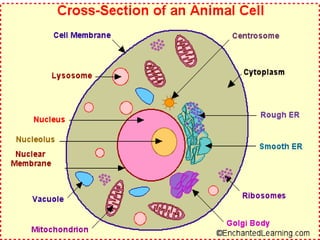
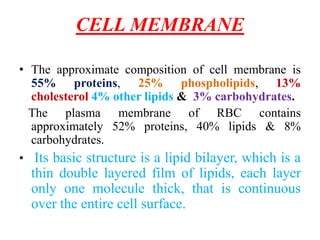
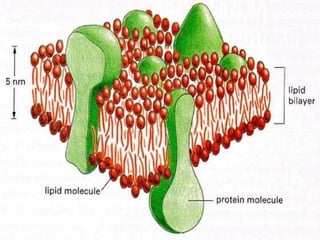
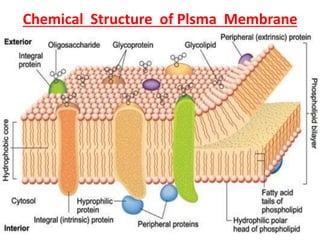
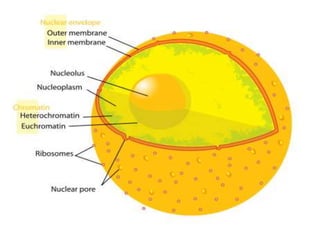
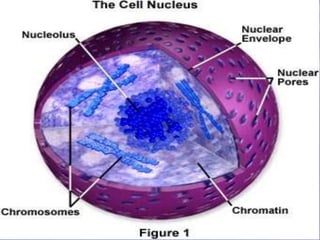
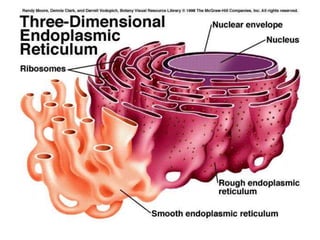
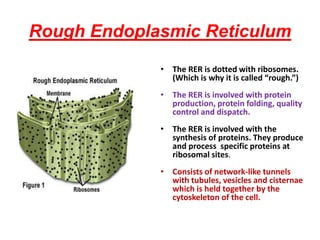
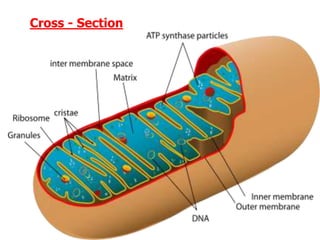
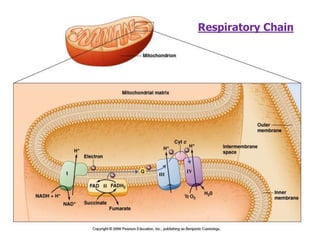
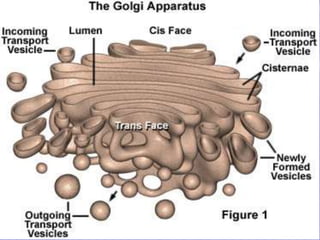
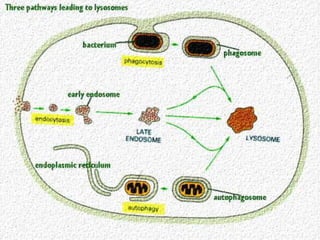
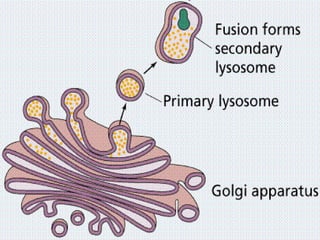
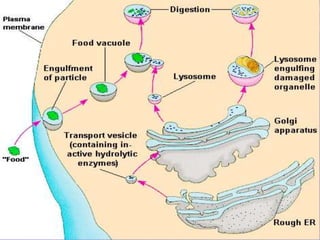
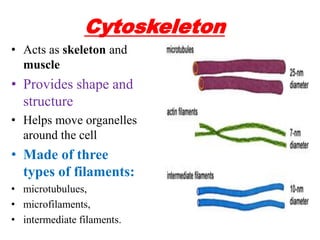
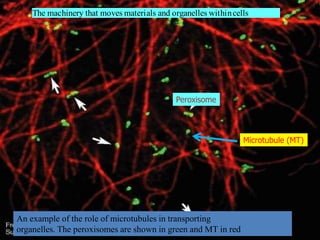
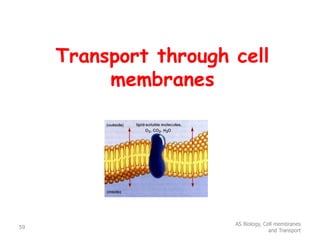
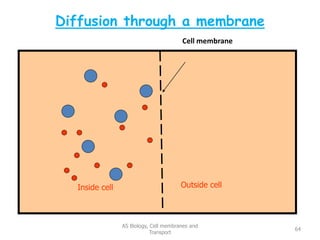
