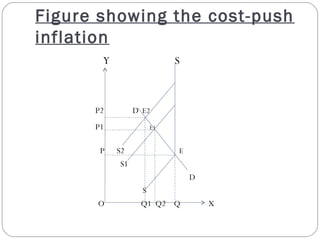
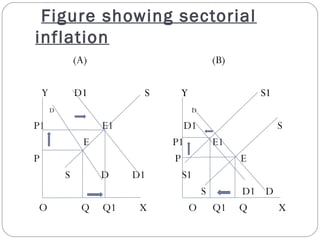
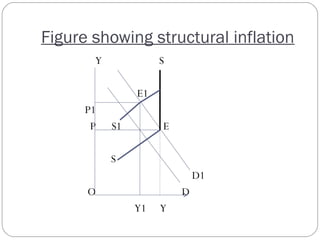
This document provides an overview of different theories of inflation including cost-push inflation, sectorial inflation, and structural inflation. Cost-push inflation occurs when increases in production costs lead to a fall in aggregate supply. Sectorial inflation refers to price rises occurring across different commercial sectors due to increases in raw material prices. Structural inflation arises due to an unstable and slower growth rate of exports, which is inadequate to support the required growth rate of the economy.