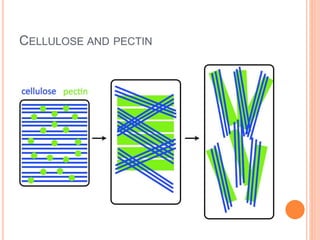
Robert Hooke first observed cells under a microscope in tree bark. Plant cell walls have three layers: the secondary cell wall, middle lamella, and primary cell wall. The cell wall provides structure, protects the cell, prevents over-expansion from water, and allows for the passage of small molecules through plasmodesmata, which connect adjacent cells and allow for communication. Cell walls vary between organisms, with plant cell walls containing cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, and lignin, while bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan and fungal cell walls contain chitin.