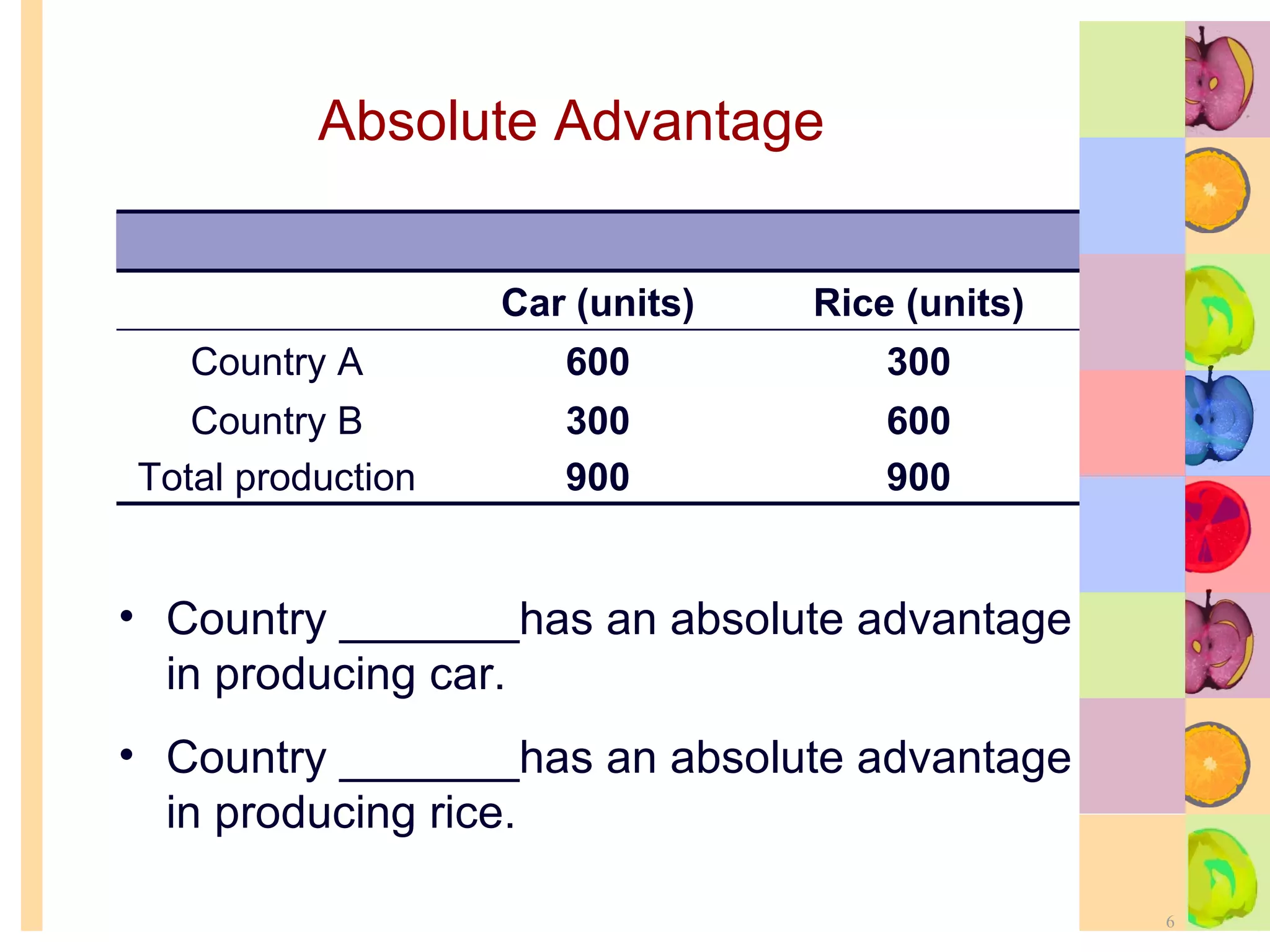
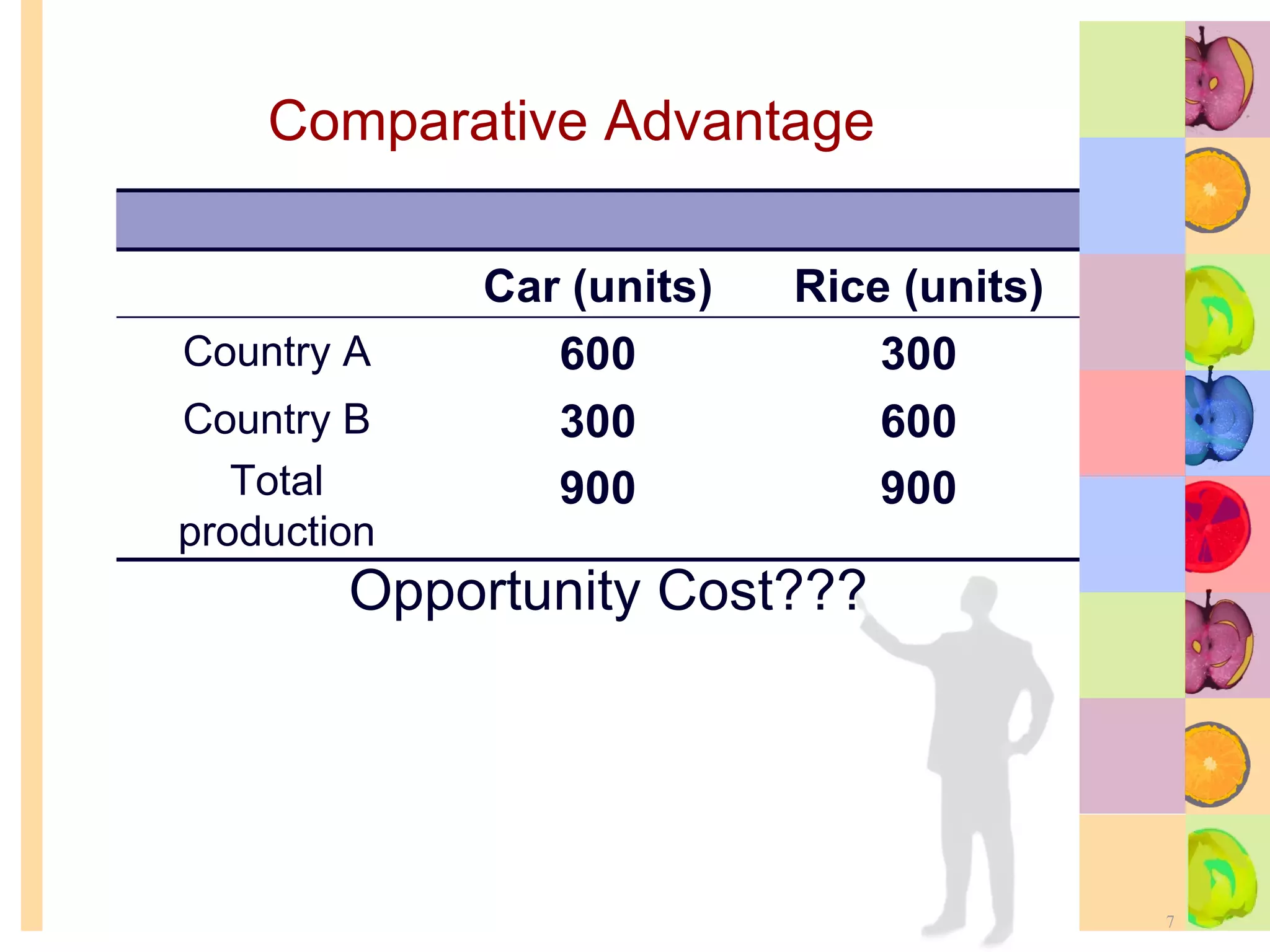
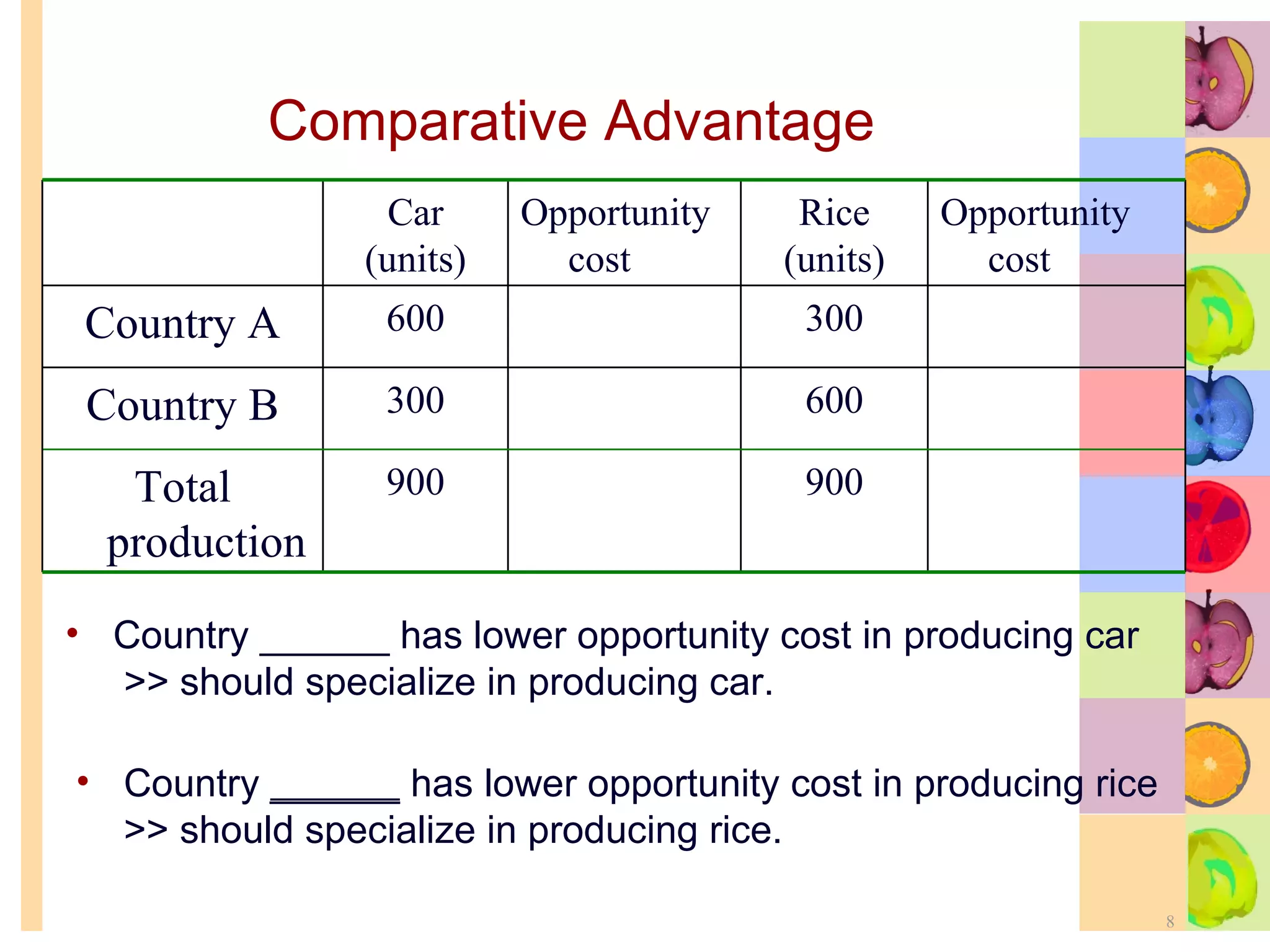
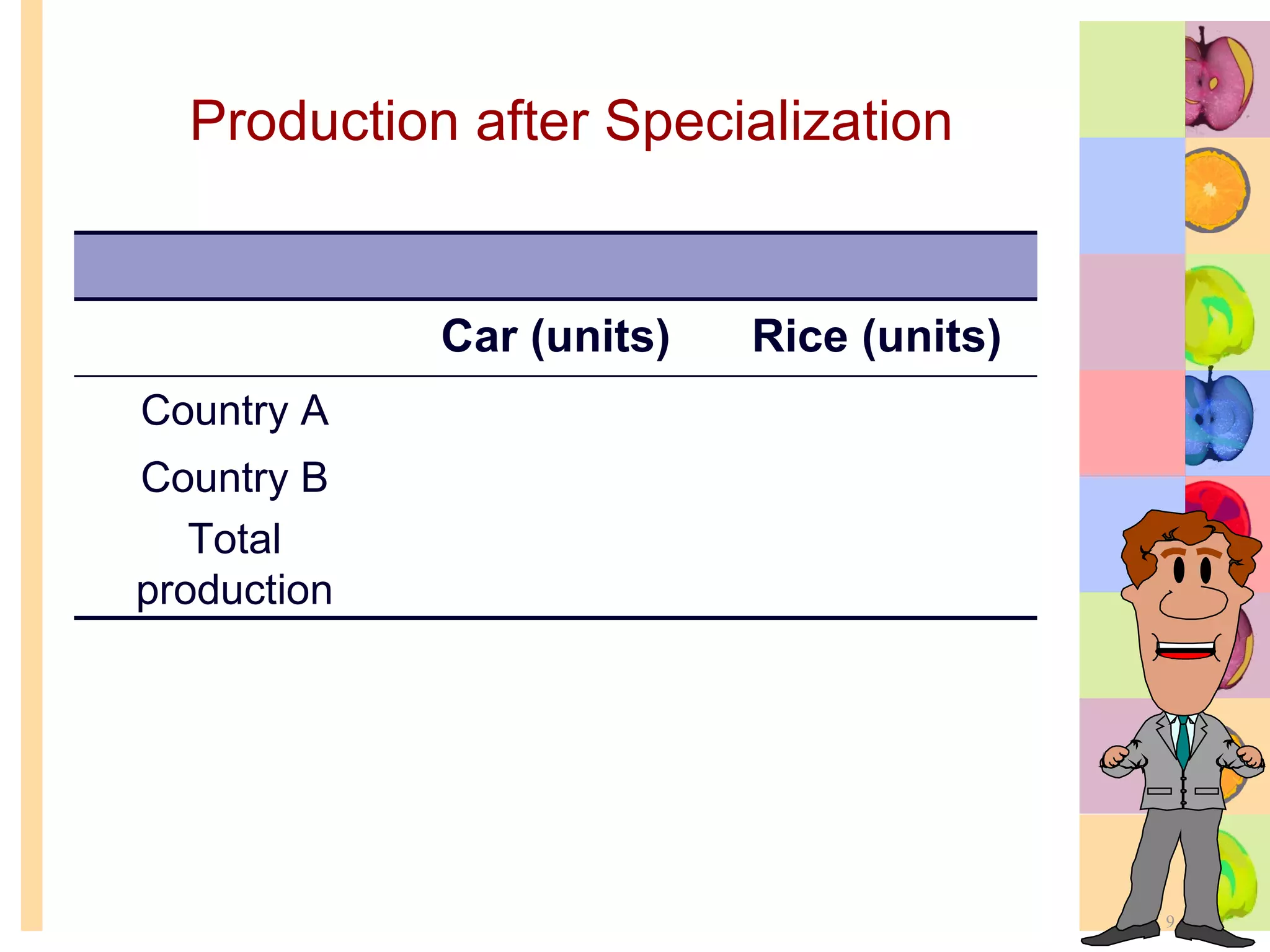
