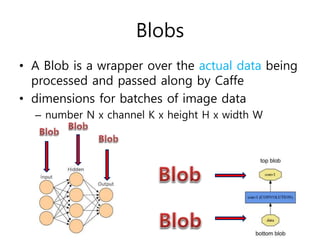
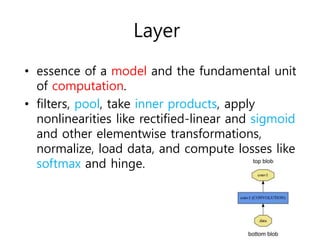
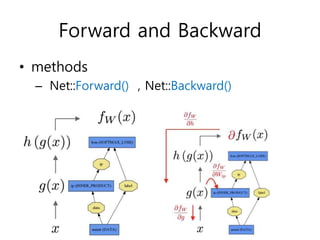
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Caffe including blobs, layers, nets, forward and backward passes, loss functions, and solvers. Blobs wrap data and define dimensions. Layers are the basic computation units, performing operations like filtering and nonlinearities. Nets define the overall model architecture by connecting layers. Forward and backward passes are used for inference and backpropagation. Loss functions drive learning, and solvers optimize models by adjusting parameters to reduce loss over iterations using techniques like stepwise learning rate decay. Data inputs and outputs are also configured through layers.



![Data: Ins and Outs
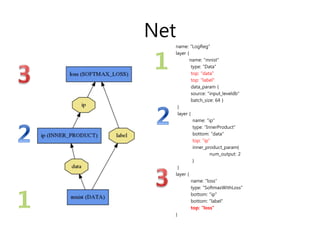
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
backend: LMDB
batch_size: 64
}
transform_param {scale: 0.00390625}
}
%해석: transform으로 [0, 255]의 MNIST data 를 [0, 1] 로 스케일 변경](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caffeframeworktutorial-150818052450-lva1-app6891/85/Caffe-framework-tutorial-8-320.jpg)