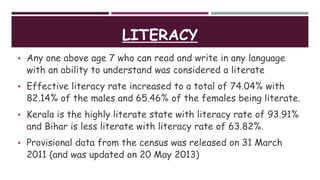
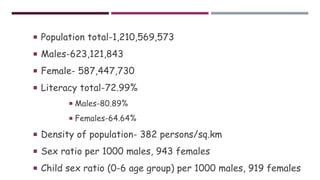
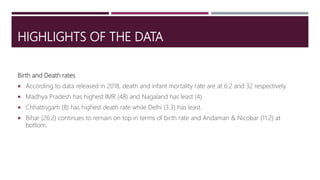
The document provides an extensive overview of demographic studies in India, focusing on the census and national family health surveys (NFHS). It details the history, features, and methods of conducting the census, along with statistical insights from the 2011 census and various rounds of NFHS, highlighting improvements in literacy, health, and population data collection. Additionally, it outlines the objectives and structure of the Sample Registration System (SRS) for reliable demographic indicators.