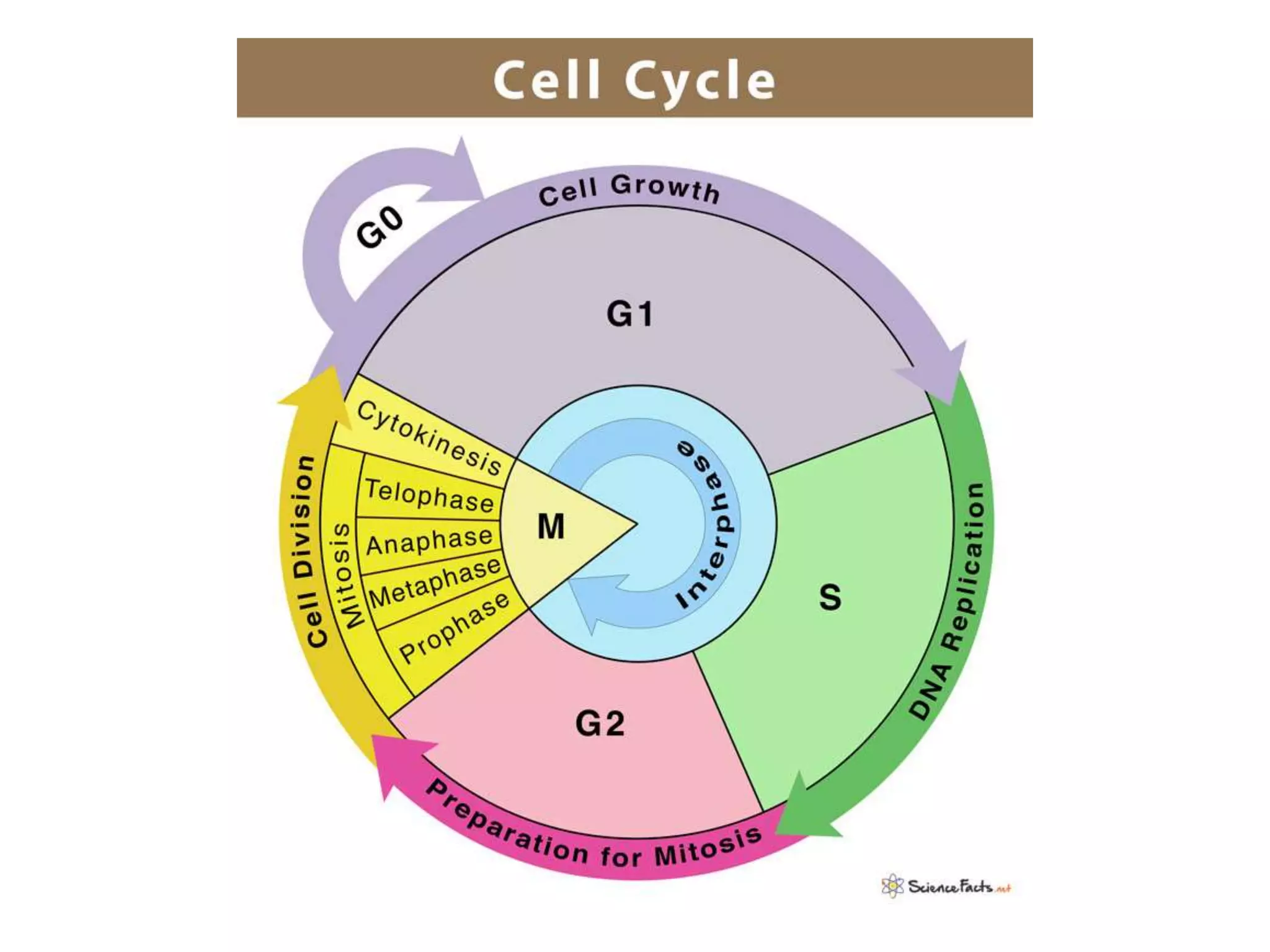