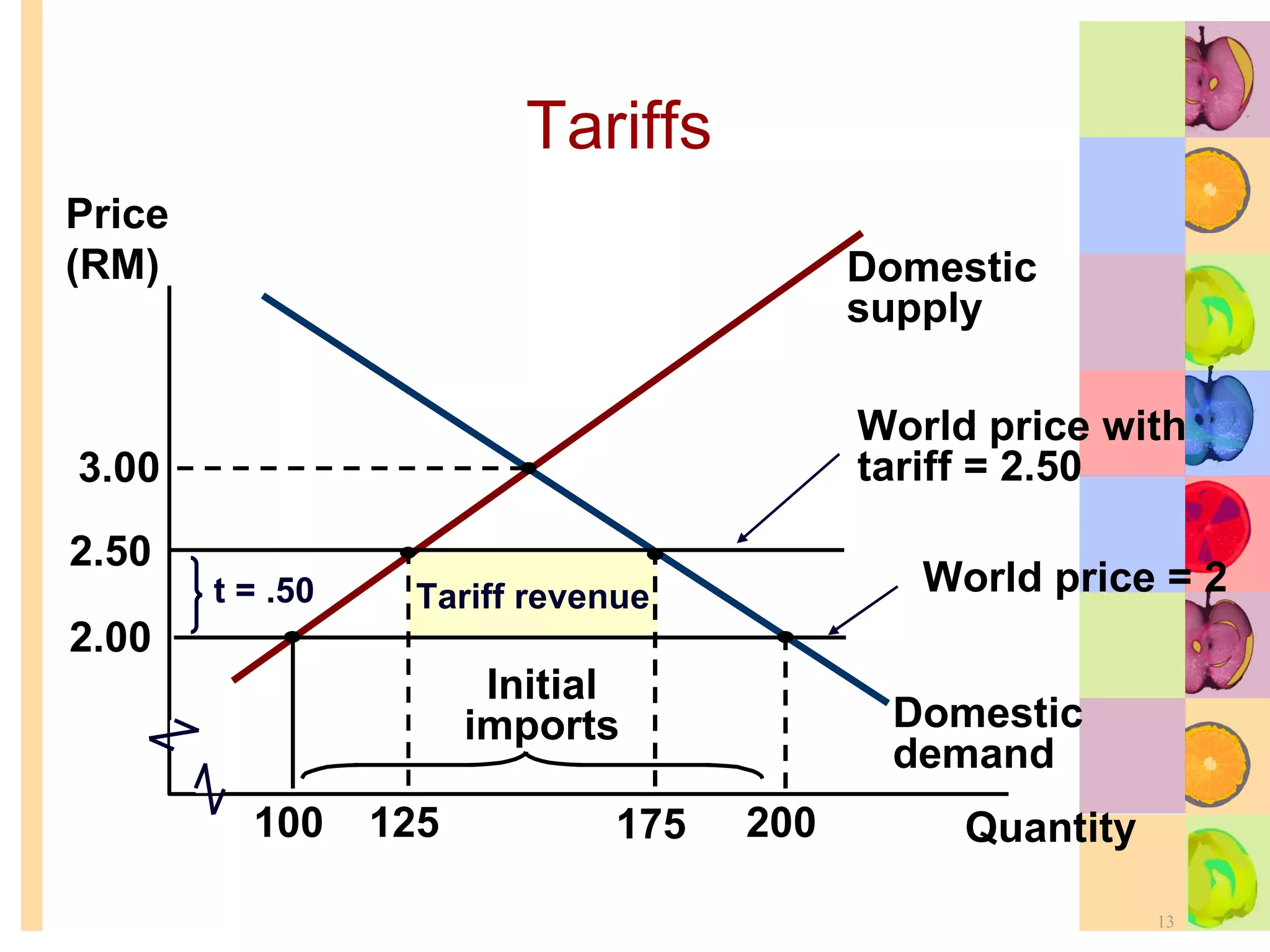
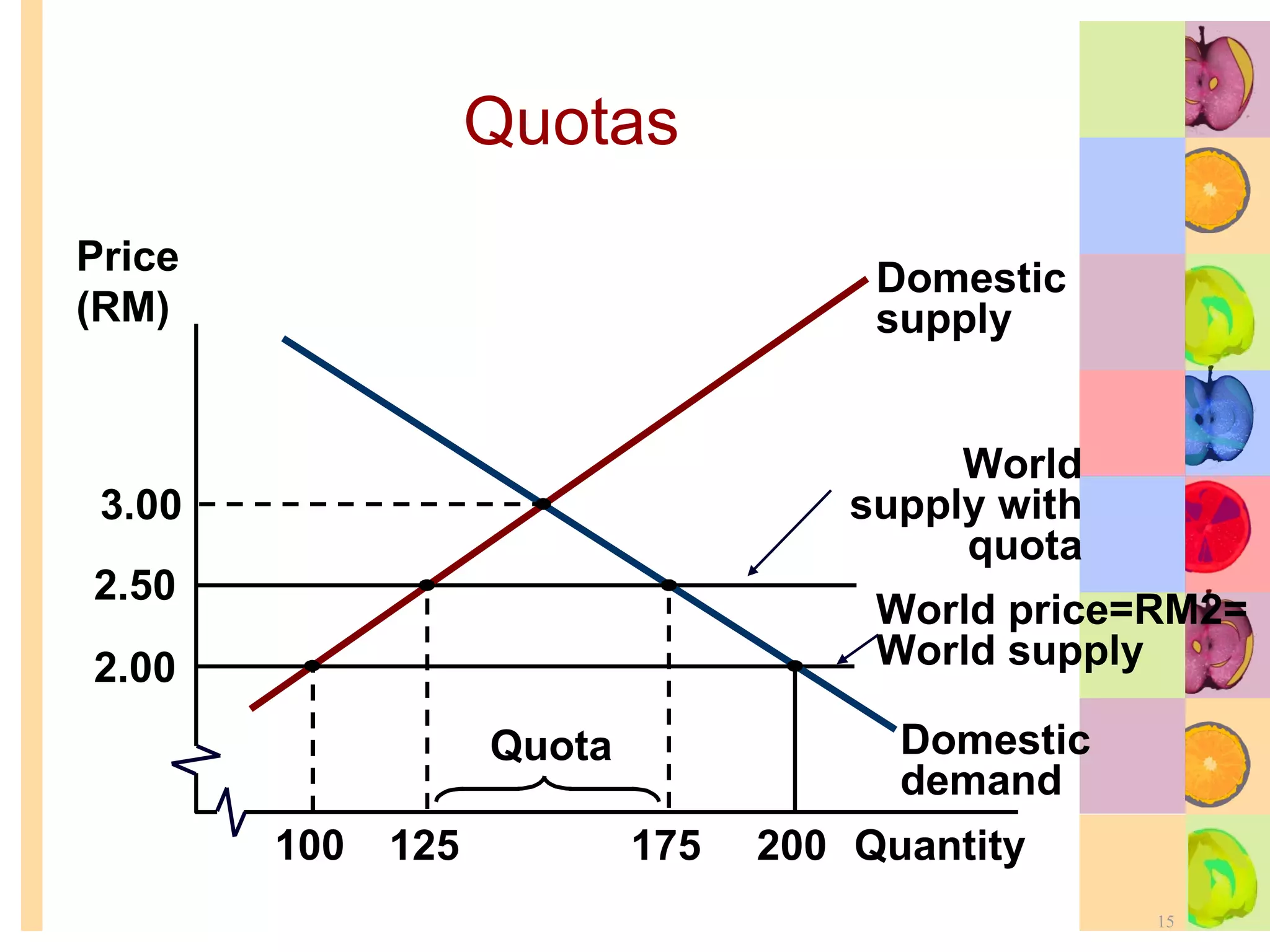
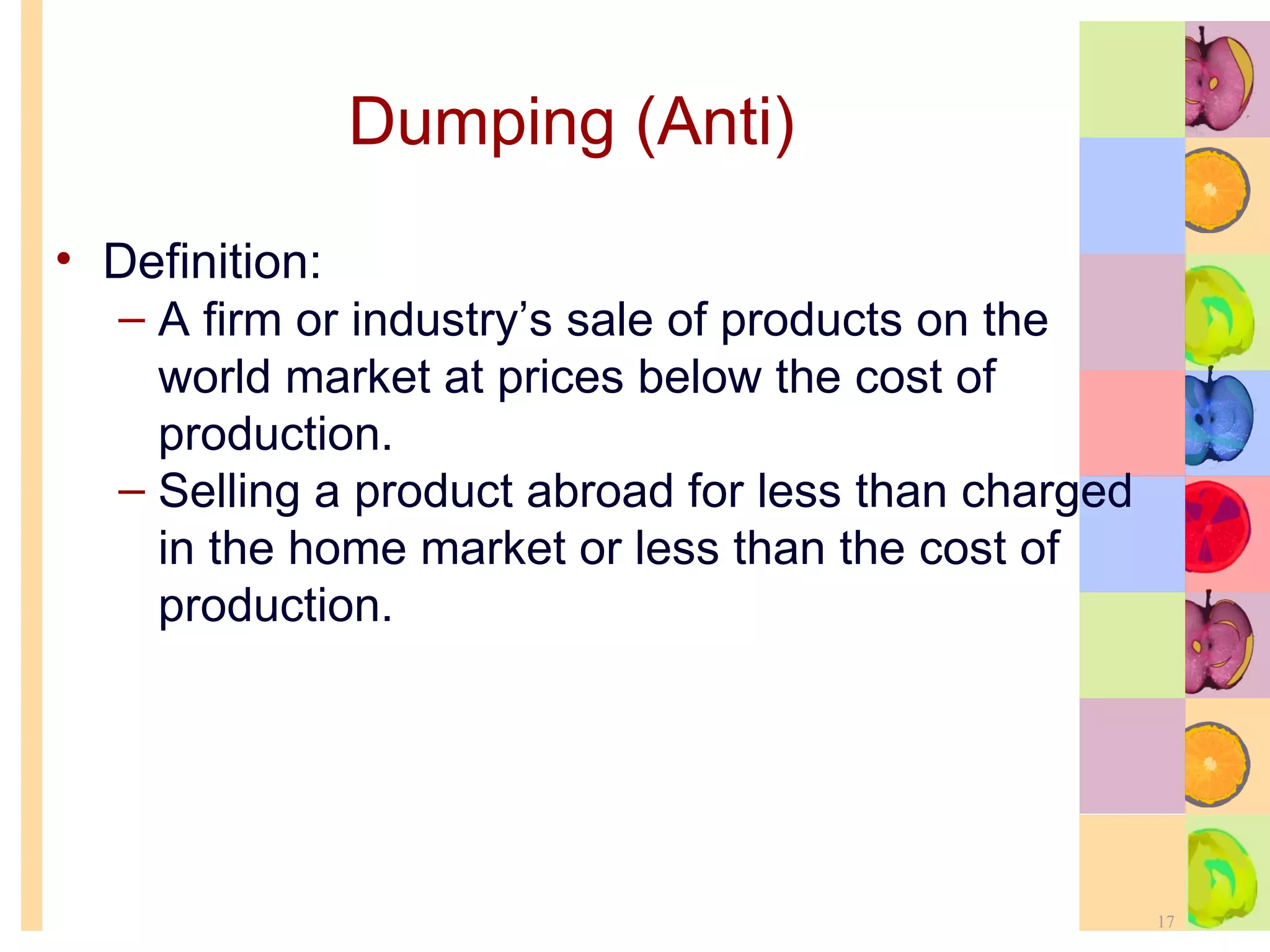
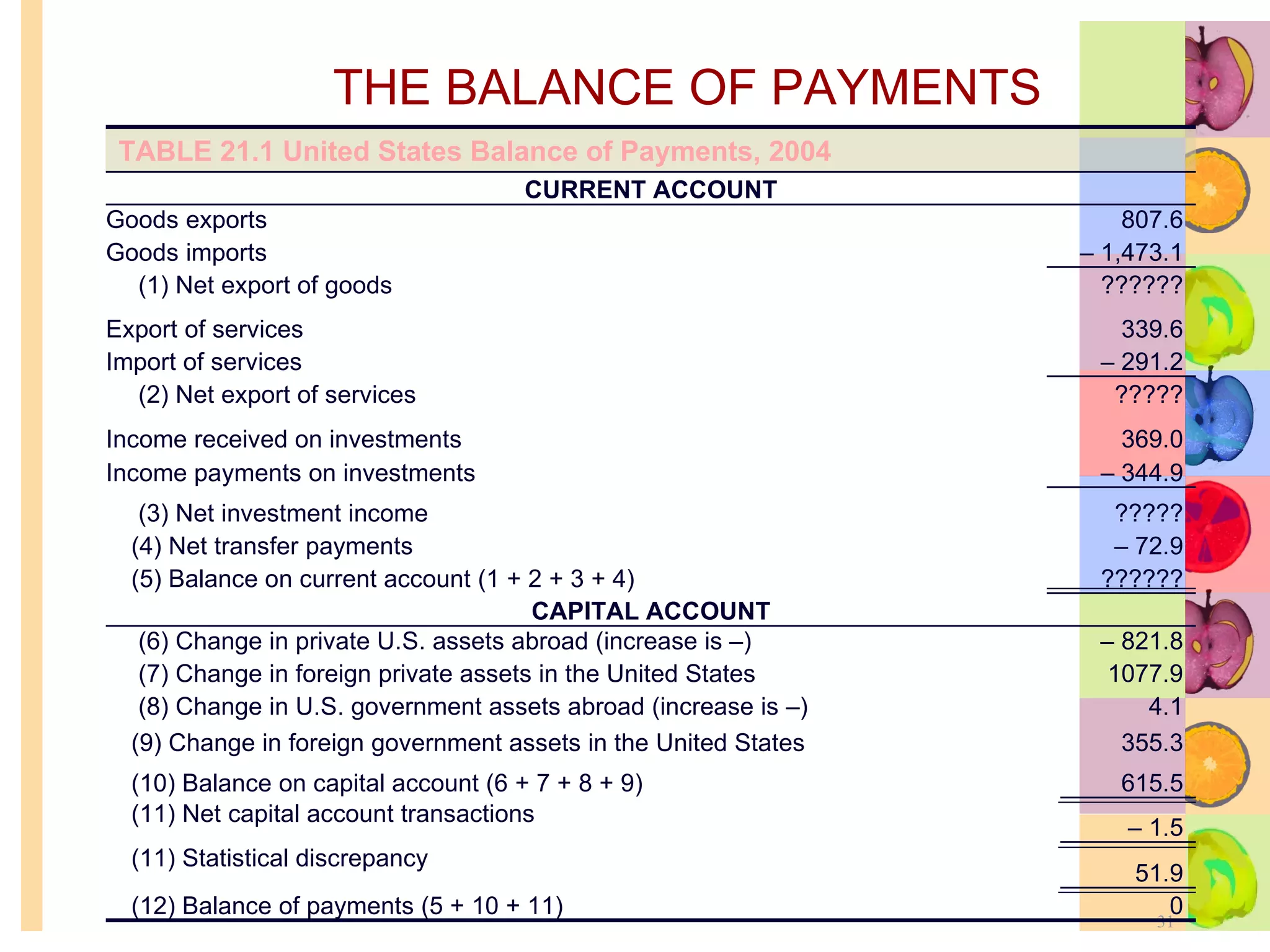
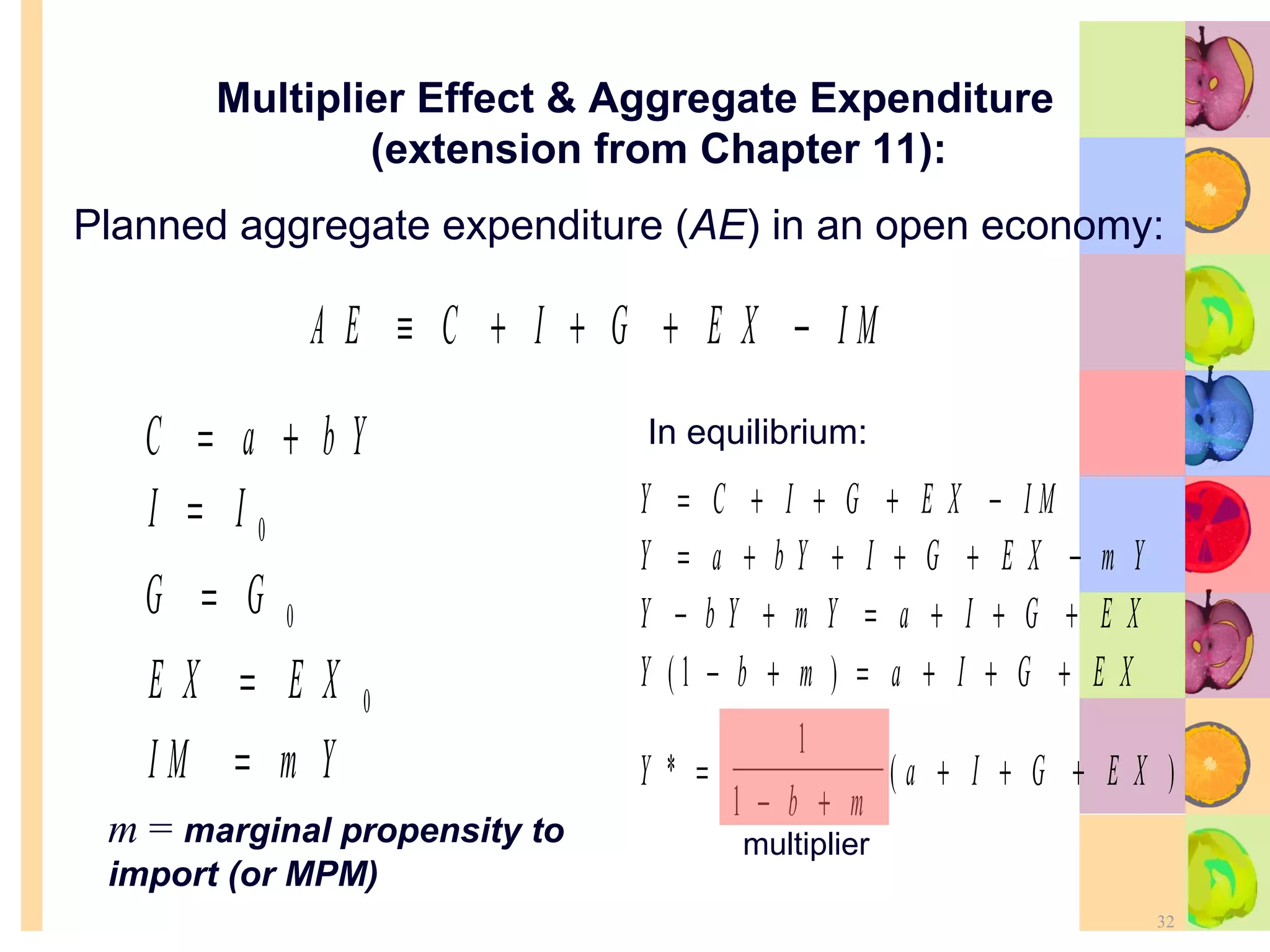
