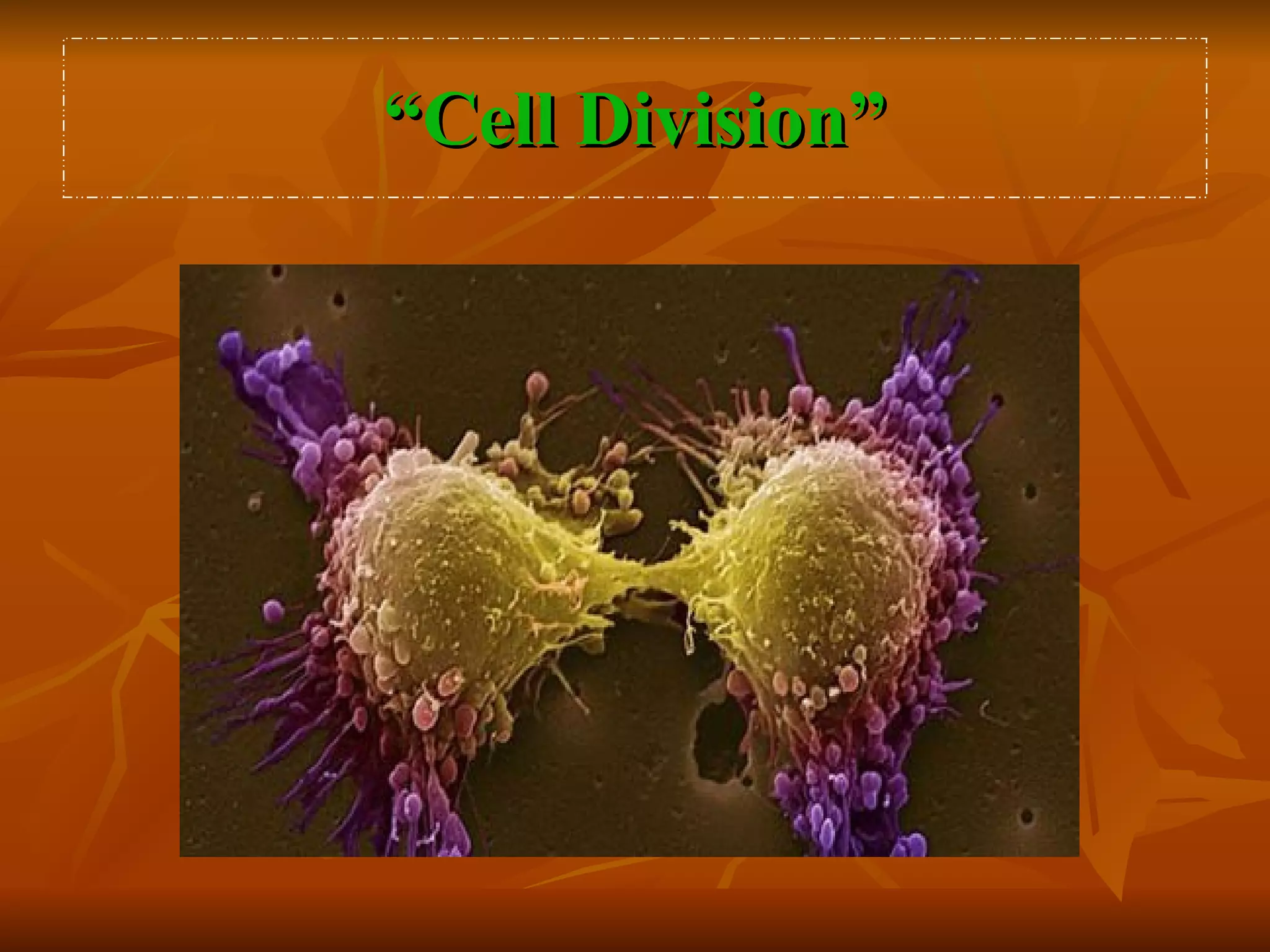
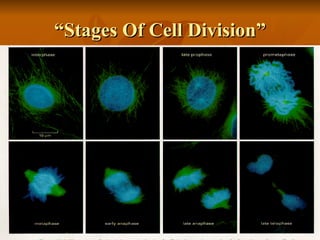
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is used for growth and cell replacement, producing two identical daughter cells. Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half and is used for sexual reproduction. The stages of cell division are interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis, which completes the splitting of the daughter cells.