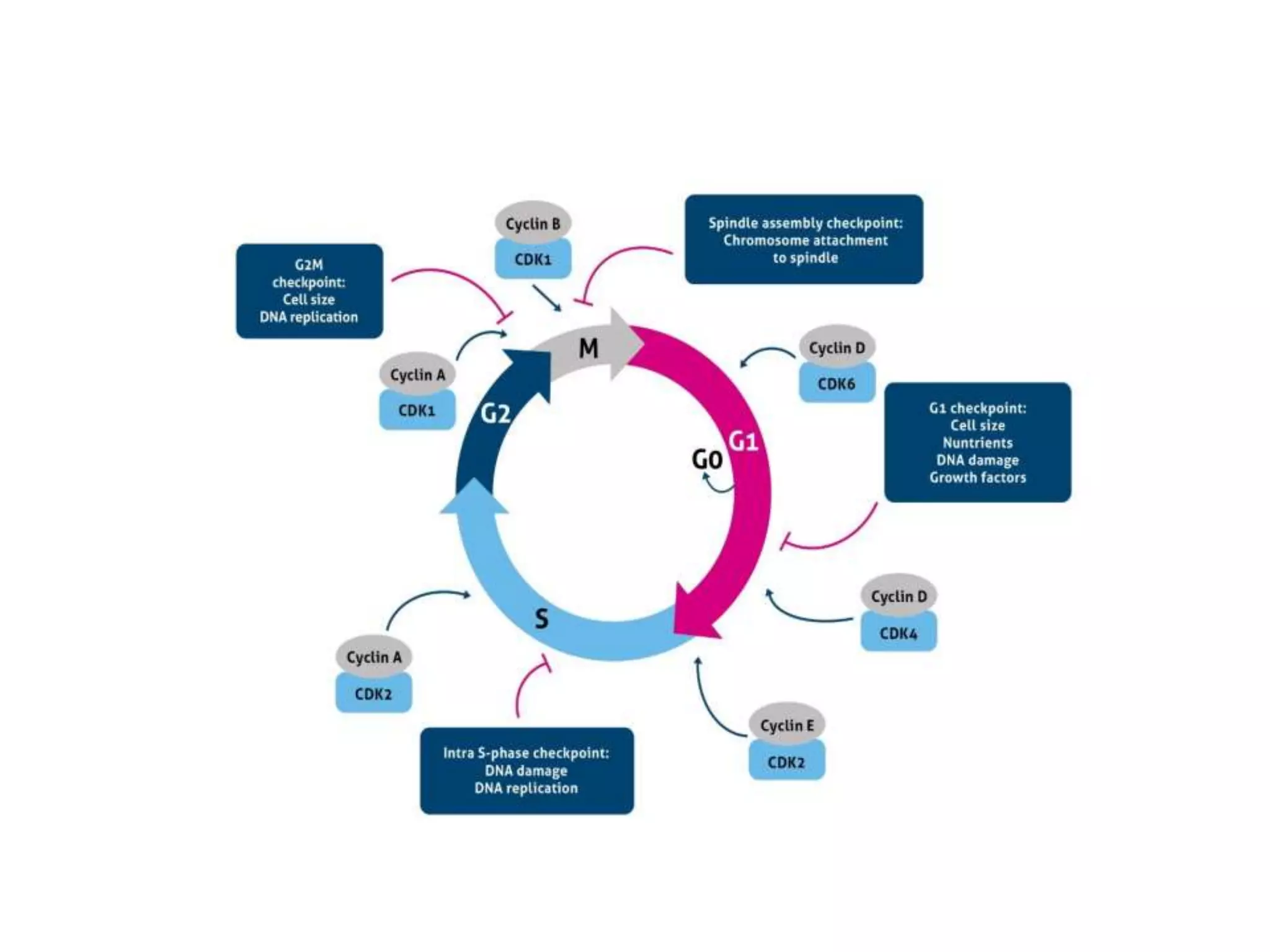
