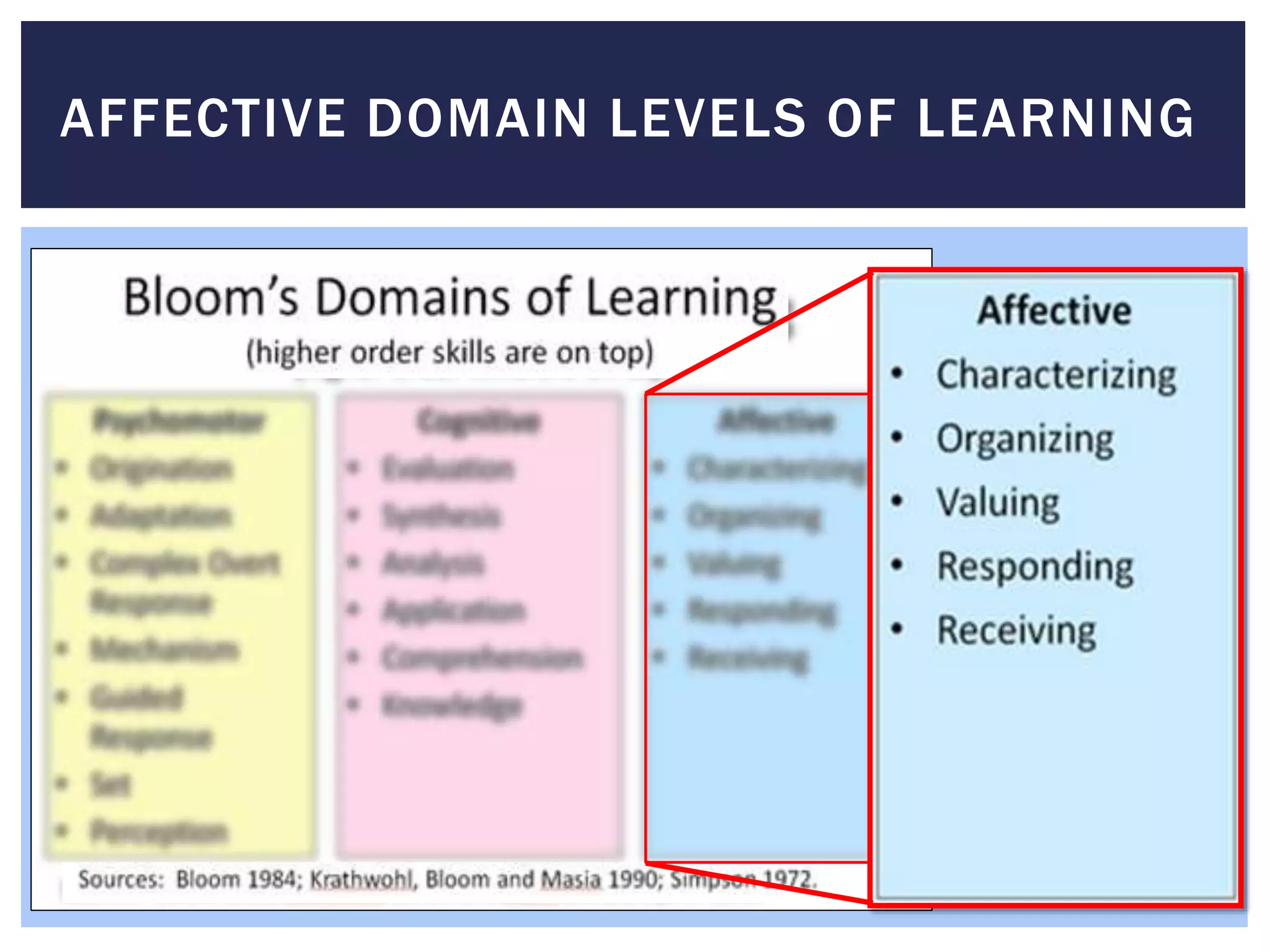
The document outlines the objectives and aims of education across various levels, including nurseries, primary, intermediate, secondary, and higher education, emphasizing the importance of sound preparation for children's future life phases. It also describes three learning domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor, detailing the skills and processes involved in each domain. The overall focus is on fostering holistic development in students through structured educational levels and targeted learning objectives.