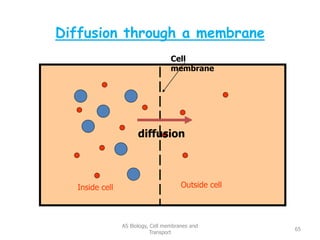
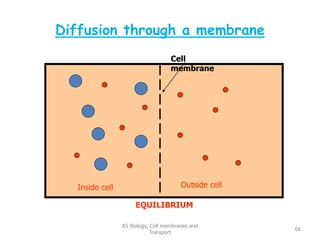
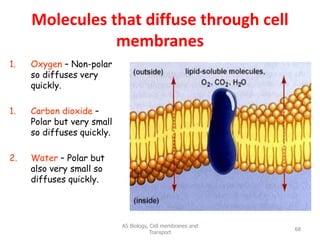
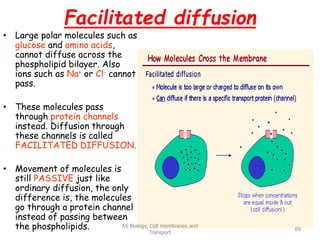
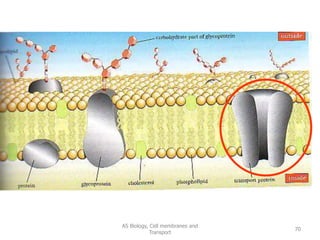
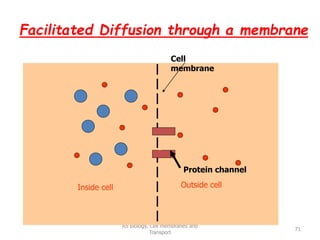
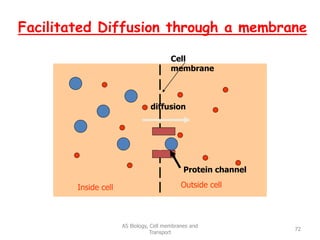
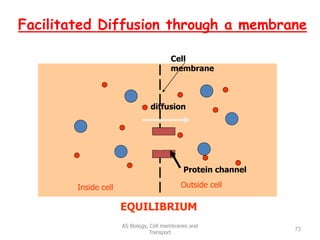
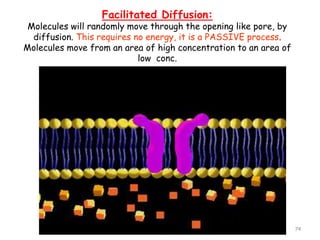
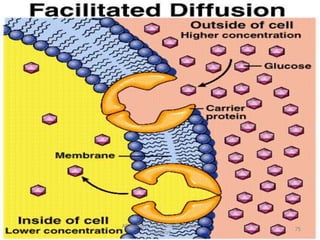
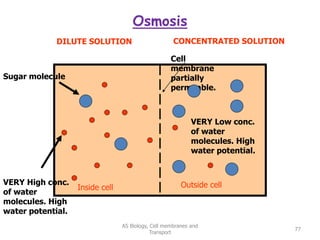
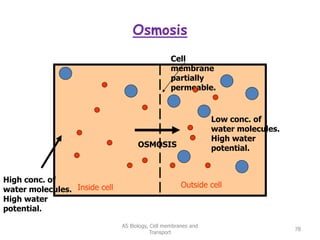
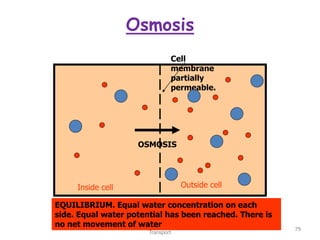
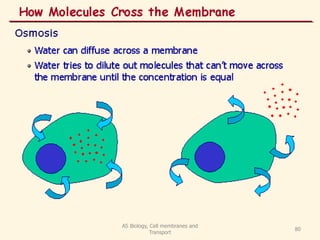
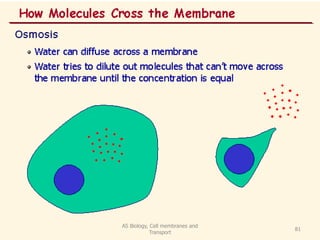
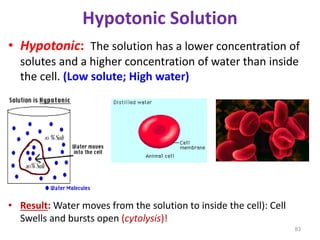
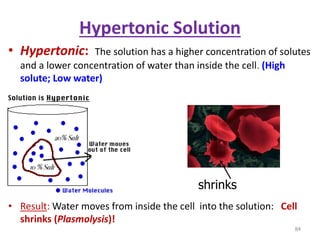
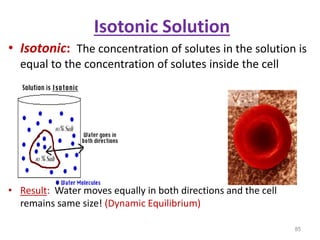
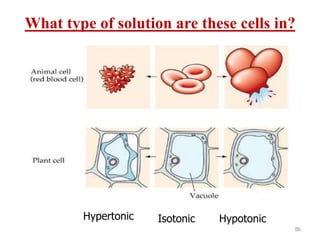