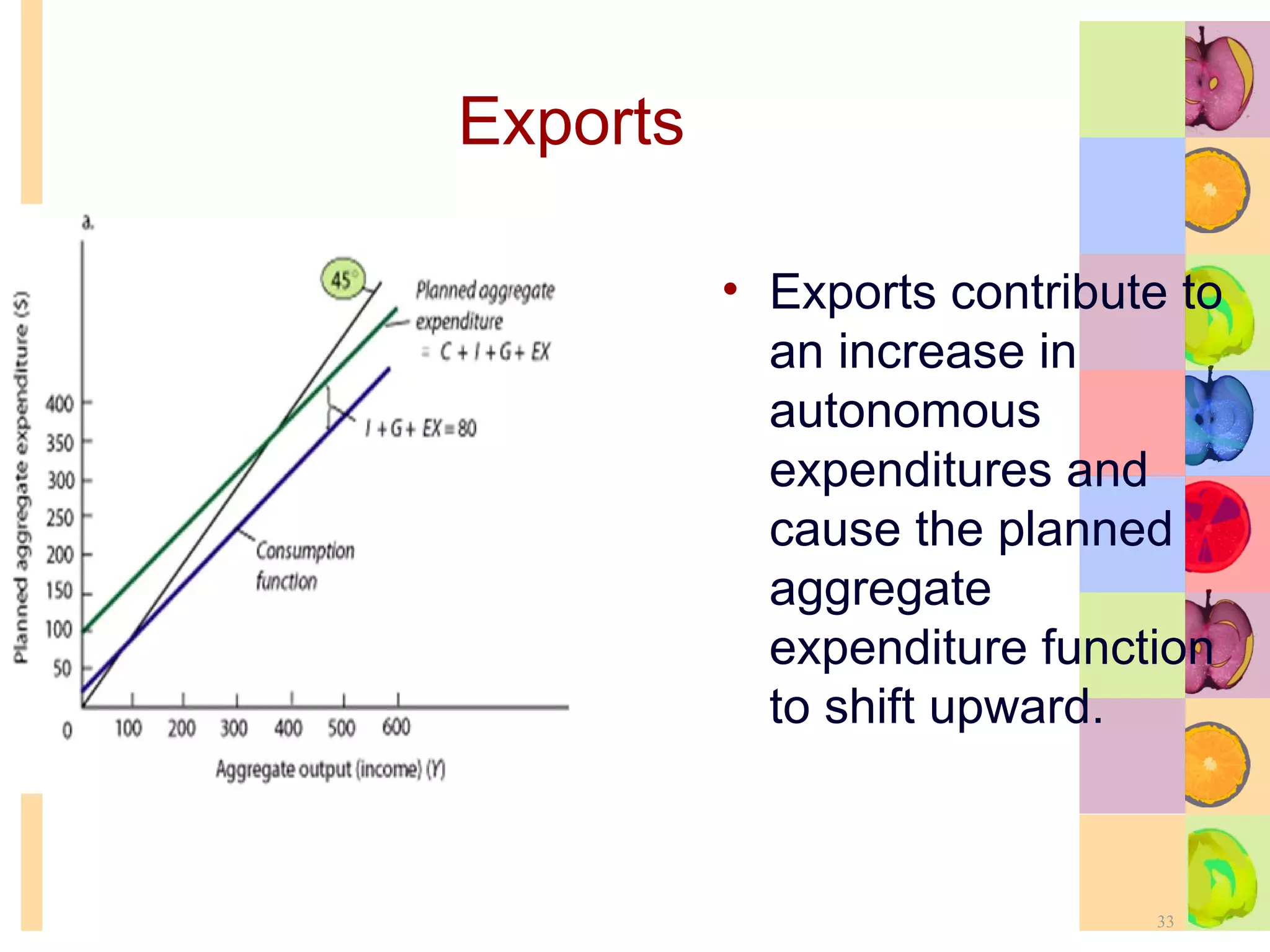
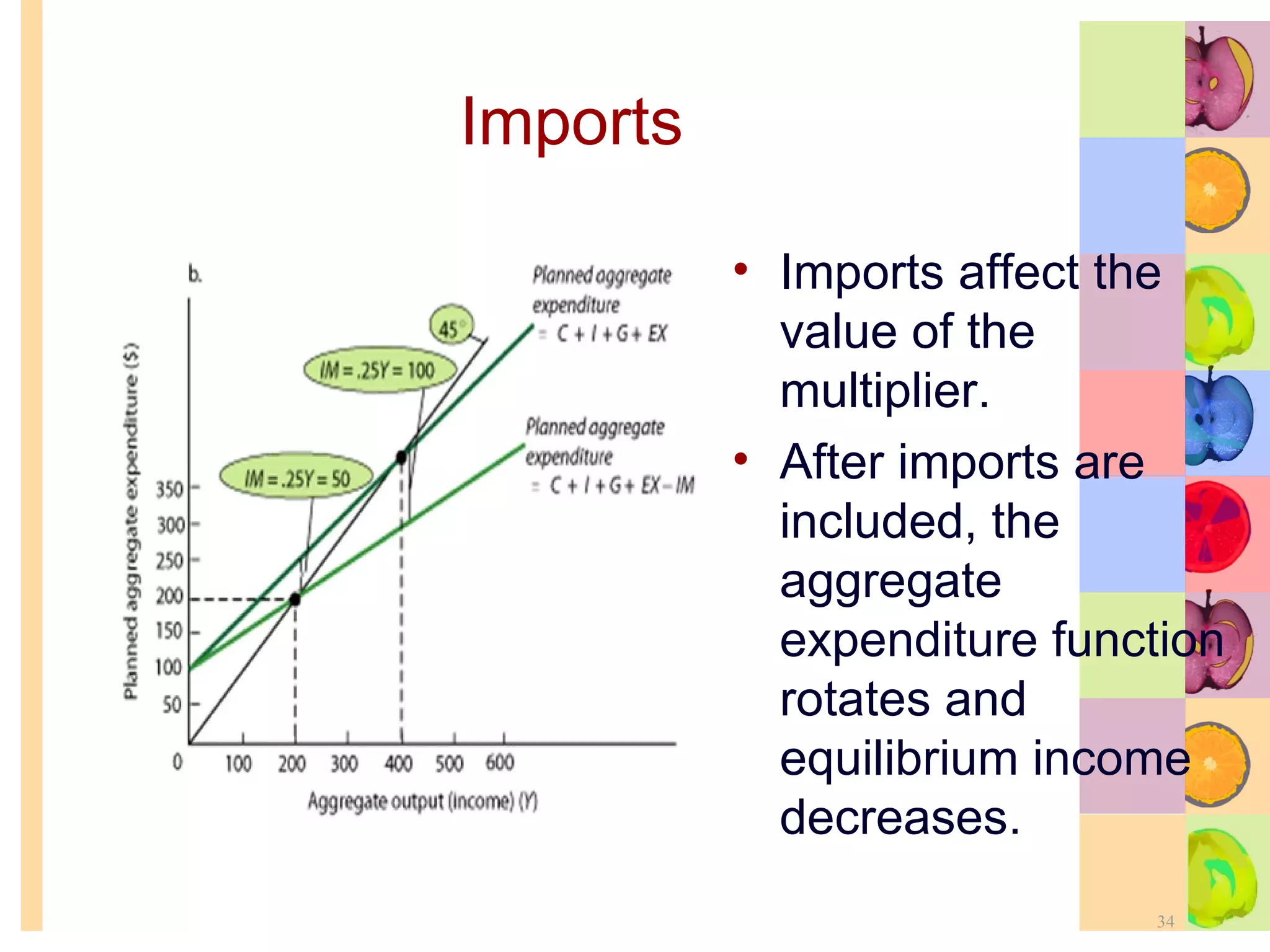
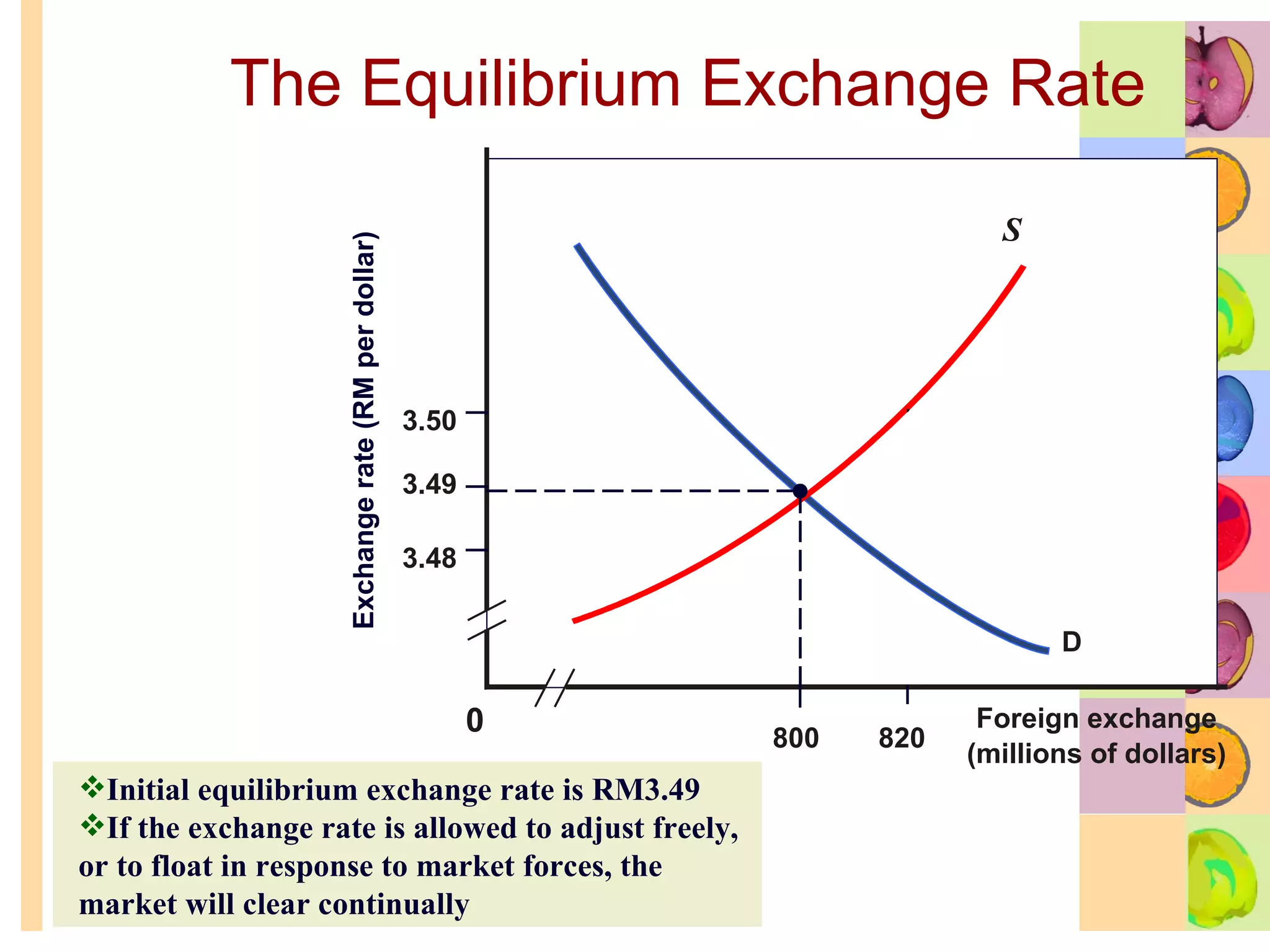
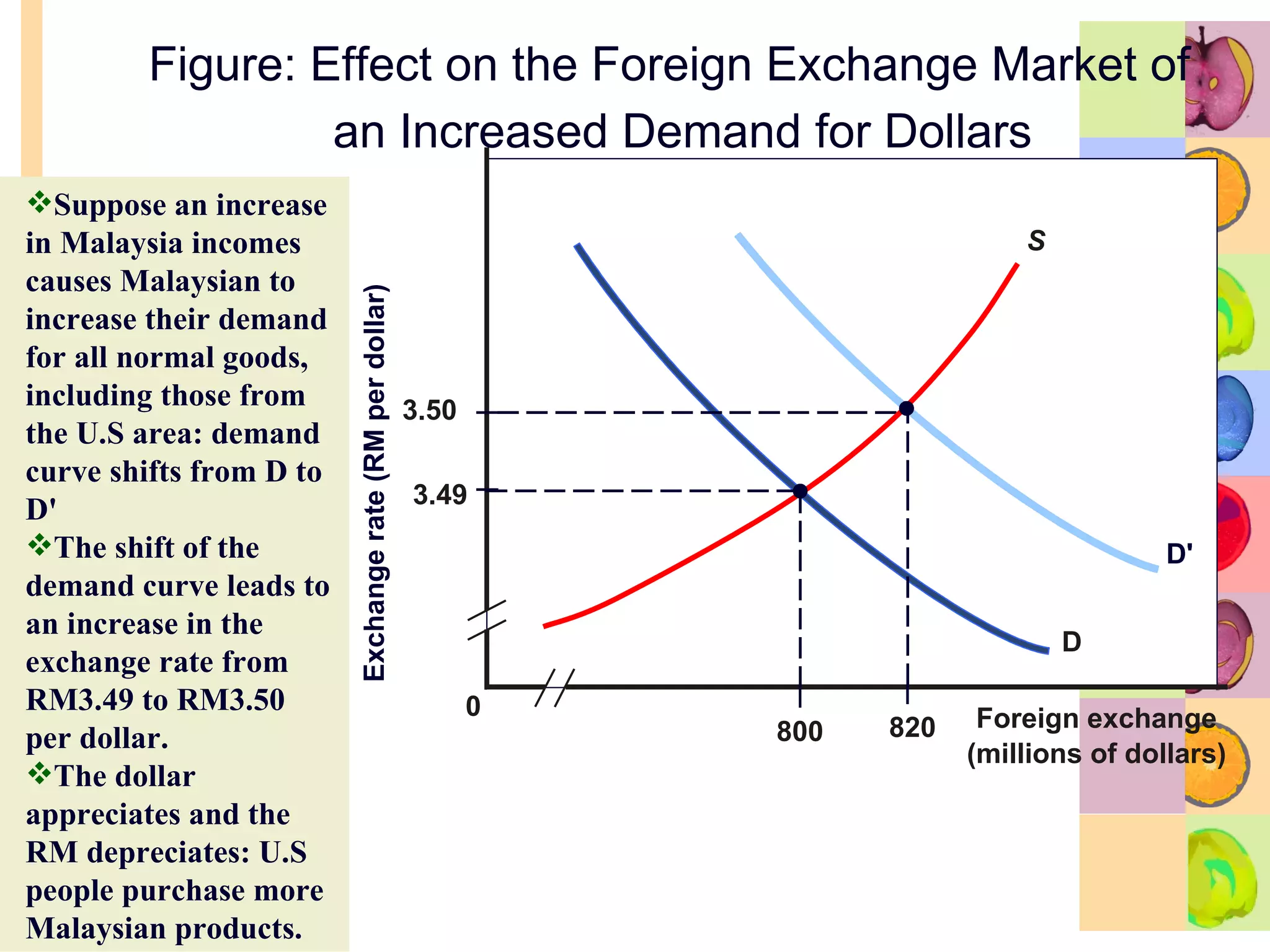
