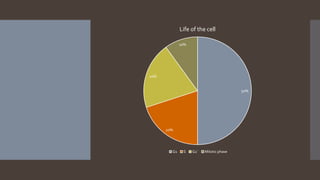
The cell cycle is the series of growth and division steps that a cell undergoes to reproduce. It includes interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA (S phase), and mitosis (M phase), where the cell divides into two daughter cells. Mitosis is further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, where the duplicated DNA is separated and distributed into the two daughter cells. Cytokinesis then separates the cytoplasm, finalizing the formation of the two new cells. The cell cycle is highly regulated and involves growth and DNA replication in preparation for accurate division.