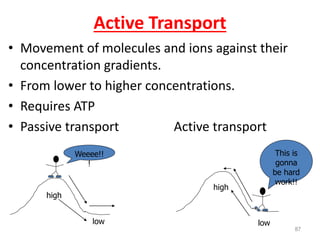
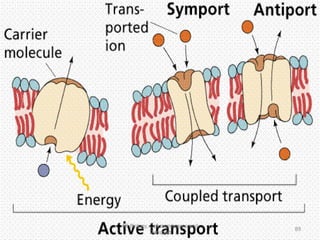
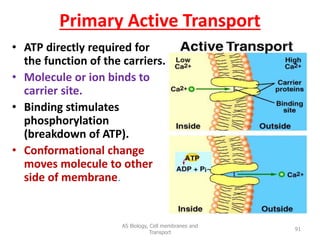
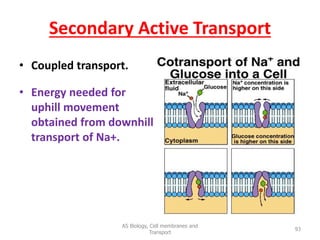
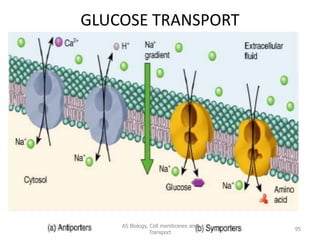
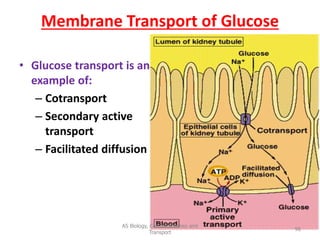
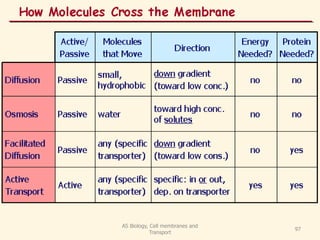
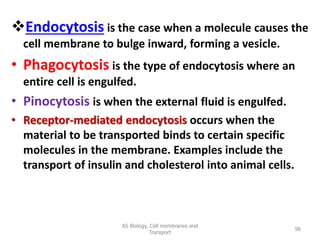
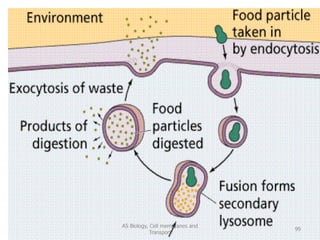
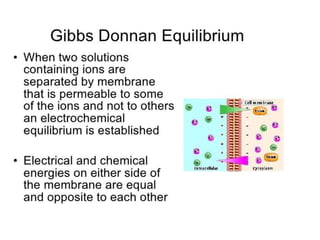
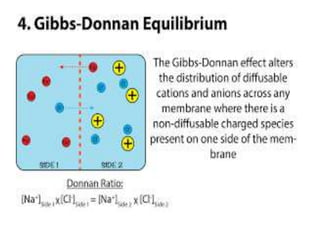
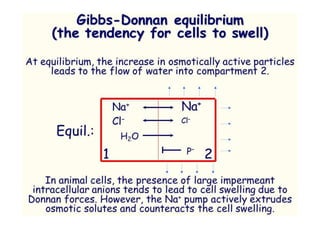
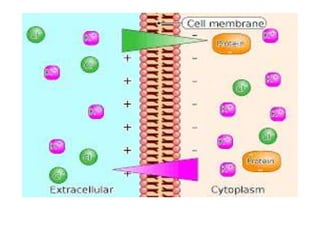
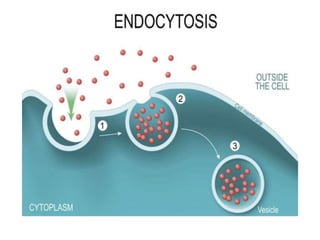
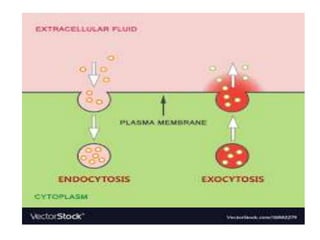
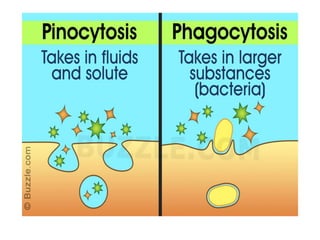
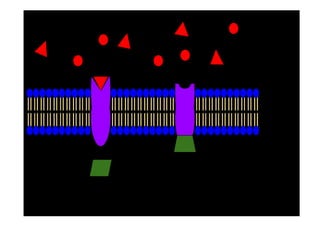
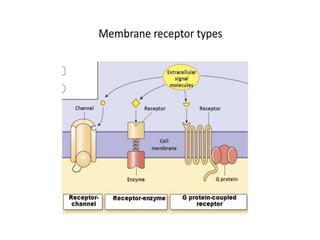
