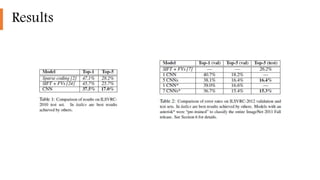
1) The document describes a study that trained one of the largest convolutional neural networks on the ImageNet dataset.
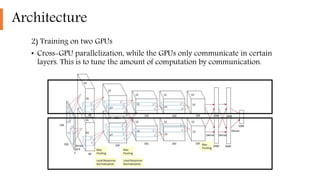
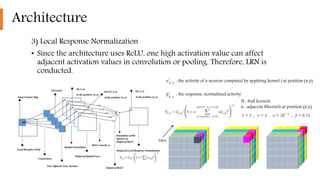
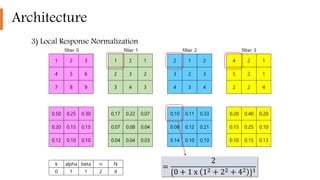
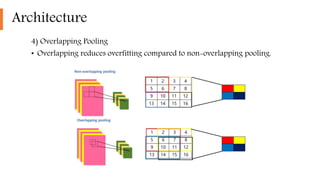
2) It implemented highly optimized GPU training of large CNNs on high resolution images and introduced features like ReLU, local response normalization, and overlapping pooling to improve performance and reduce overfitting.
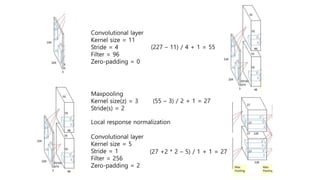
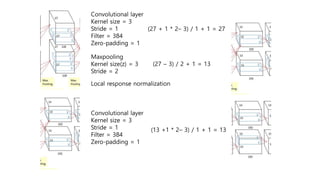
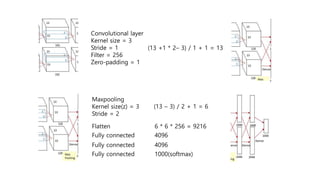
3) The network architecture consisted of 5 convolutional layers and 3 fully-connected layers and was trained on two GPUs with techniques like dropout and data augmentation to reduce overfitting.