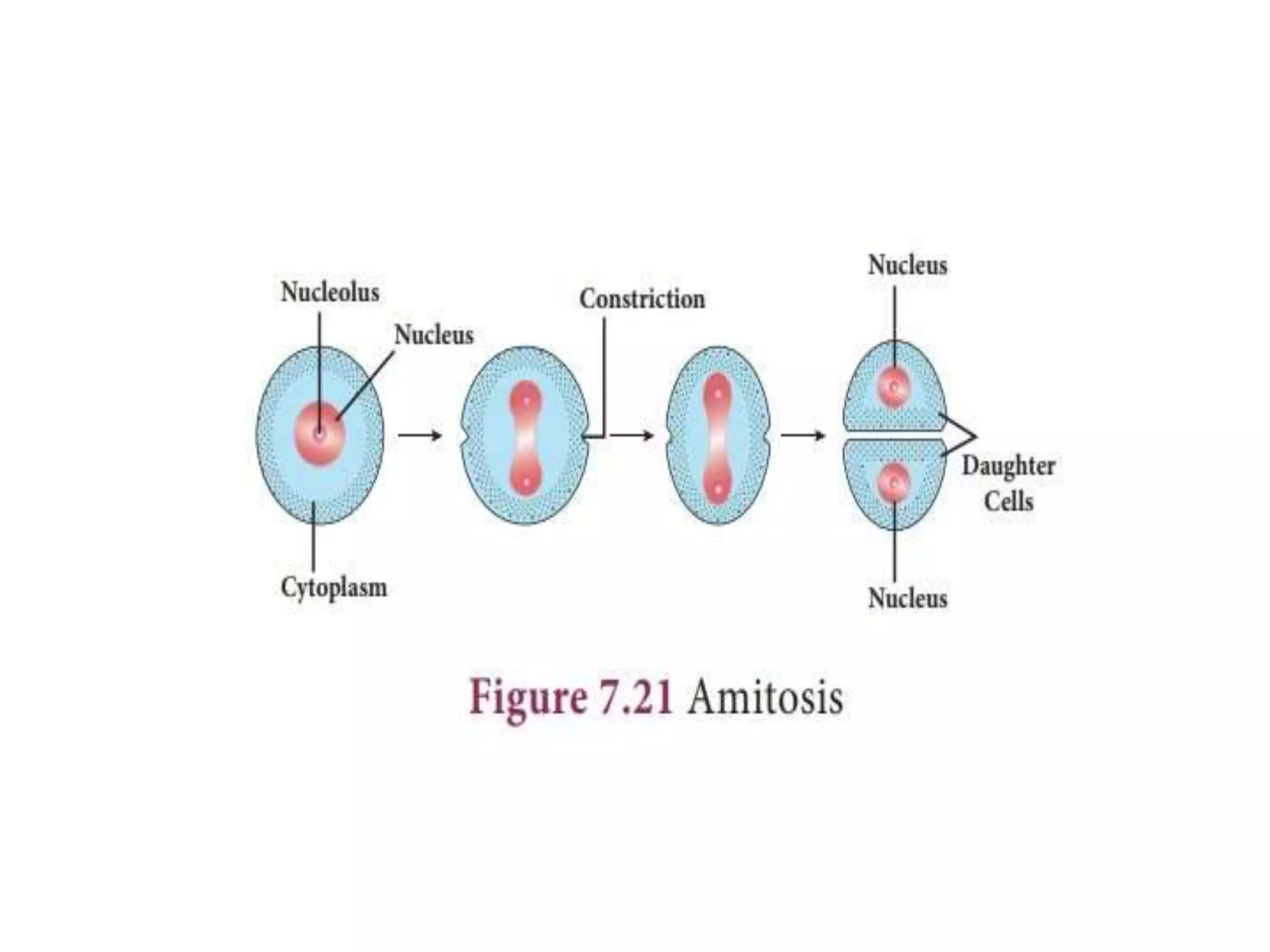
