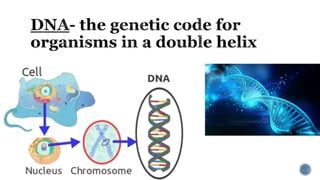
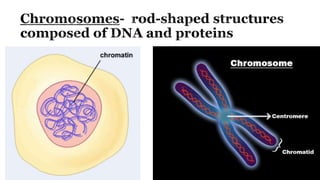
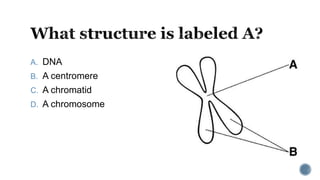
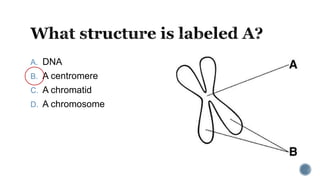
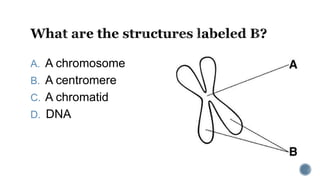
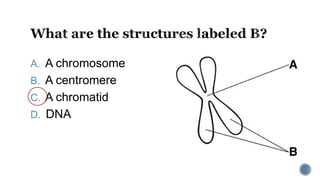
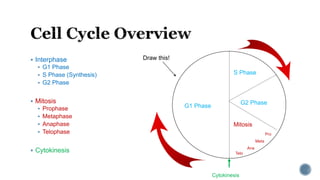
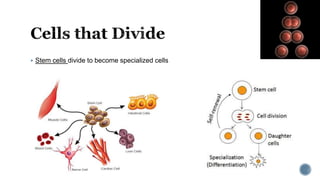
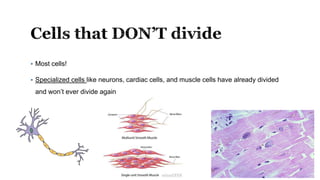
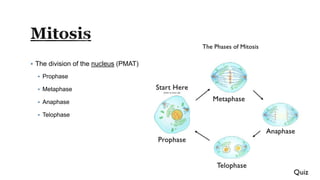
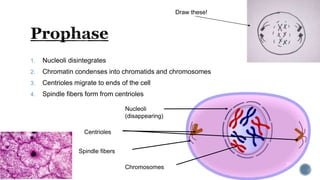
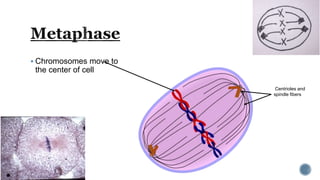
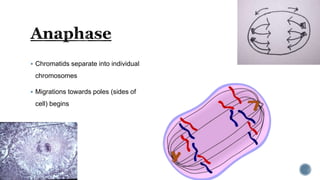
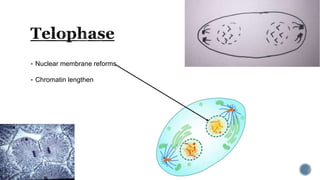
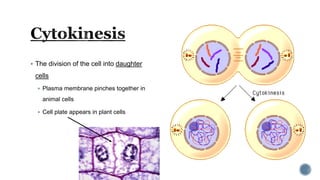
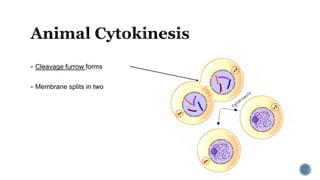
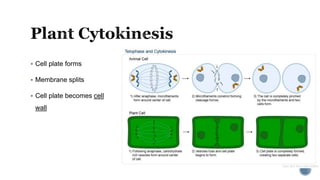
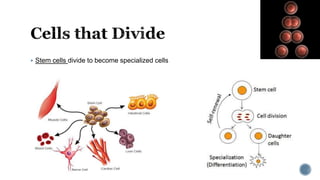
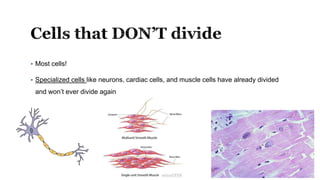
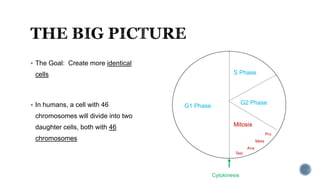
The document describes the cell cycle and its key phases. It explains that stem cells undergo the cell cycle to become specialized cells, while most other cells are already specialized. The cell cycle consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. Mitosis is then described in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the duplicated chromosomes separate. Finally, cytokinesis divides the cell into two daughter cells.