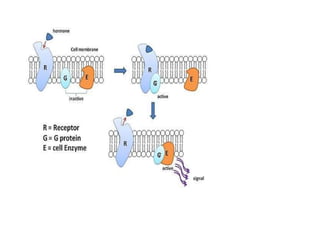
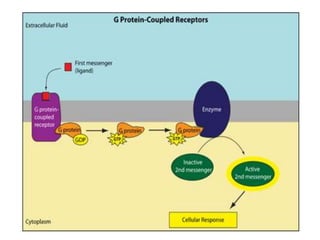
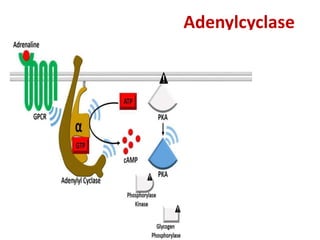
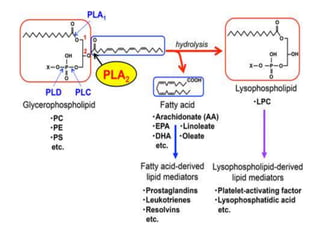
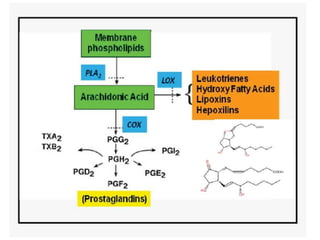
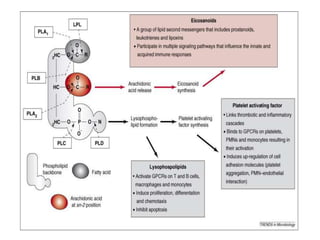
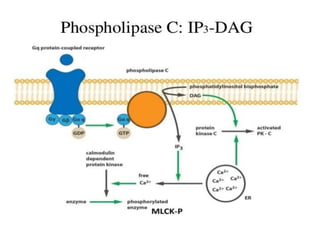
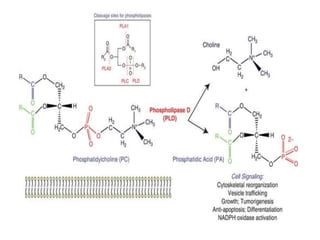
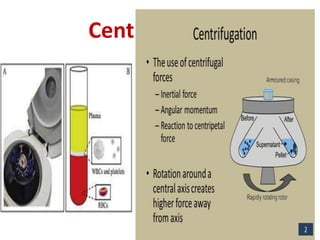
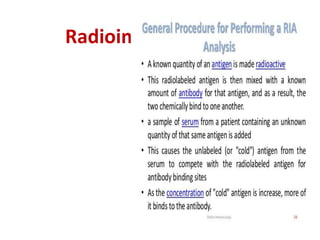
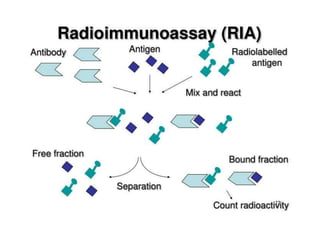
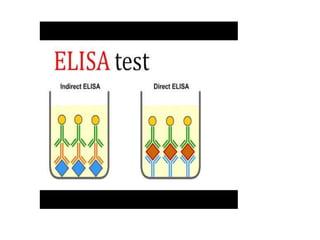
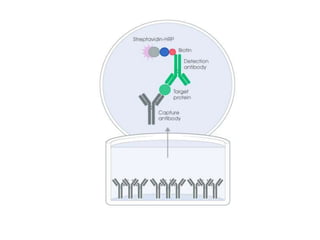
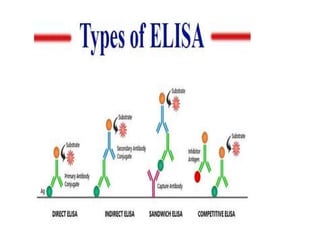
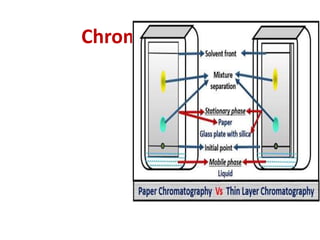
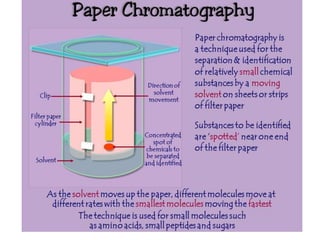
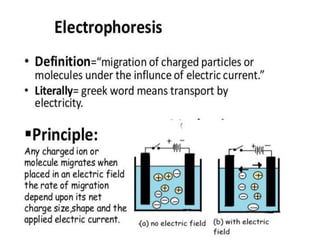
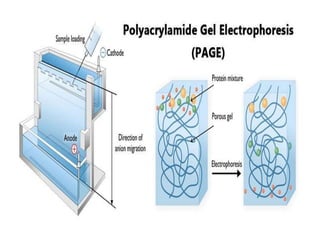
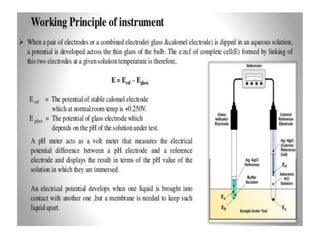
