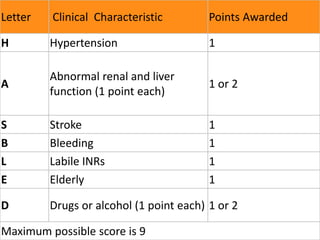
The CHADS2 scoring system is a clinical prediction rule used to assess the risk of stroke in patients with non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation. It assigns points based on various risk factors, with a higher total score indicating greater risk of stroke. It is used to determine if anticoagulation therapy is required. The HAS-BLED scoring system evaluates bleeding risk for patients on oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation by assigning points for different risk factors, with a score of 3 or more indicating increased risk of major bleeding within one year.













![The risk of major bleeding within one year in atrial fibrillation patients enrolled in the Euro
Heart Survey.
HAS-BLED, acronym: Hypertension [uncontrolled, >160 mmHg systolic), Abnormal renal/liver
function, Stroke, Bleeding history or predisposition [anemia], Labile INR [i.e.
therapeutic time in range <60%], Elderly (>65) and Drugs/alcohol concomitantly [antiplatelet
agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] [Maximum score 9].
HAS-BLED score n Bleeds, n Bleeds/100 patients*
0 798 9 1.13
1 1286 13 1.02
2 744 14 1.88
3 187 7 3.74
4 46 4 8.70
5 8 1 12.50
Any score 3071 48 1.56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chads2scoringsystem-130805102250-phpapp02/85/CHA2DS2-VASc-Score-CHADS2-score-and-Hasbled-score-15-320.jpg)
