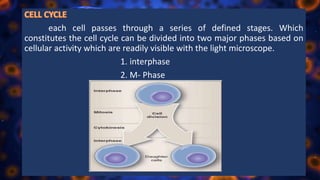
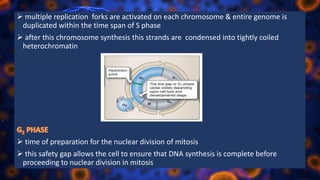
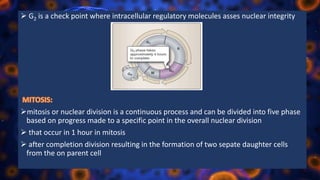
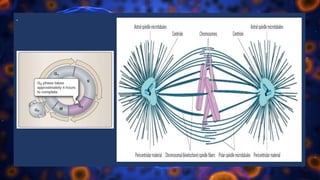
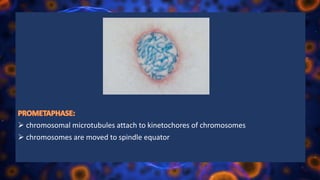
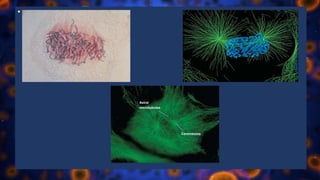
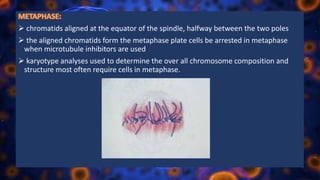
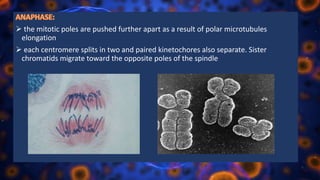
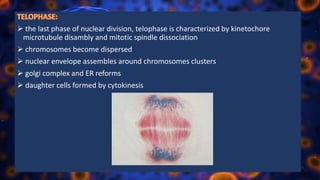
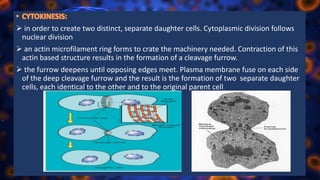
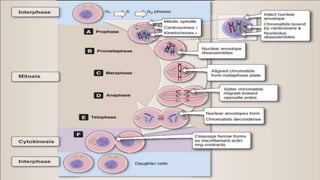
Multicellular organisms rely on cell division for growth and the replacement of lost cells, with somatic cells generated through a controlled sequence known as the cell cycle, comprising notable phases: interphase and mitotic (M) phase. Interphase involves cell growth and DNA synthesis across distinct G0, G1, S, and G2 stages, while mitosis is a rapid process divided into five phases culminating in the formation of two identical daughter cells. The document details how these processes function and regulate cellular activity, leading to proper division and the generation of new cells.