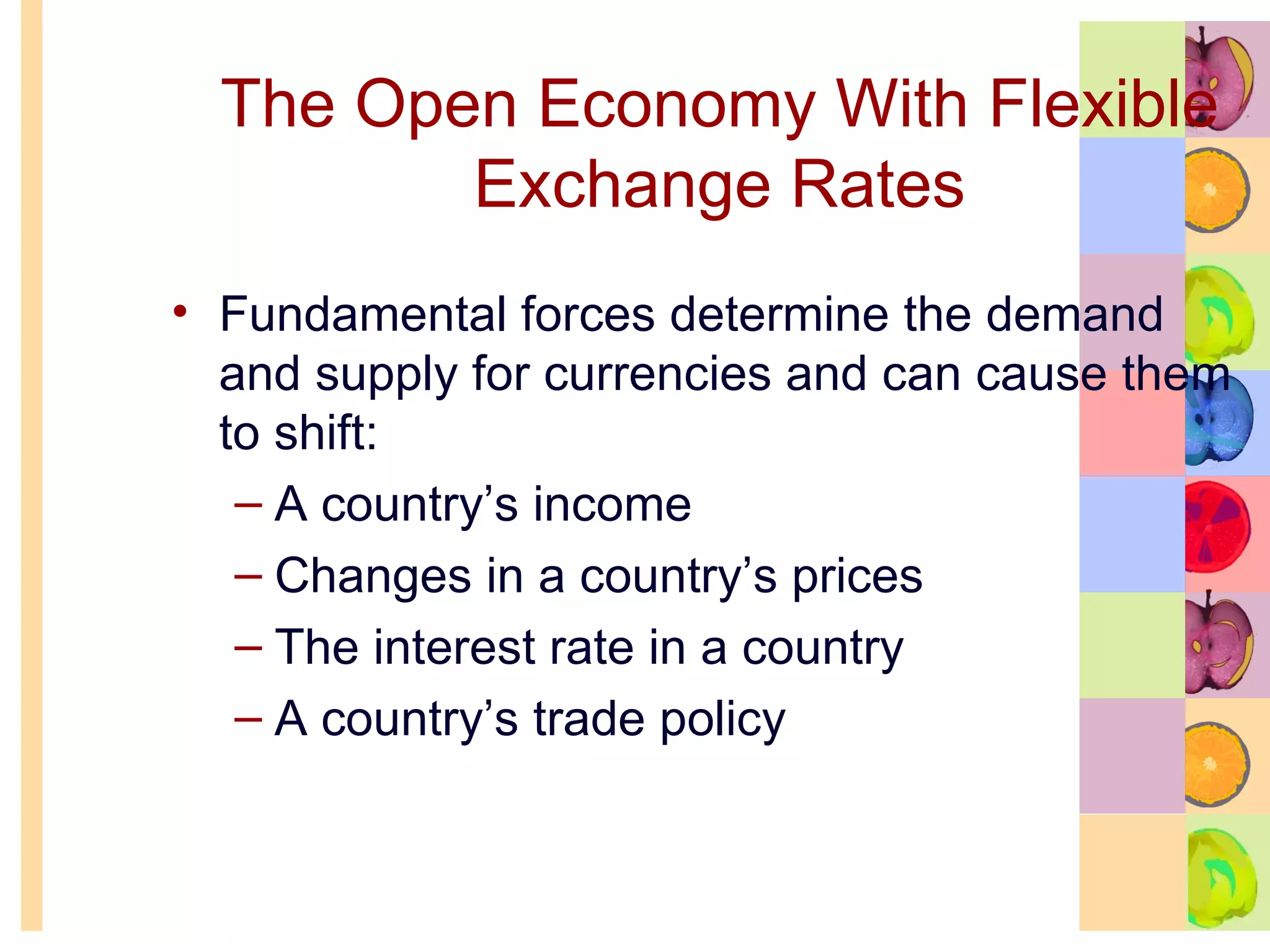
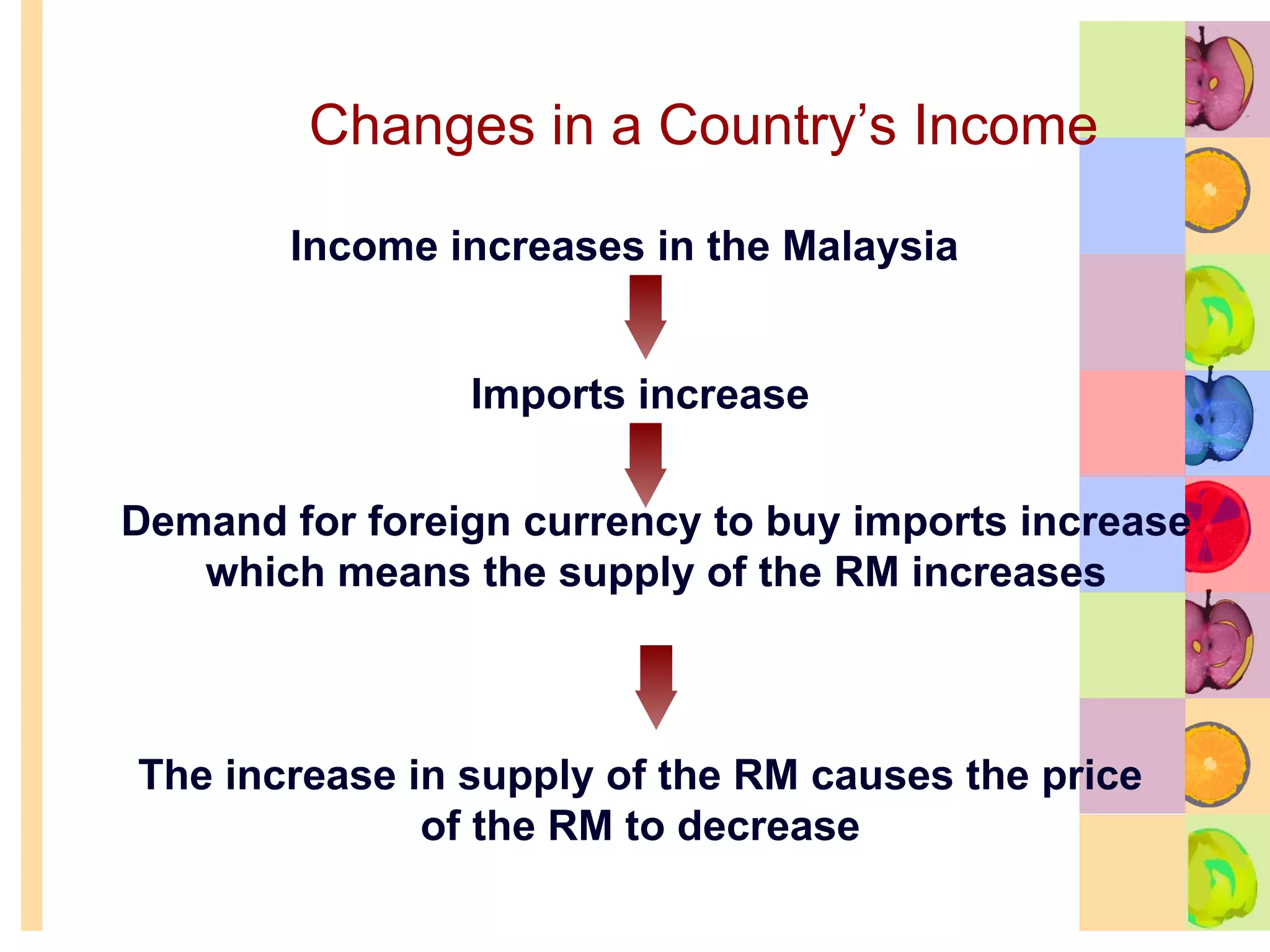
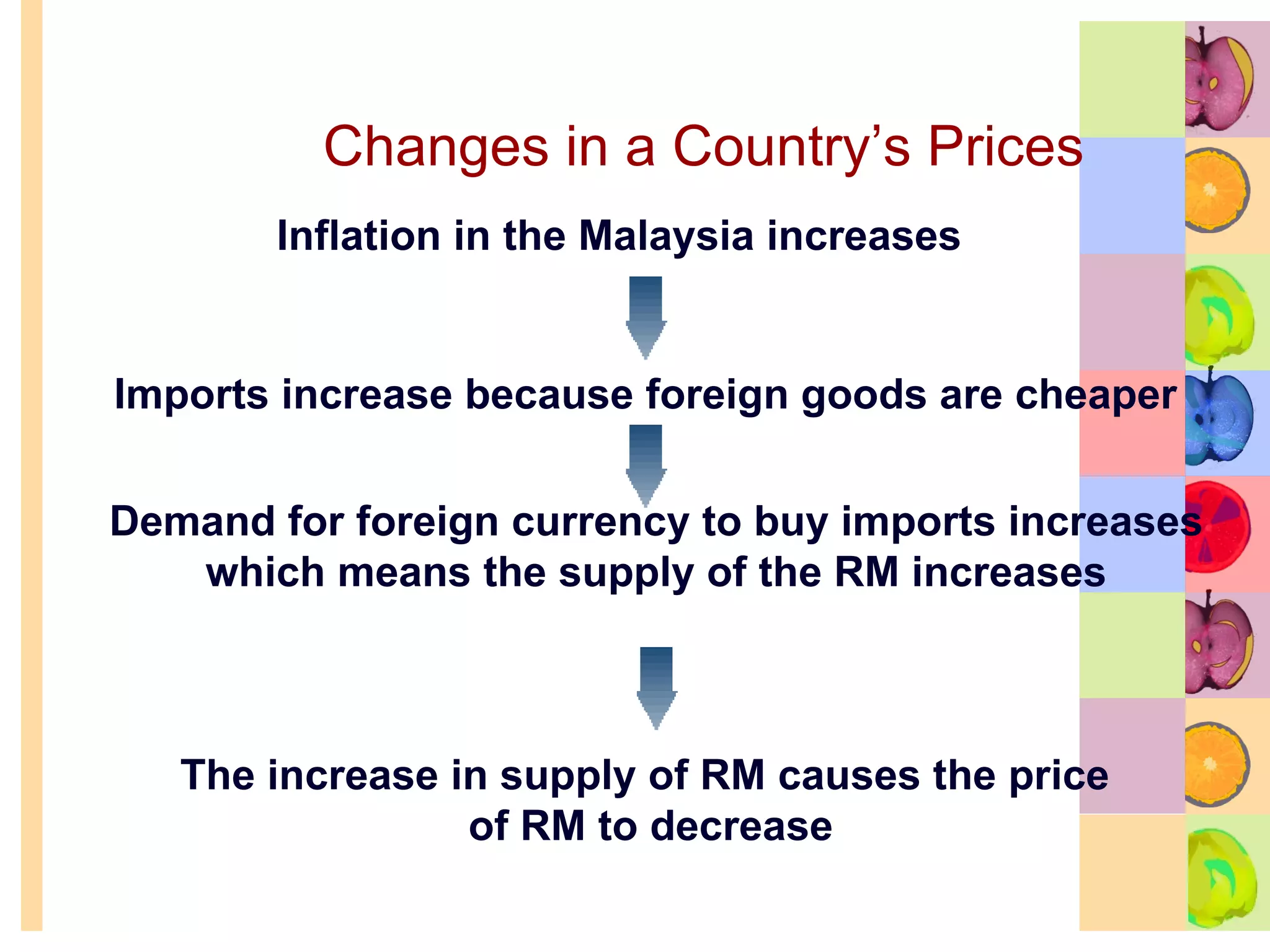
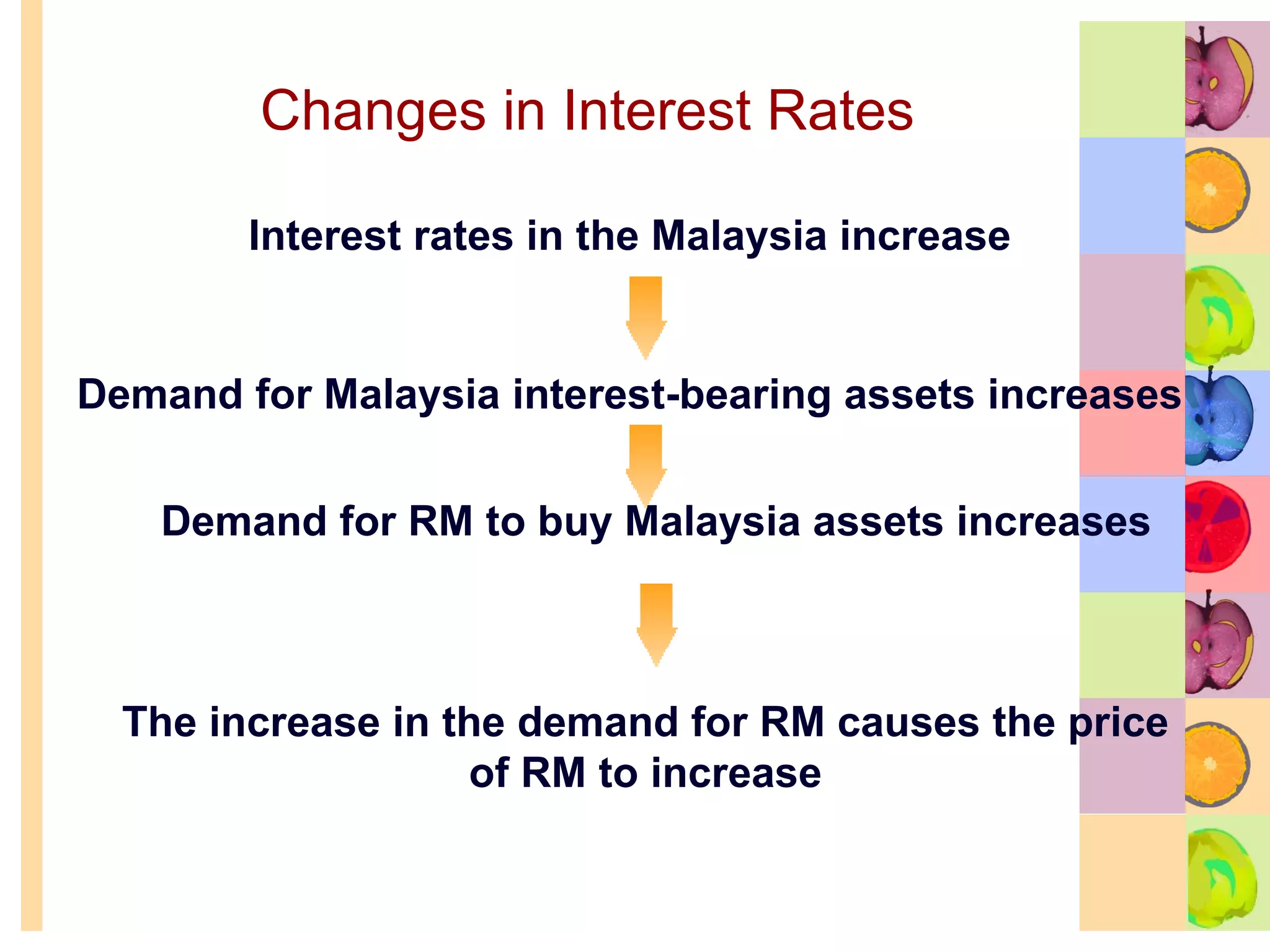
