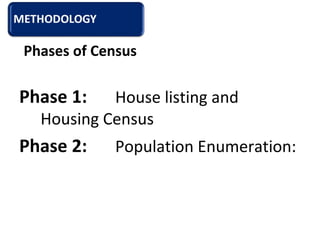
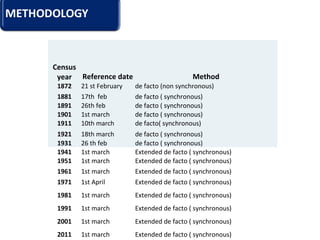
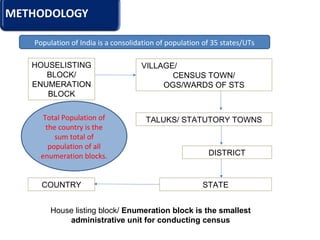
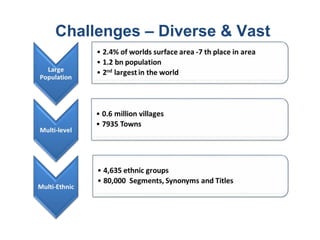
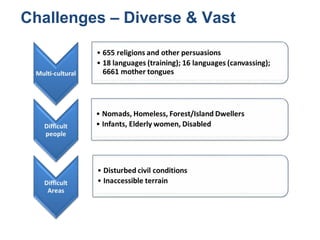
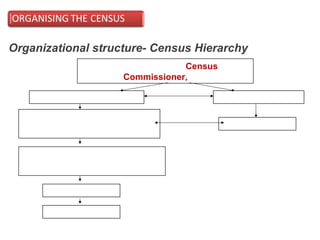
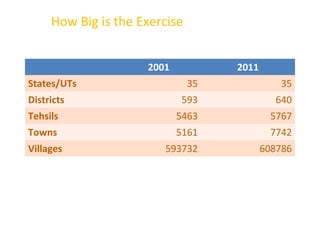
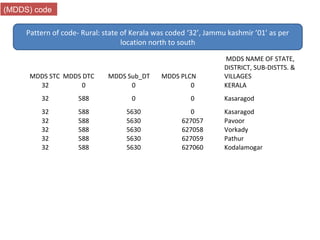
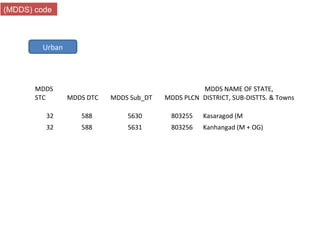
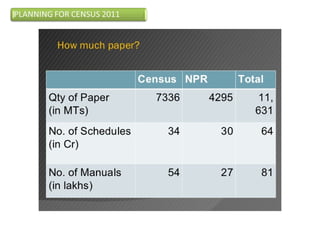
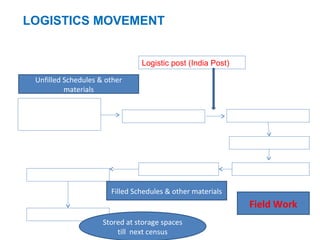
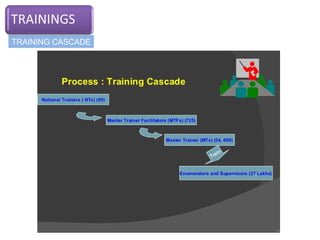
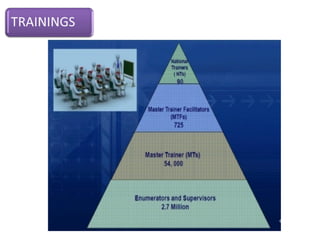
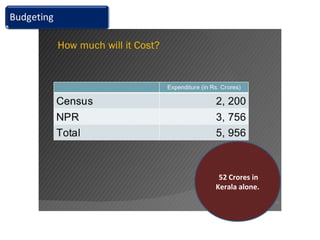
The document provides information about the planning process for the Census of India 2011. It discusses updating the administrative boundaries and assigning location codes to all villages, towns, districts etc. to create a complete frame for the census. It also describes the organizational structure established with officials at national, state, district and local levels to conduct the census. The census follows a de facto method using direct visits to households over a 3-week period to collect demographic and other data from all individuals in the country.