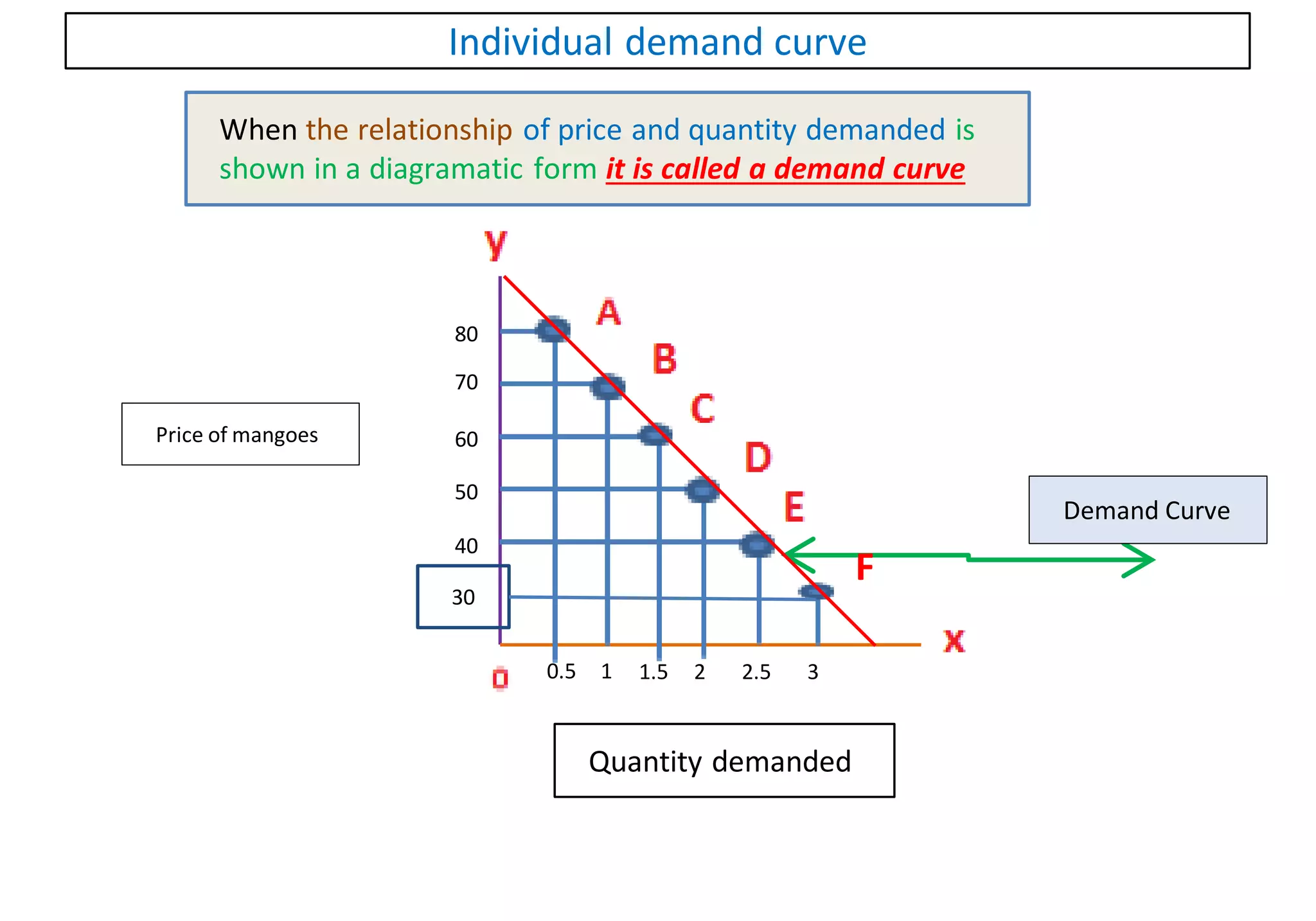
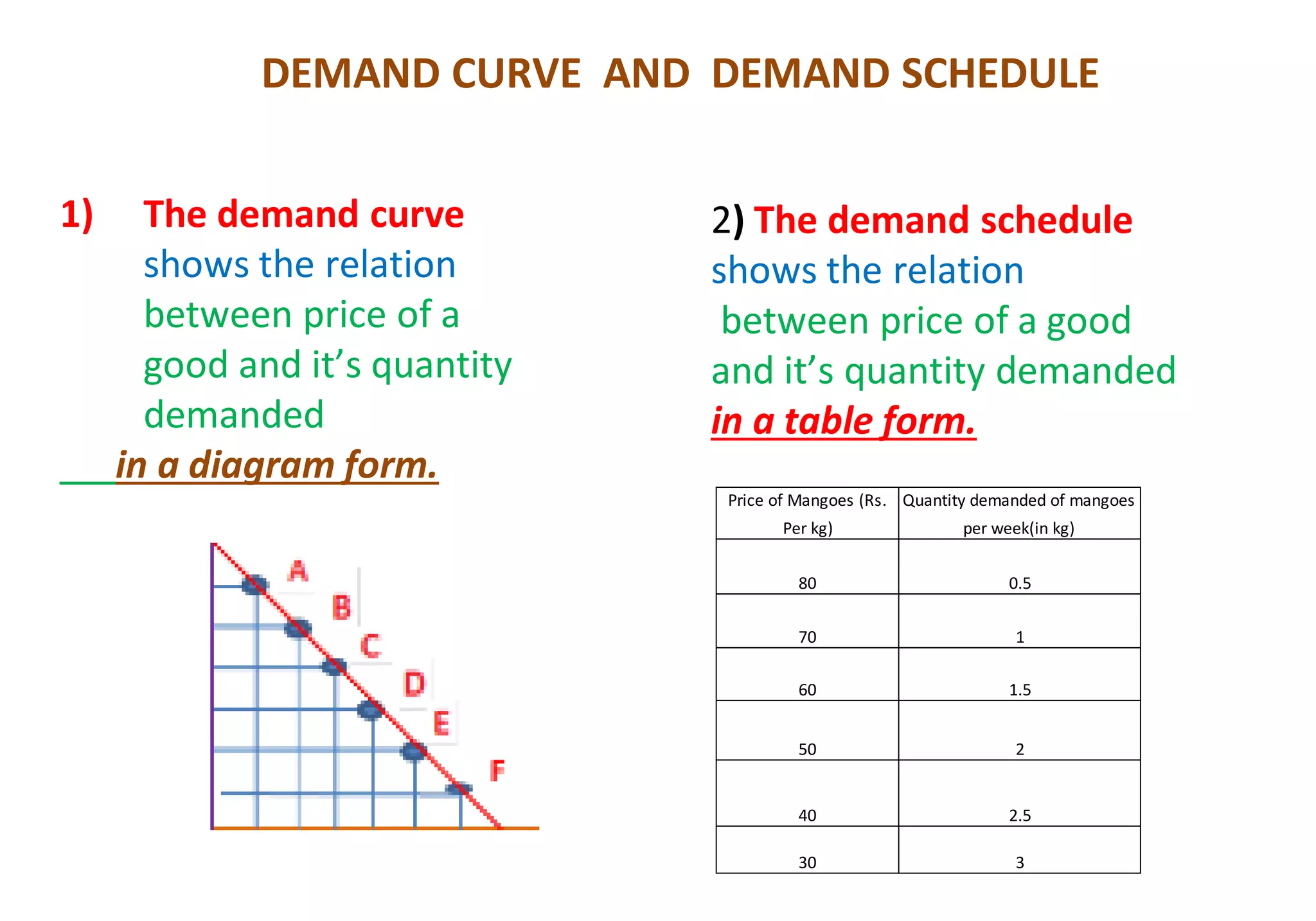
1. Demand is defined as the quantity of a good purchased at a given price at a given time. It has three components: quantity, price, and time.