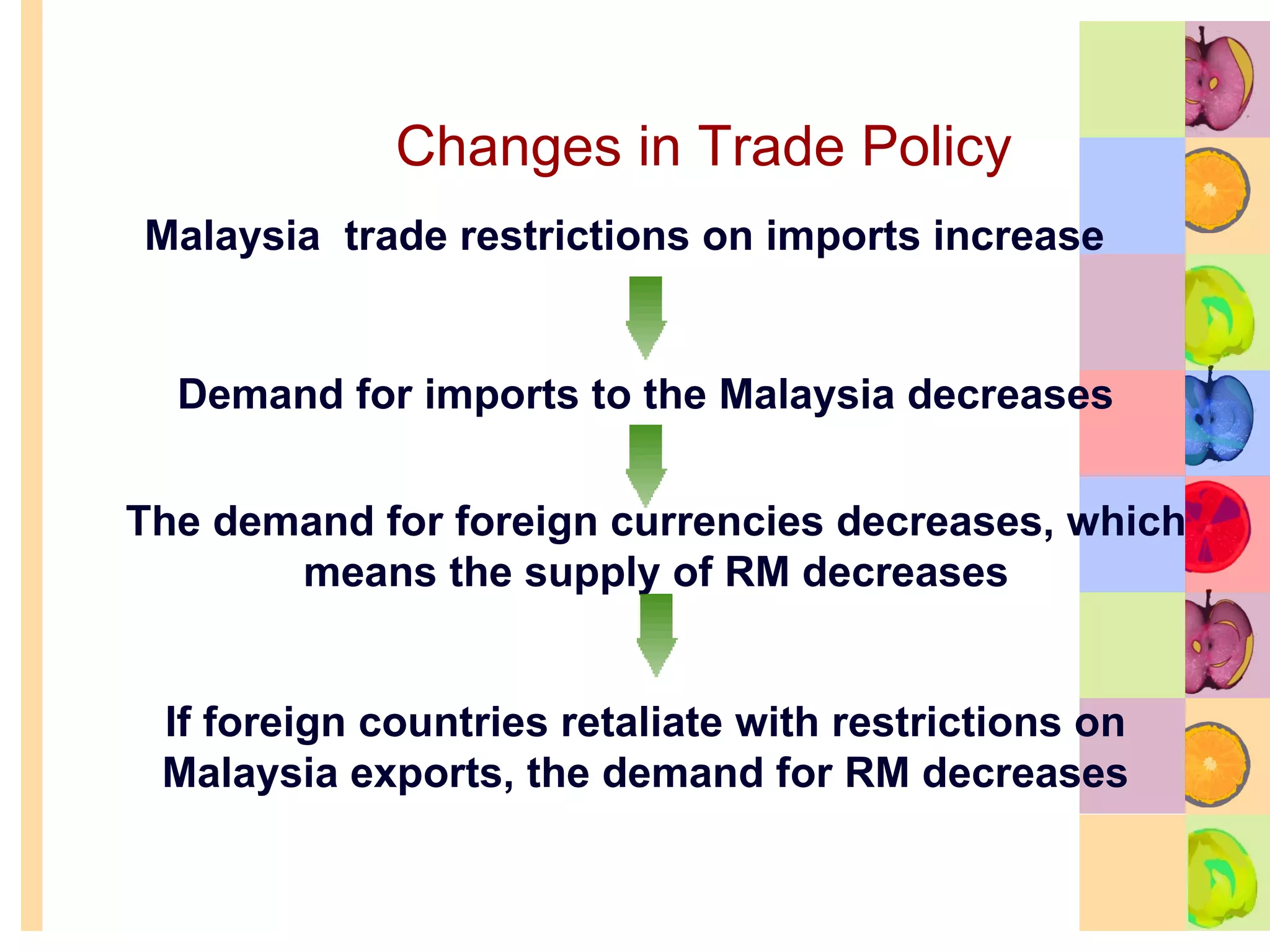
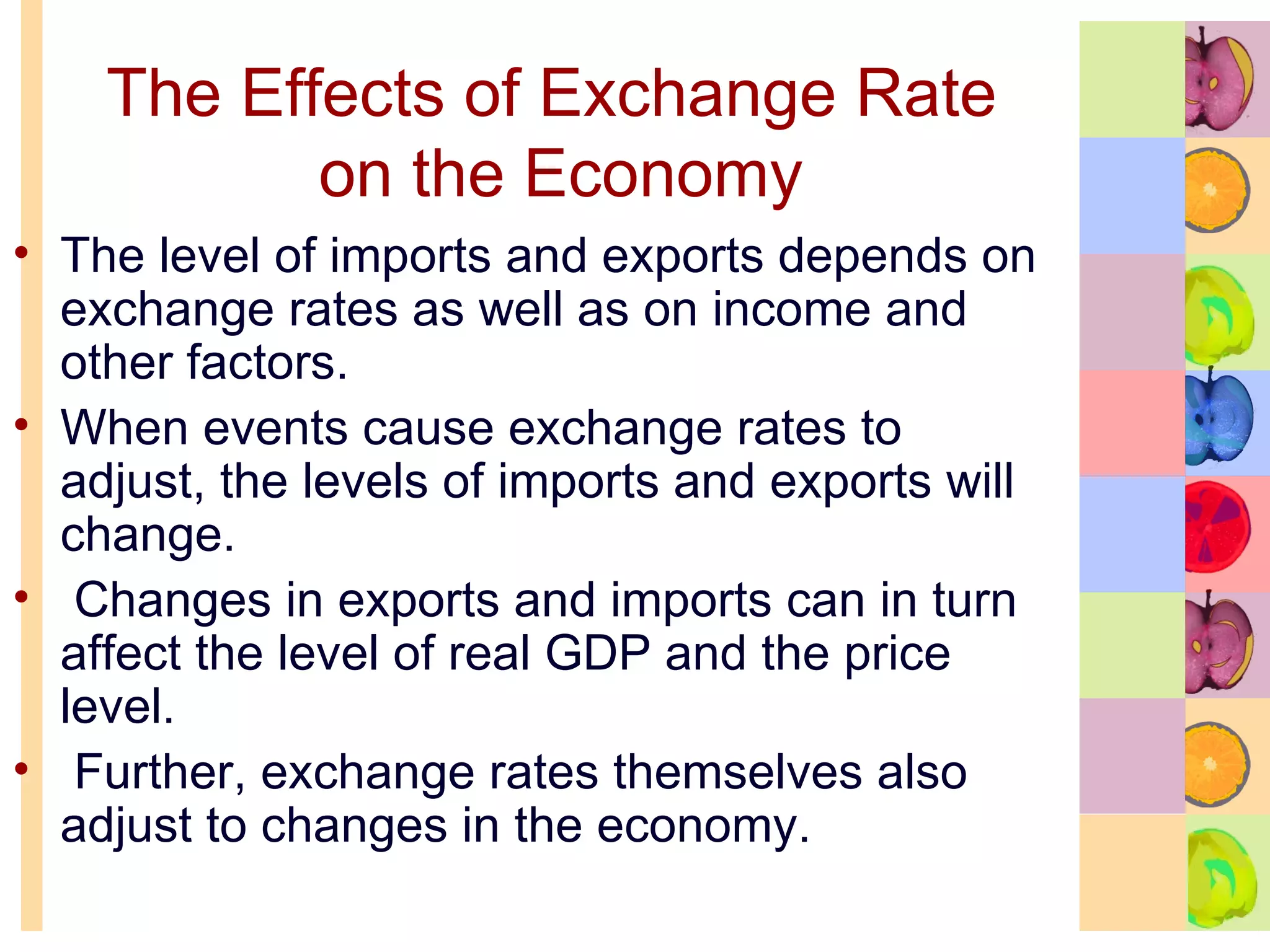
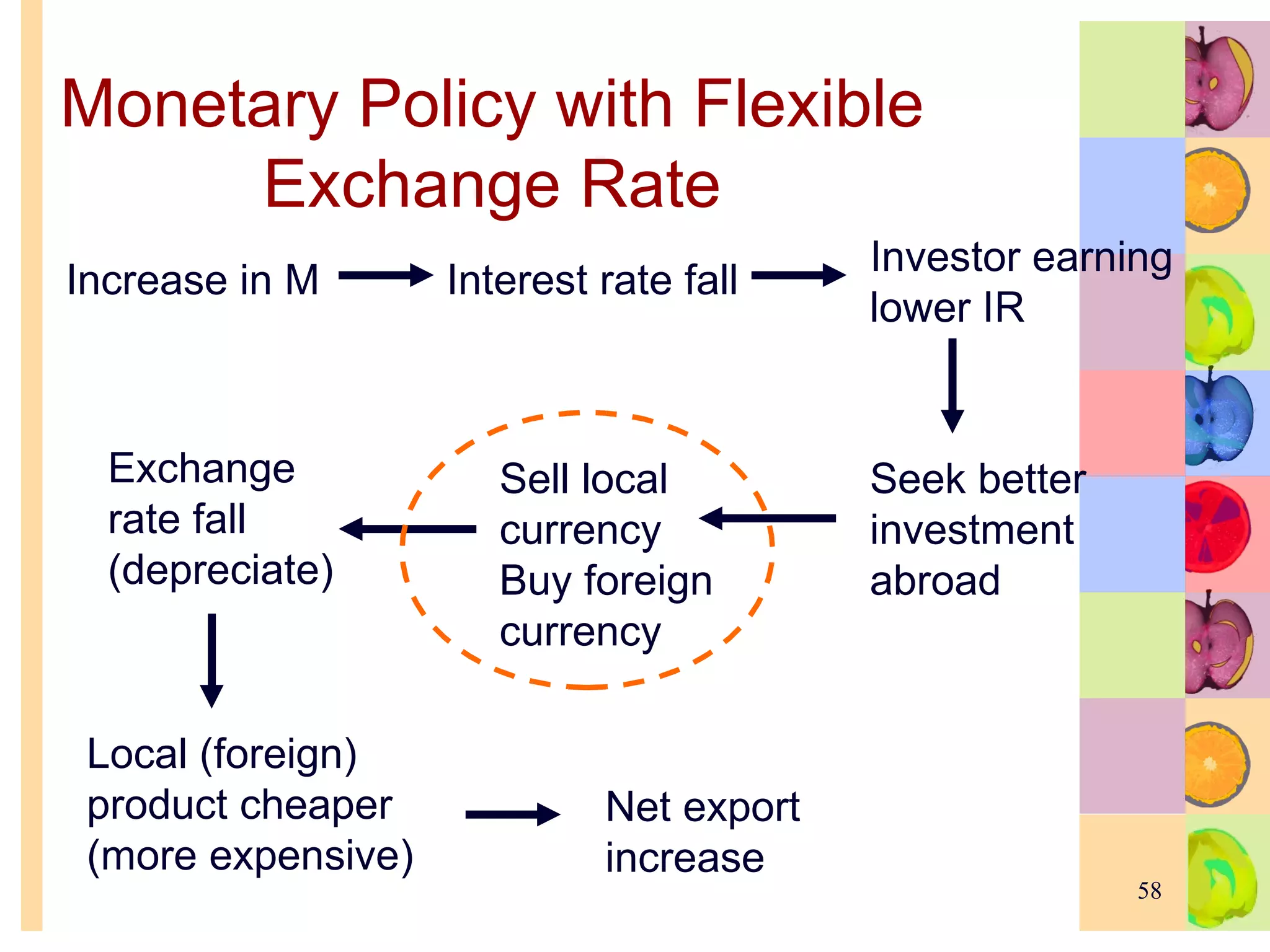
This document summarizes key concepts in international trade and exchange rates discussed in Chapter 13. It covers absolute and comparative advantage, types of trade barriers, components of the balance of payments, and exchange rate systems. Country A has an absolute advantage in cars and Country B has an advantage in rice, but Country B has a lower opportunity cost of cars, so it should specialize in car production. The current account records trade in goods, services, income, and transfers. Exchange rates can be fixed, flexible, or managed to balance trade and stability.