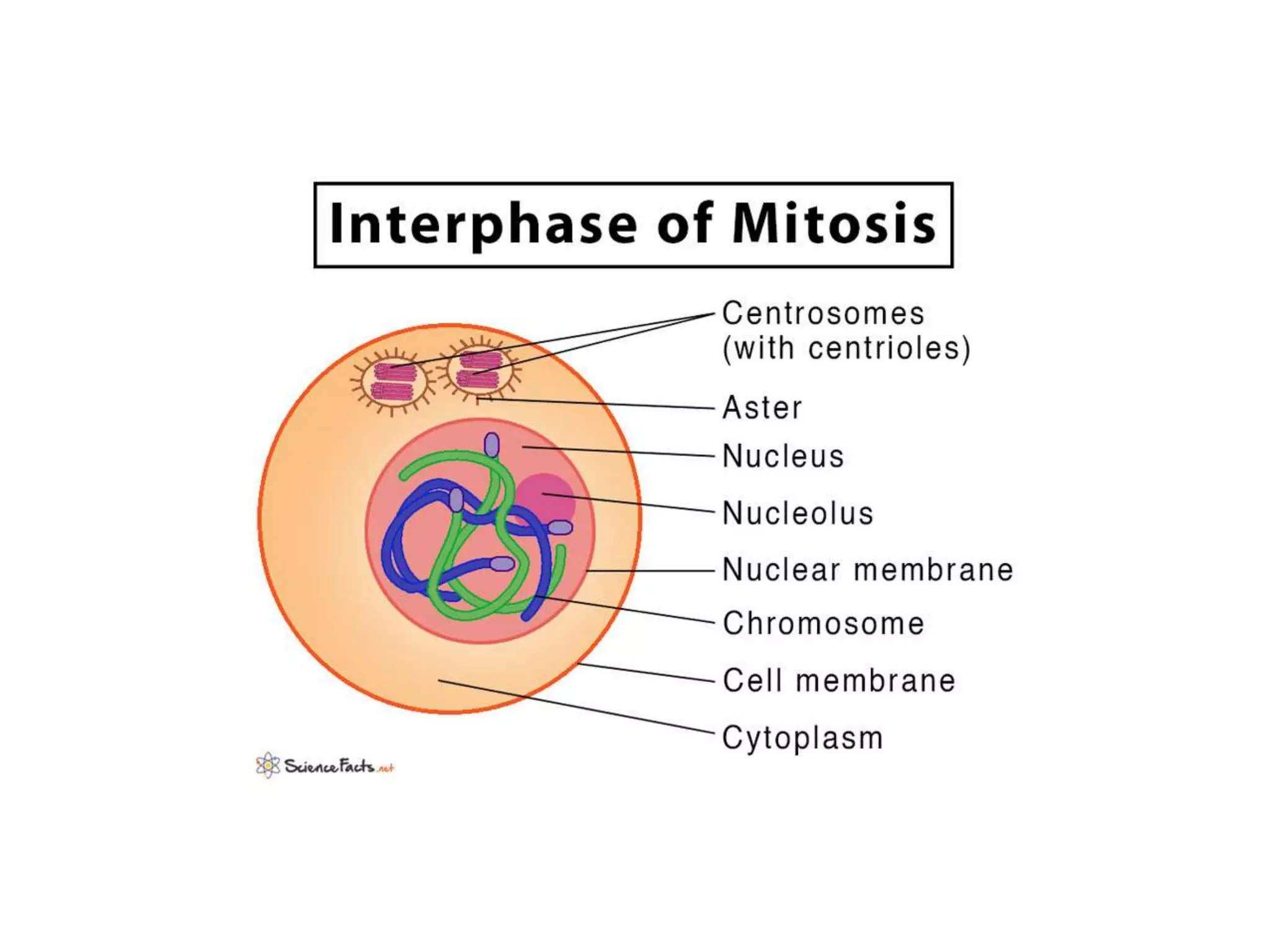