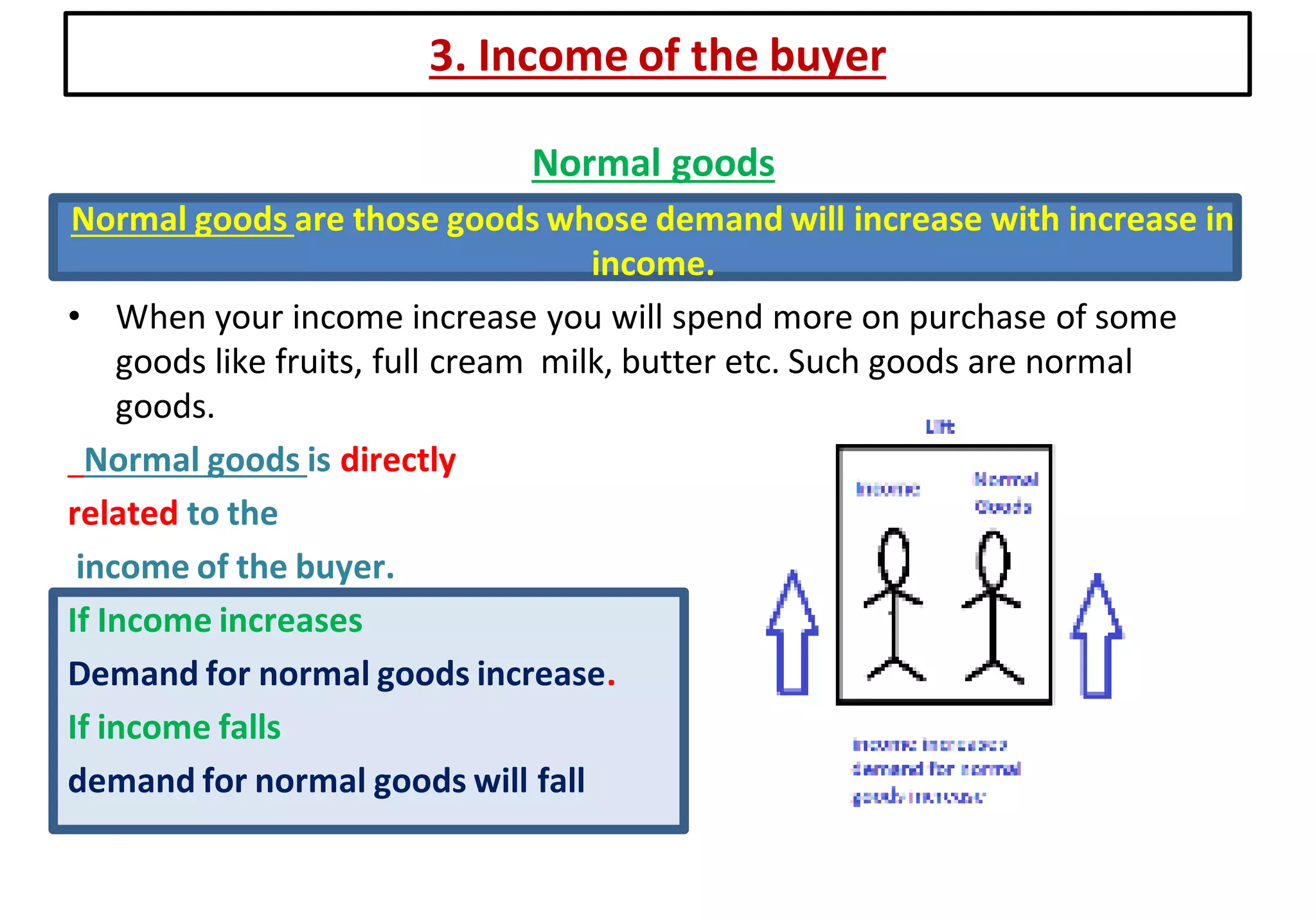
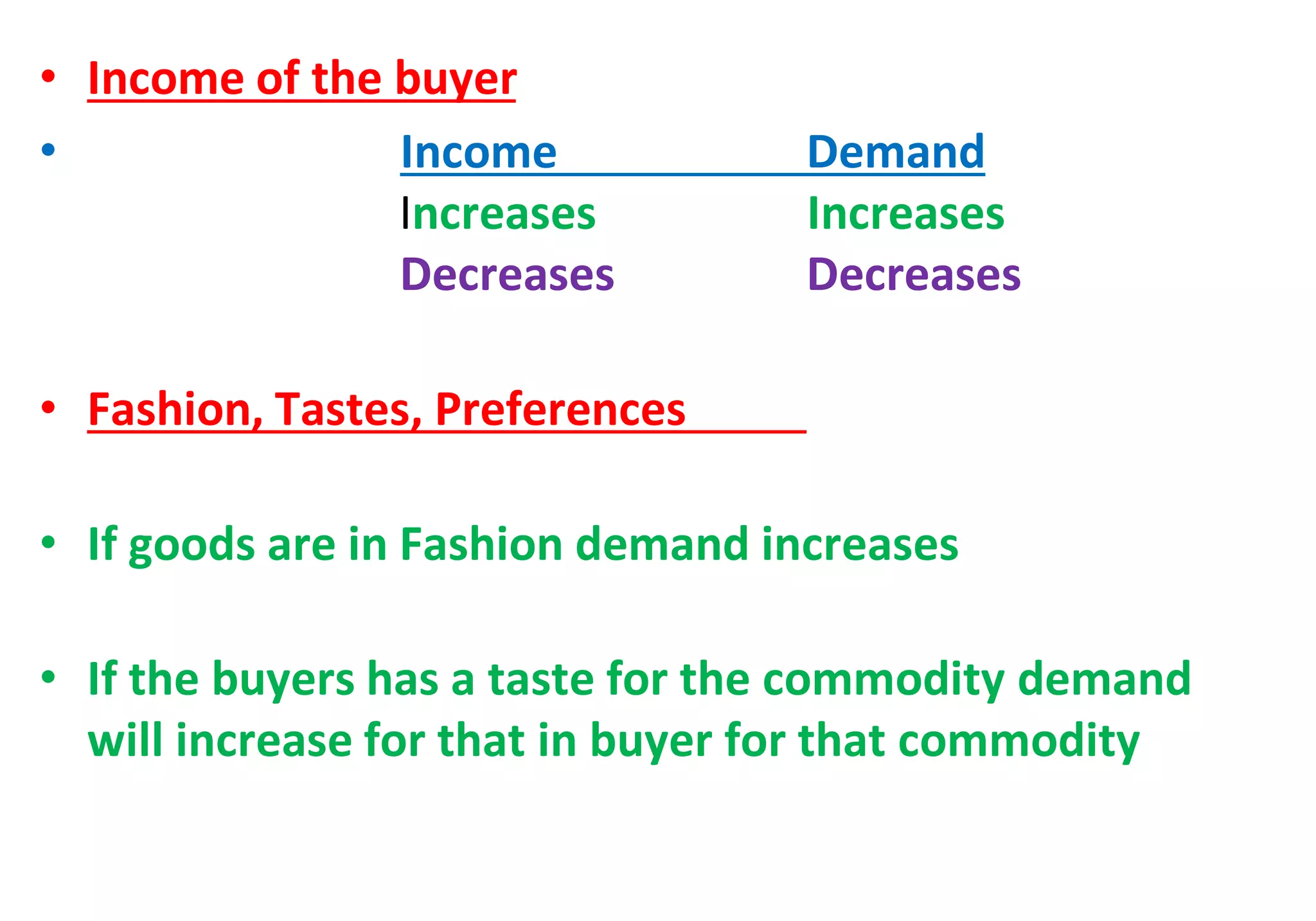
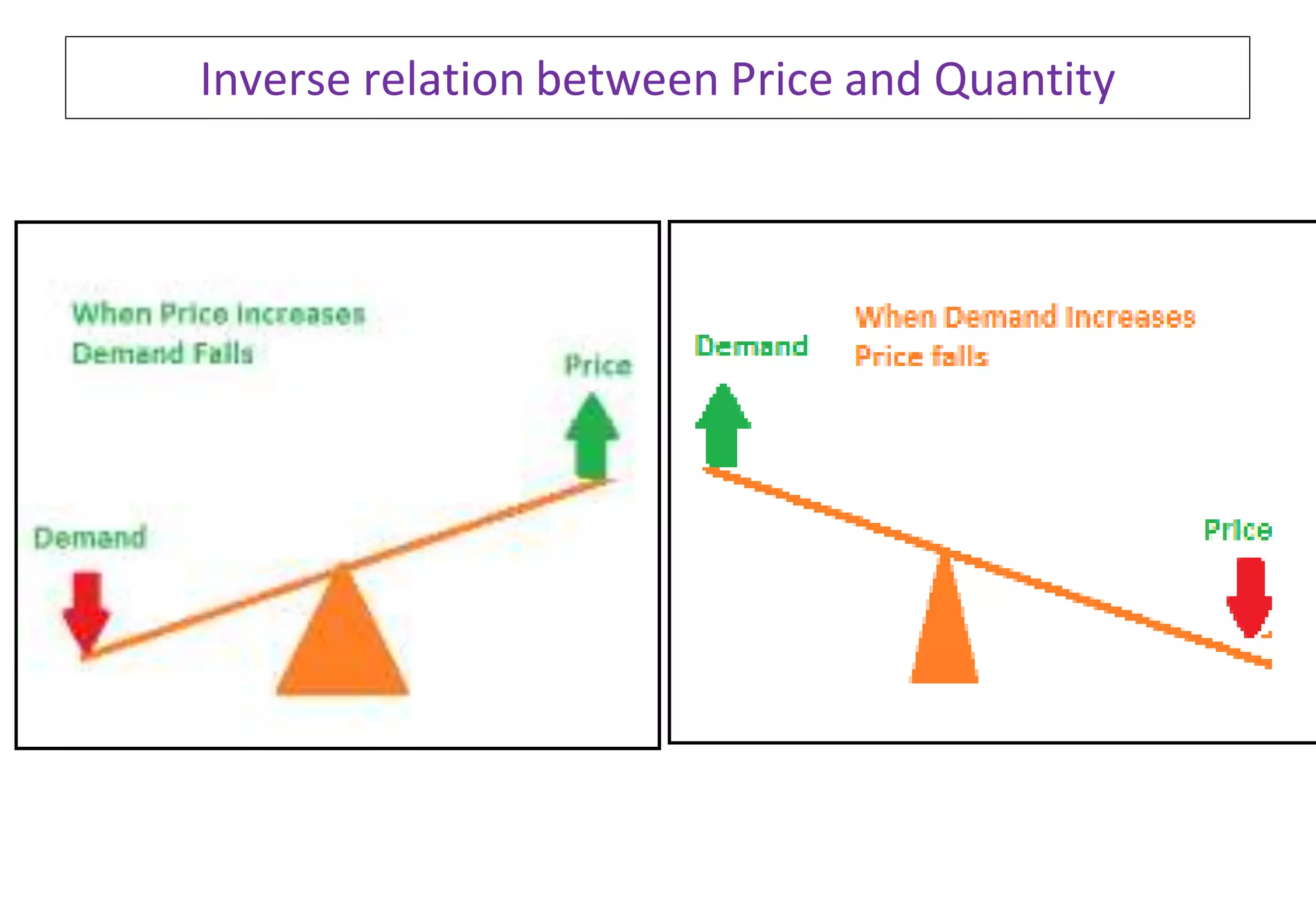
2. Factors that affect individual demand include: price of the good, price of related goods, income of the buyer, and tastes/preferences. Demand increases when price decreases and decreases when price increases.
3. Market demand is the total quantity demanded by all buyers in the market. It is affected by the number of buyers, distribution of income/wealth, and climatic conditions.






















![Factors affecting market demand (BDC)
• 1) Number of buyers [Buyers demand ]
• If the number of buyers of a good increases, market demand also
increases.
• 2) Distribution of income and wealth
• (i) If the market has more of rich buyers, then market demand will be
more for goods consumed by the rich people.
• (ii) If the market has more of poor buyers, then market demand will be
more for goods consumed by the poor buyers.
• 3) Climatic conditions
• (i) Market demand changes according to climatic changes.
• (ii) Example – market demand for umbrellas and raincoats will be
more during monsoon.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch9demand-150811065457-lva1-app6891/75/Ch-9-demand-28-2048.jpg)


