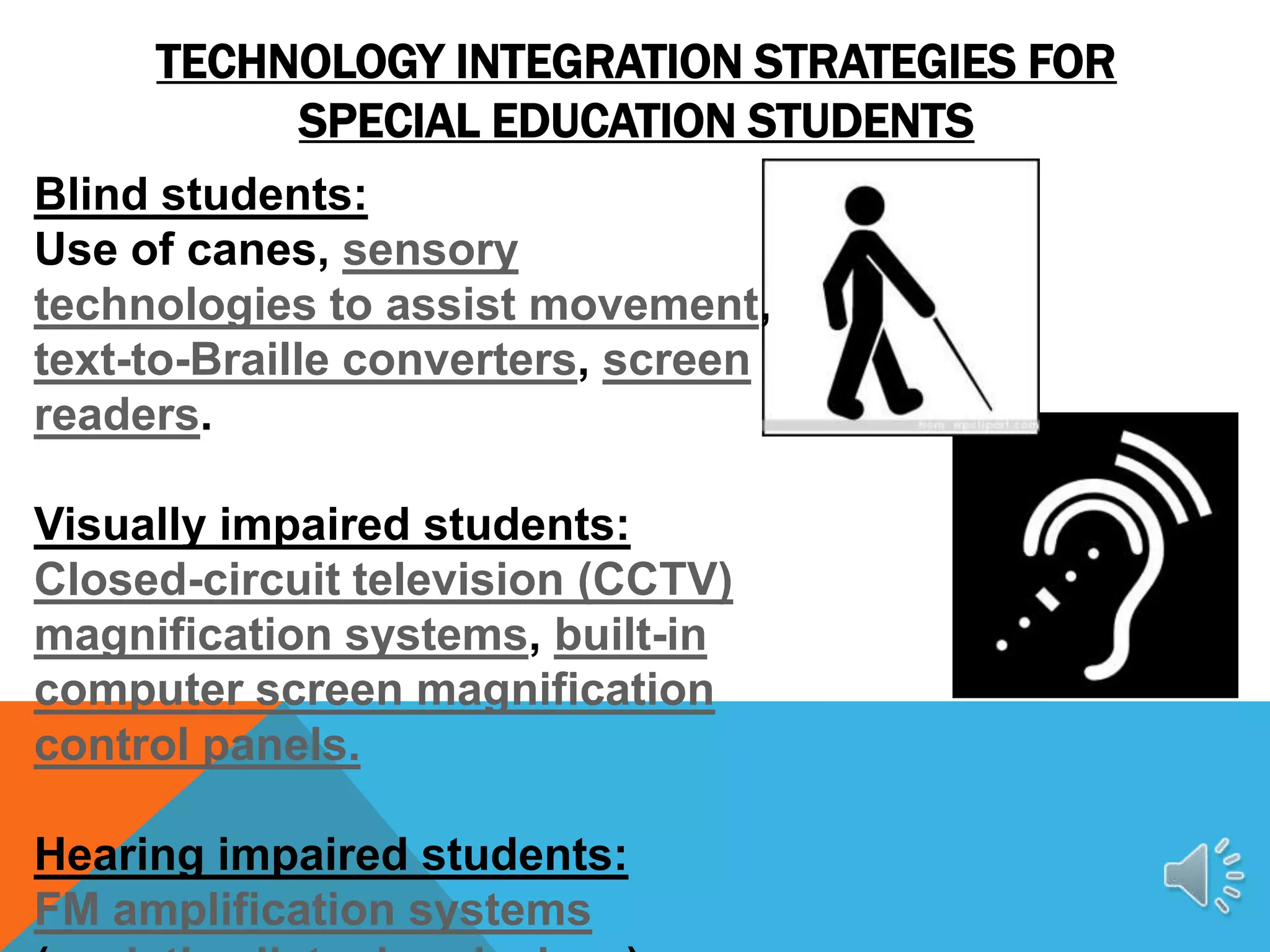
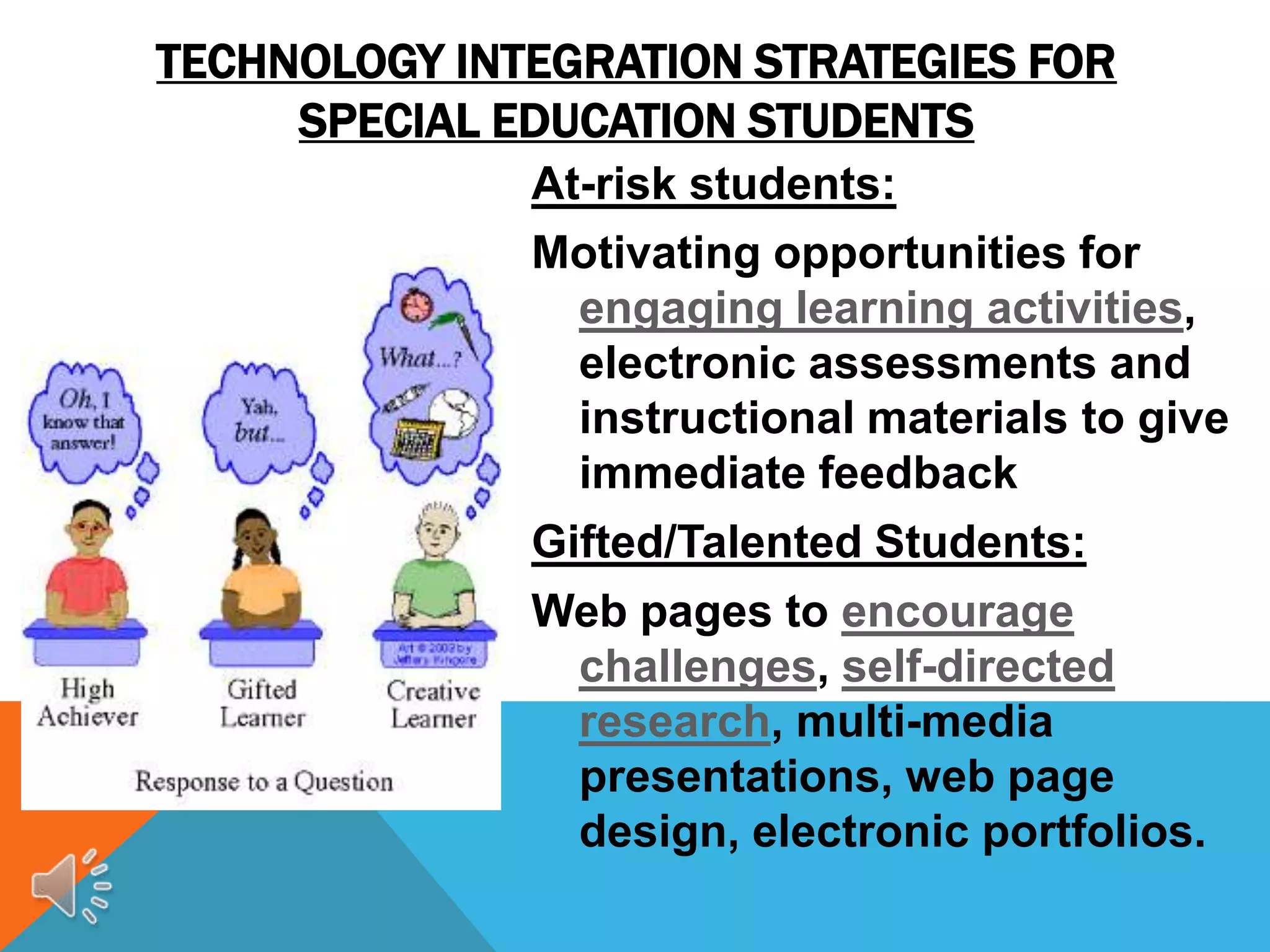
This document discusses special education and the challenges for educators. It covers what special education entails, legal directives regarding assistive technology, and trends showing more students requiring special education services. The document also outlines challenges around universal design and inclusion. Finally, it discusses various technology integration strategies for different types of special education students to help address their needs through assistive technologies, software, and adaptive devices.