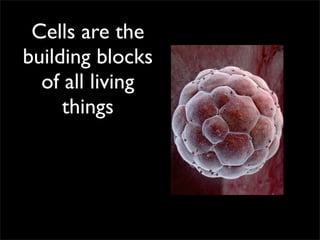
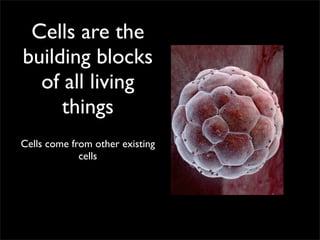
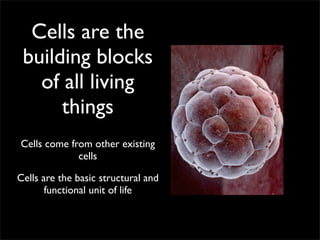
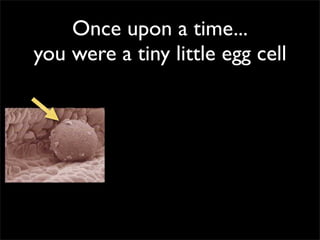
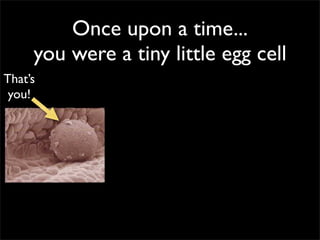
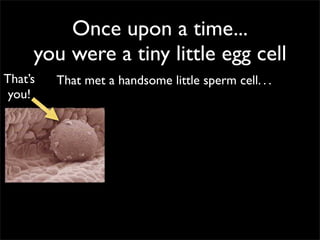
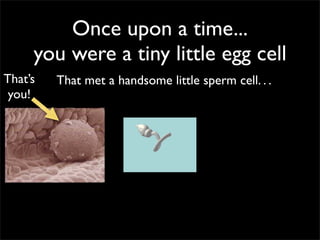
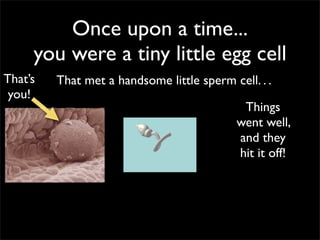
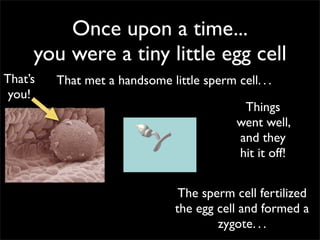
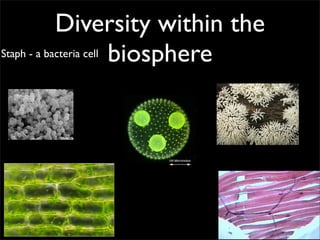
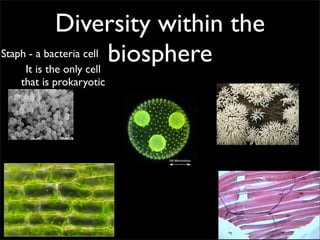
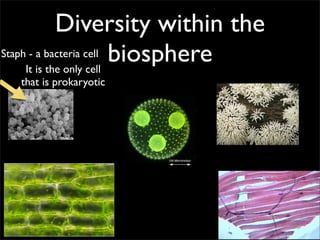
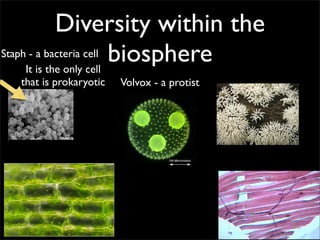
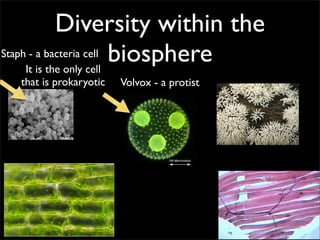
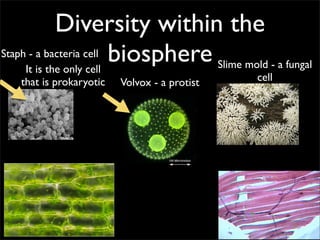
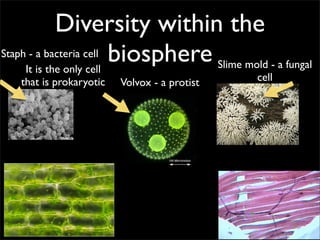
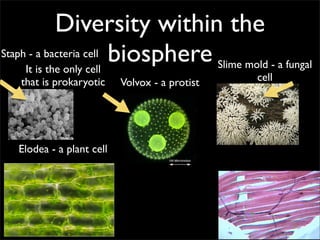
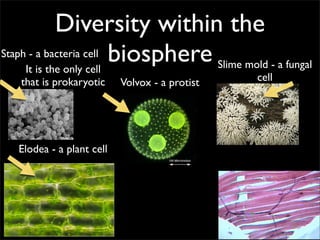
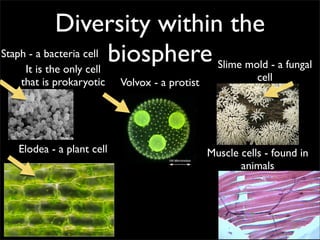
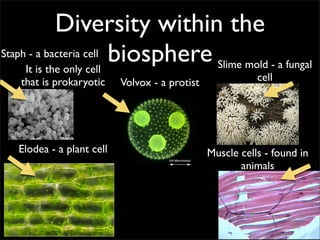
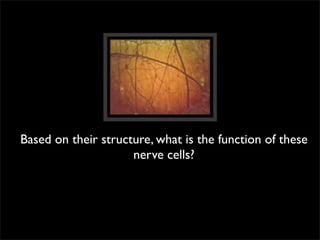