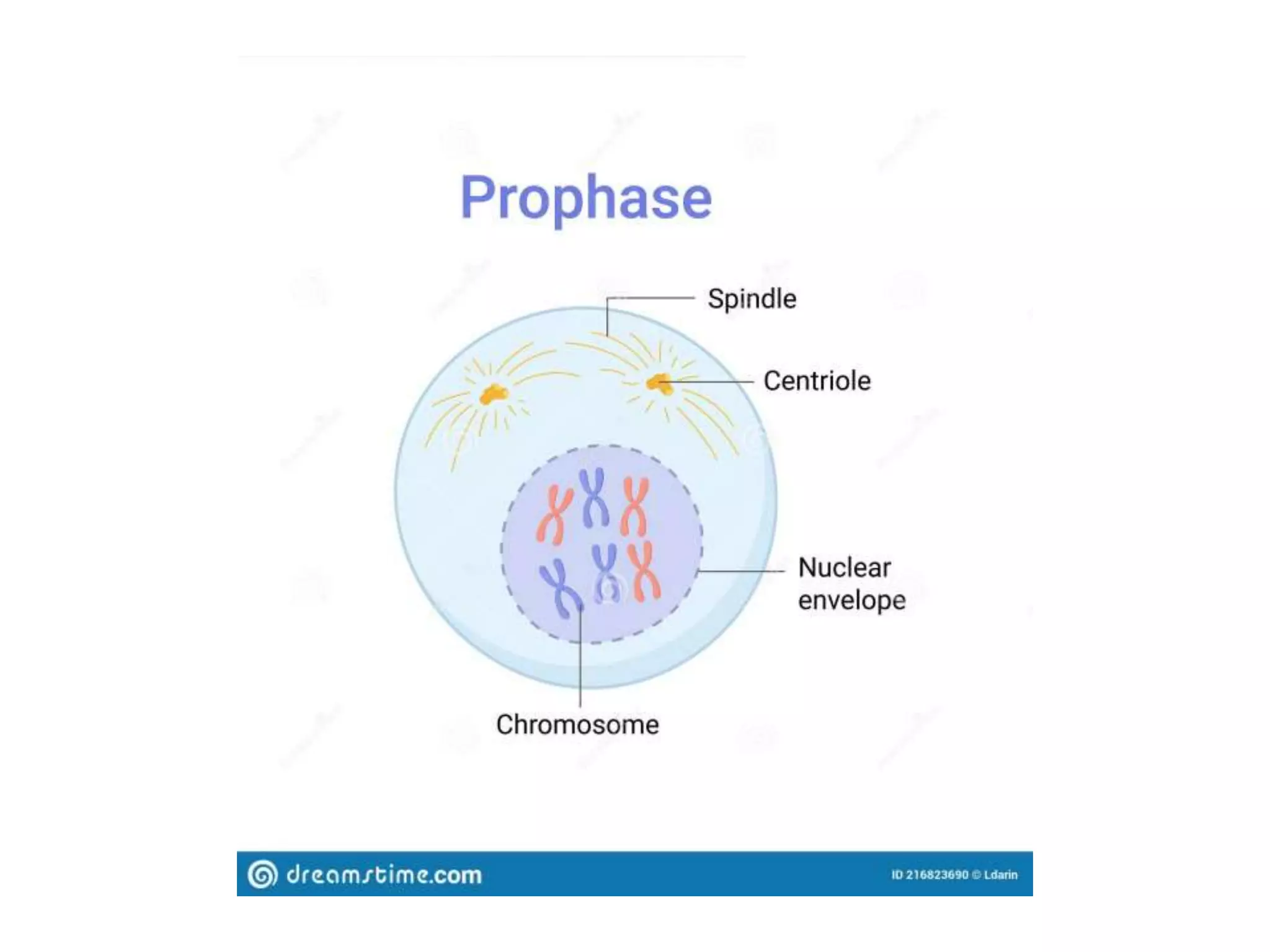
