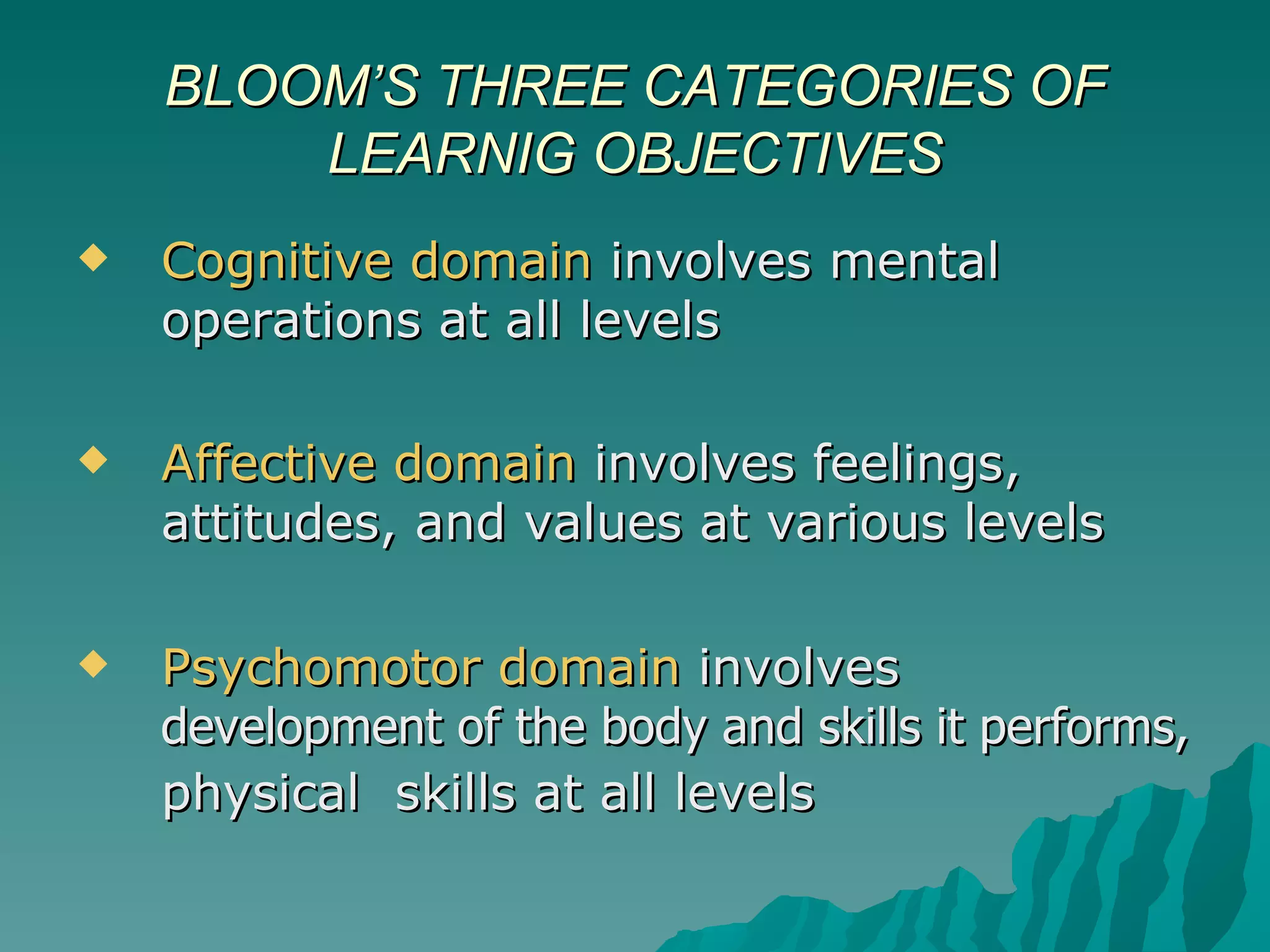
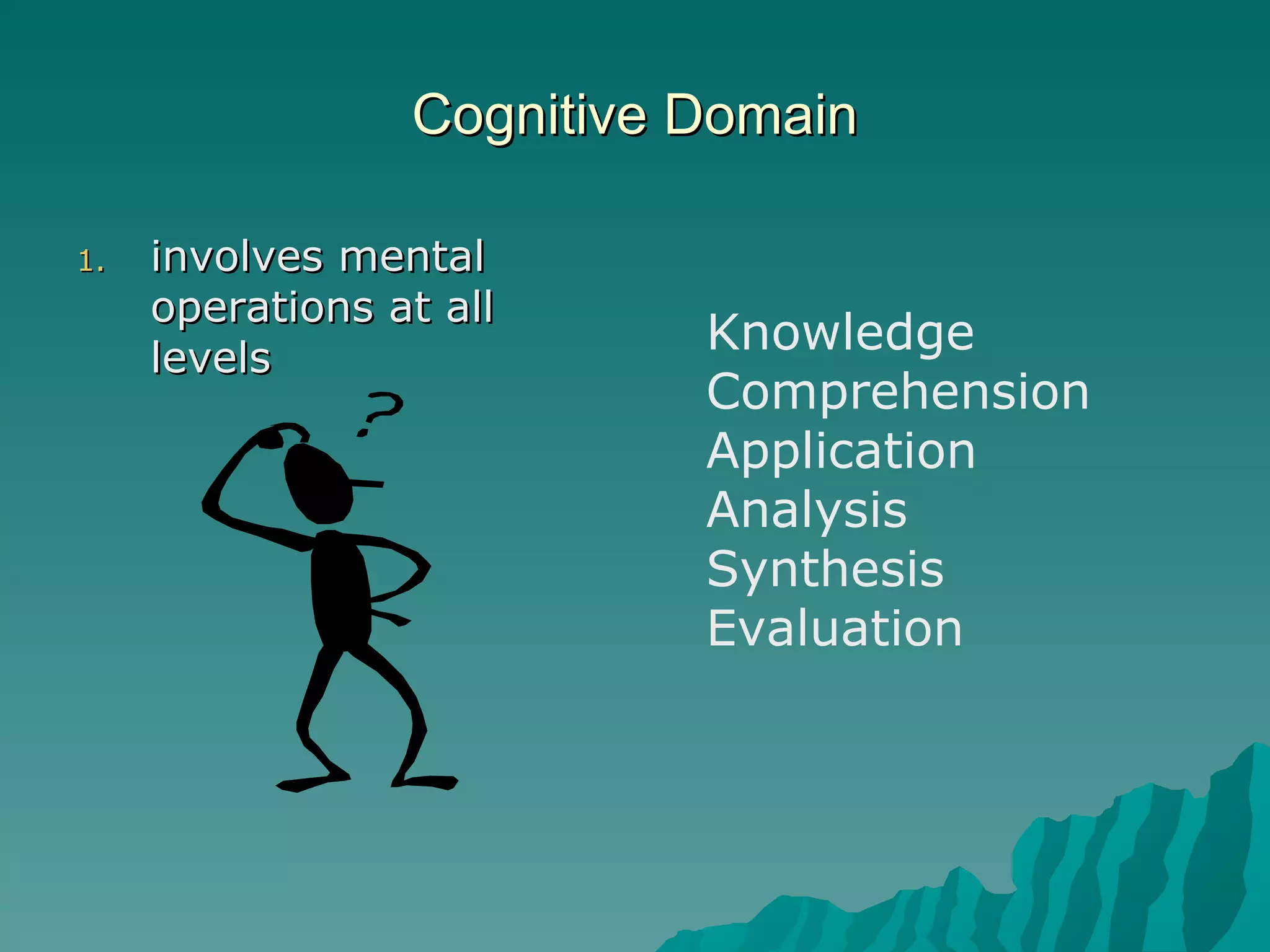
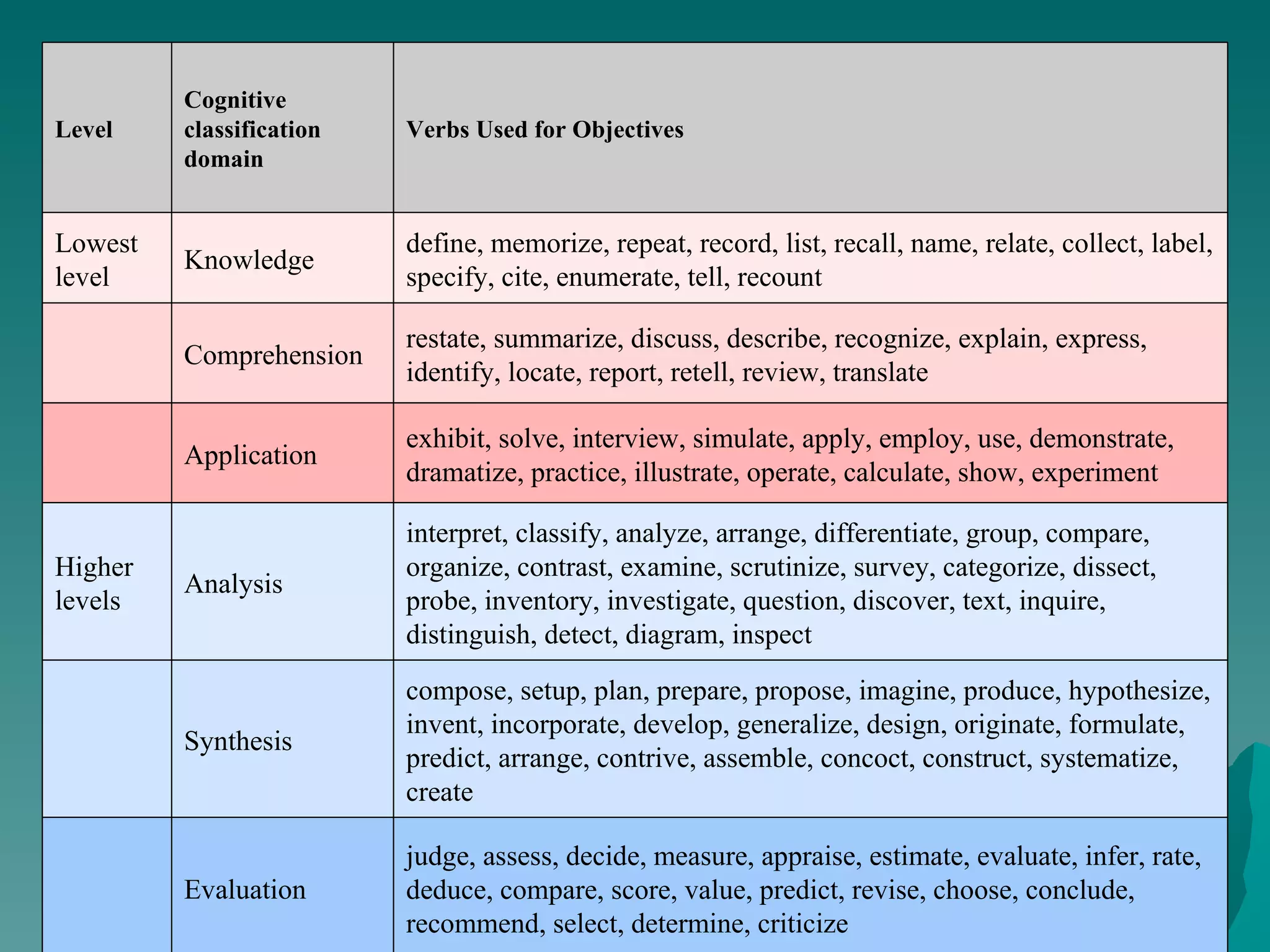
The document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies learning objectives into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain involves mental skills and ranges from basic recall to evaluation. The affective domain involves attitudes, values, and feelings. The psychomotor domain involves physical skills. Verbs are provided as examples to write learning objectives for each level within the domains.