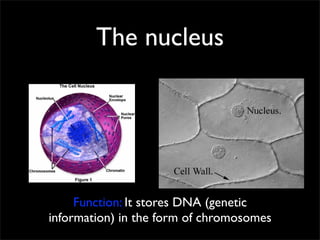
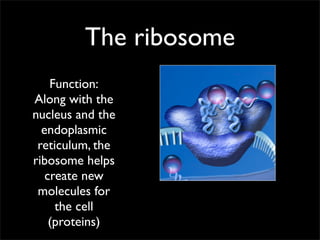
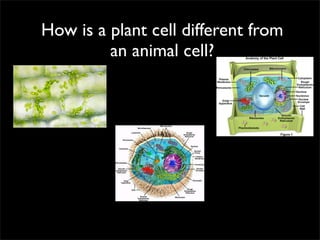
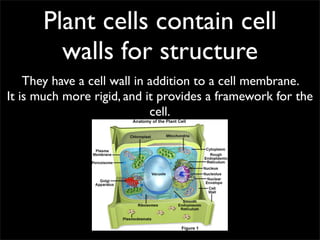
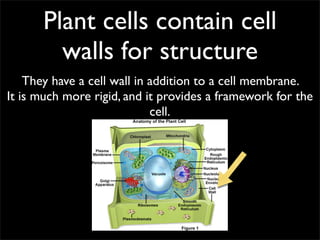
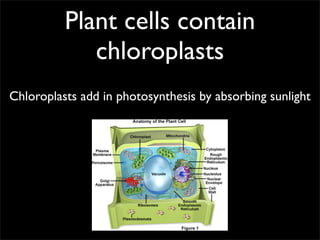
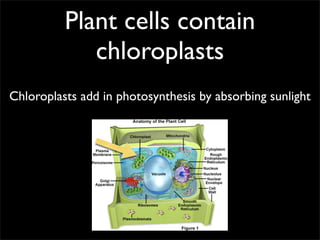
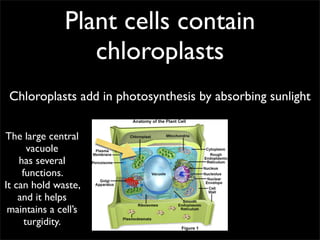
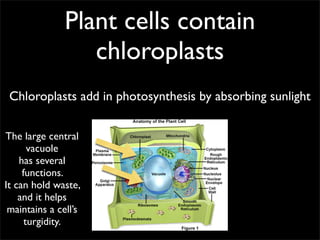
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells come from existing cells through cell division. The document describes the process of fertilization where an egg and sperm cell fuse to form a zygote, which then divides into more cells through cell differentiation and growth. It discusses the diversity of cell types including bacteria, protist, fungal, plant, and animal cells. It also describes several organelles and their functions in animal and plant cells.