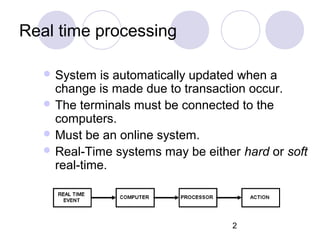
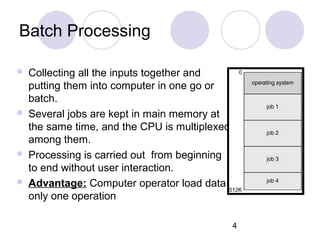
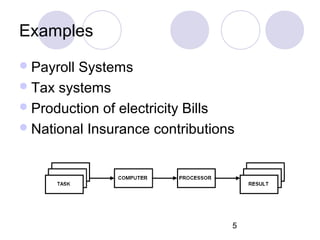
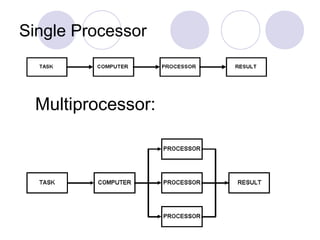
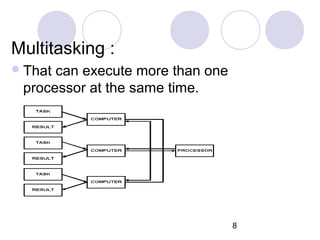
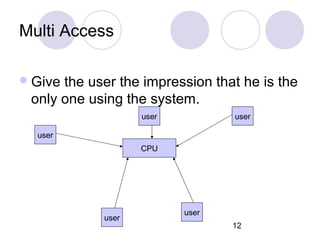
This document discusses various types of computer operations including real-time processing, batch processing, multiprogramming, multitasking, transaction processing, interactive processing, timesharing, and multi-access. Real-time processing automatically updates the system when changes occur. Batch processing collects all inputs together and processes them at once without user interaction. Multiprogramming and multitasking allow a computer to run multiple processes simultaneously. Transaction processing handles individual data items as they occur. Interactive and timesharing systems allow multiple users to access the system simultaneously through terminals.