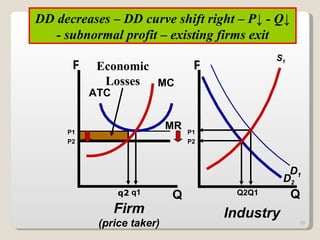
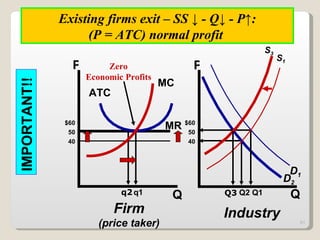
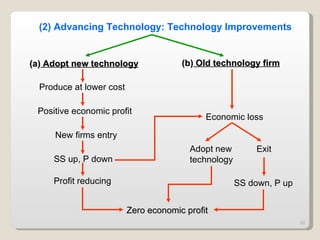
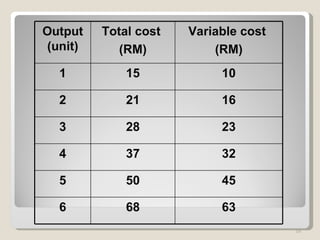
2. In the short run, firms will shut down if price falls below average variable cost or operate at a loss if price is between average variable and average total cost. In the long run, zero economic profits are achieved through free entry and exit of firms.
3. External changes like shifting demand curves or new technology can impact market equilibrium price and quantity in both the