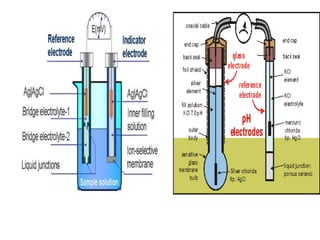
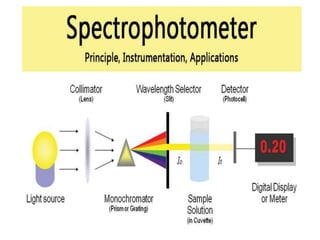
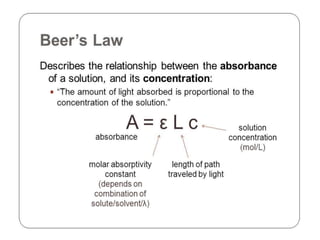
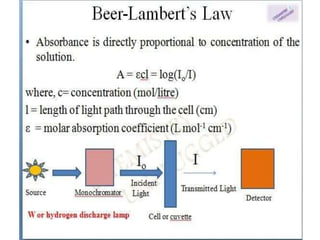
This document discusses cell membranes and transport mechanisms. It describes the four main mechanisms of transport through cell membranes: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration down a concentration gradient. Facilitated diffusion utilizes membrane proteins to transport specific molecules. Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a membrane, moving from an area of lower solute concentration to higher. Active transport requires energy and transports molecules against a concentration gradient using membrane proteins like pumps and channels.