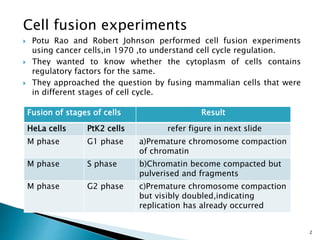
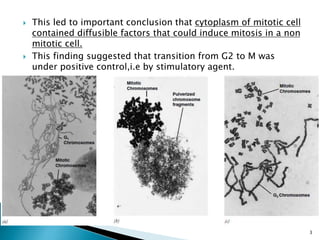
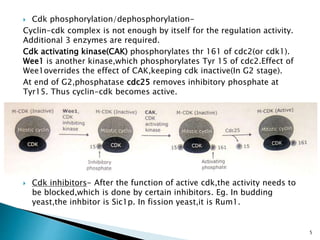
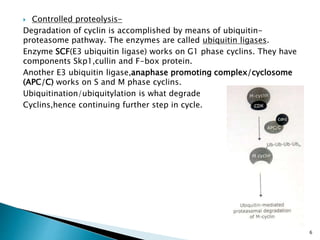
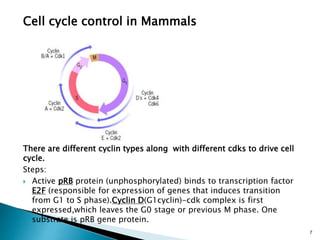
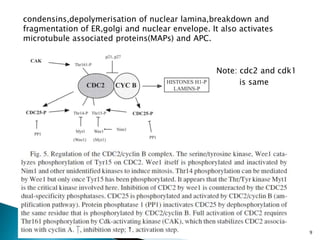
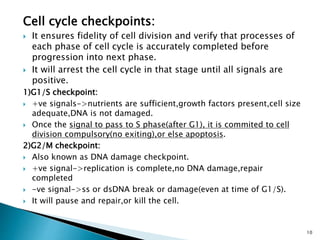
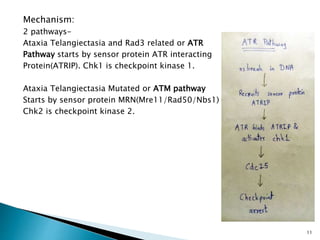
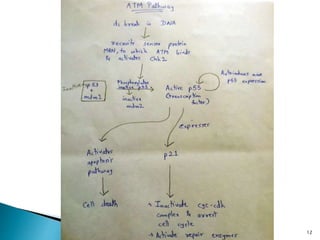
Cell fusion experiments in 1970 showed that the cytoplasm of mitotic cells contained diffusible factors that could induce mitosis in non-mitotic cells, suggesting cell cycle transition from G2 to M phase is under positive control. Cyclin-dependent kinases and cyclins play key roles in cell cycle regulation, with cyclins activating CDKs and undergoing regulated synthesis and degradation. Cell cycle checkpoints at G1/S, G2/M, and metaphase ensure fidelity of cell division by verifying completion of each phase before progression.