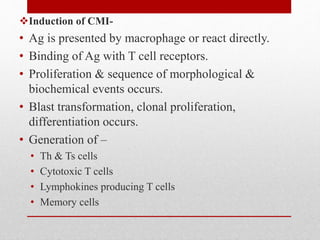
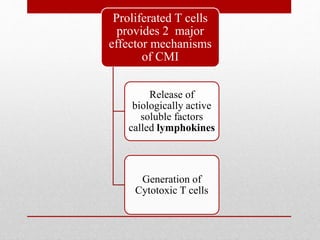
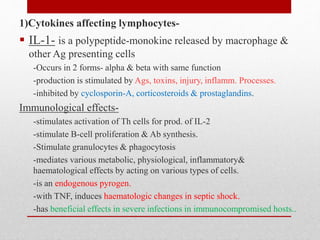
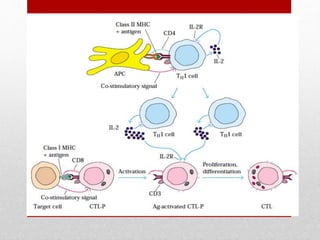
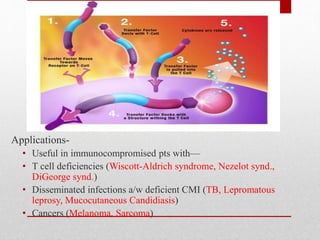
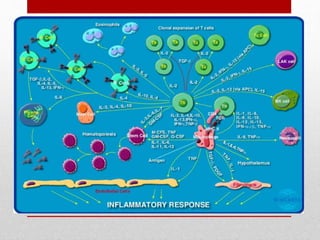
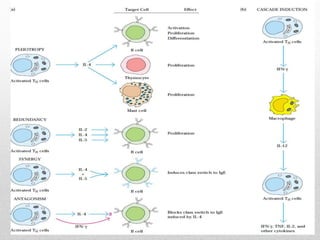
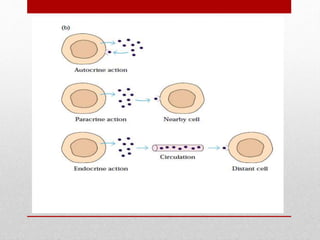
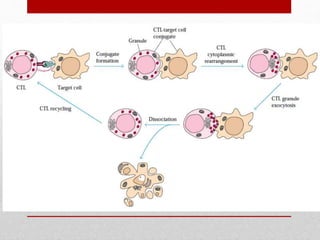
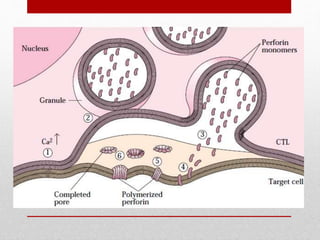
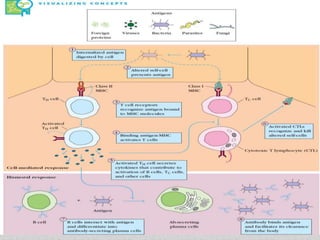
This document summarizes cellular immune response (CMI) mediated by sensitized T cells. It describes how CMI is induced through antigen presentation and T cell receptor binding, leading to T cell proliferation and differentiation. The two main effector mechanisms of CMI are the release of cytokines like interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor, and the generation of cytotoxic T cells. Cytokines regulate immune cells and have various metabolic and inflammatory effects. Cytotoxic T cells directly kill target cells like virus-infected cells. Tests to detect CMI include skin tests and lymphocyte transformation assays in vitro. CMI plays an important role in immunity against intracellular pathogens and transplants.