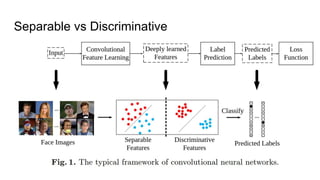
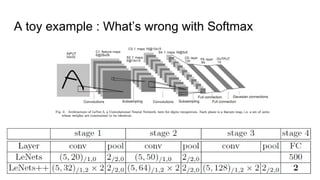
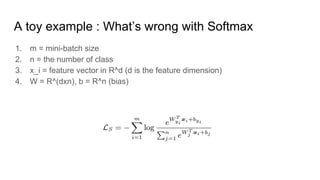
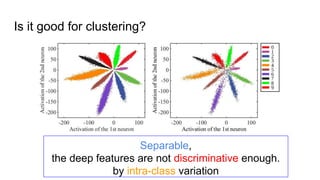
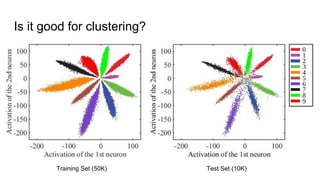
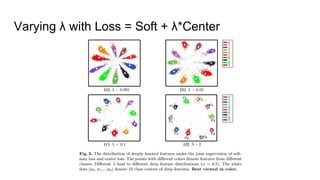
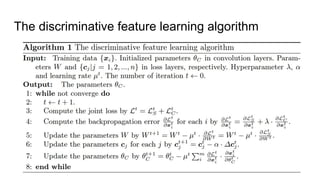
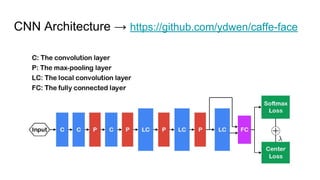
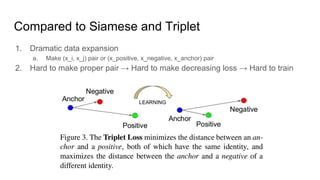
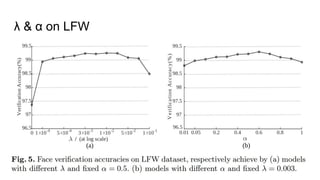
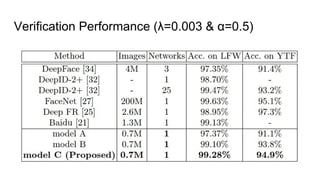
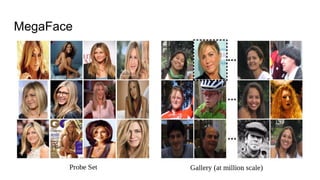
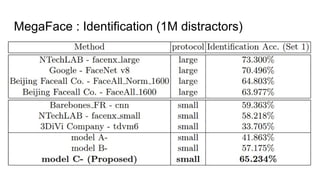
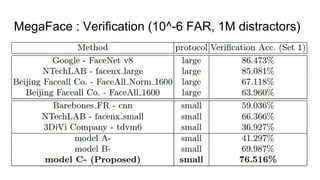
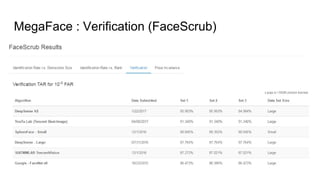
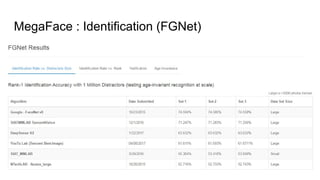
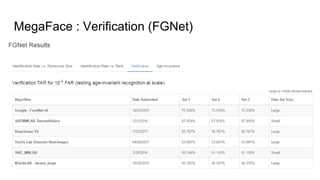
This paper proposes a discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition using a center loss function in addition to softmax loss. The center loss aims to learn discriminative features that reduce intra-class variations. It works by minimizing distances between feature vectors and their corresponding class centers, which are updated during training. Experimental results on benchmarks like LFW, YTF, and MegaFace demonstrate state-of-the-art performance for face verification and identification tasks when using the proposed softmax loss combined with center loss. While performance improvements are achieved, the paper also acknowledges there is still room for enhancing results to meet practical demands involving large-scale datasets with millions of distractors.