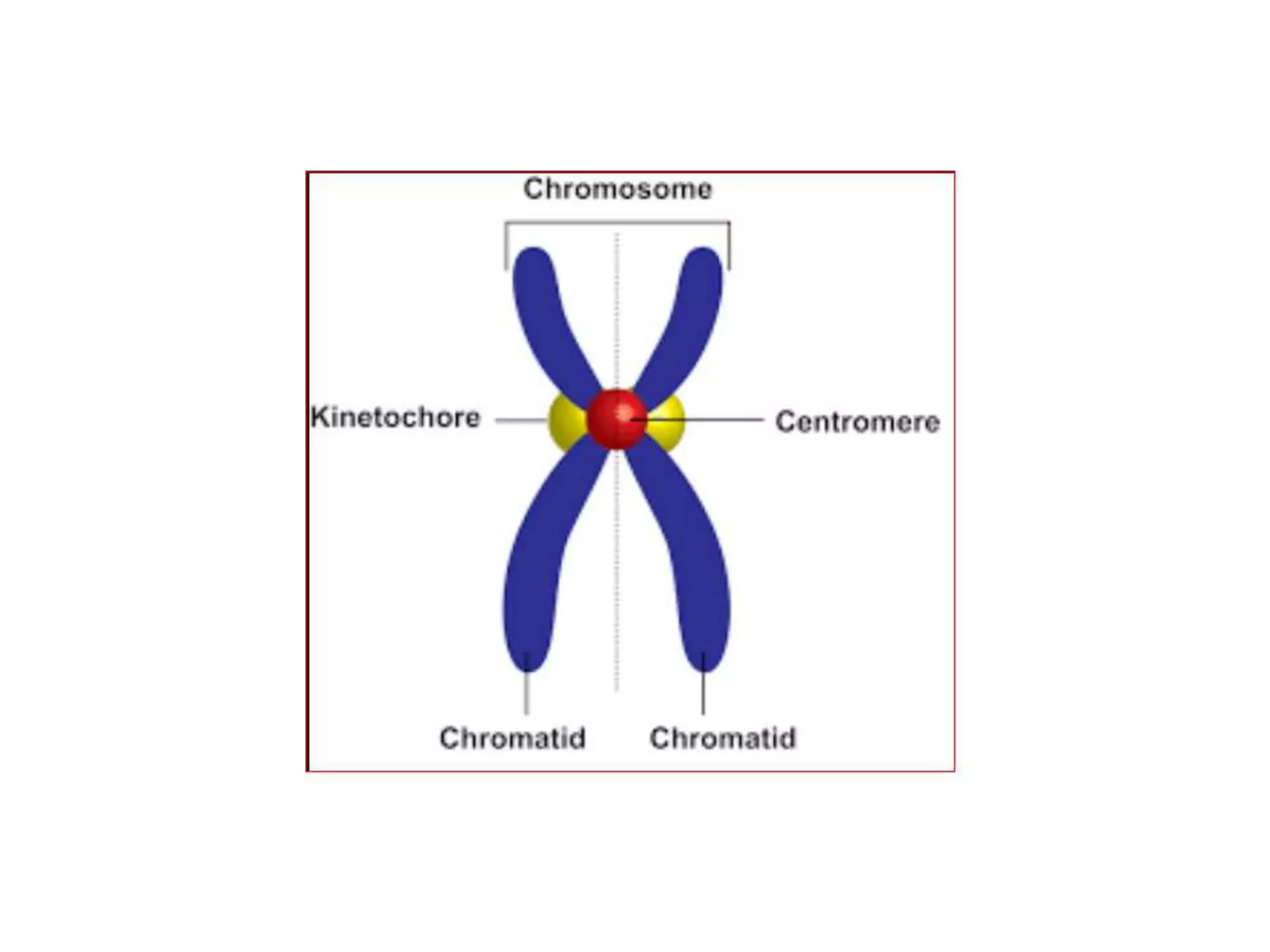
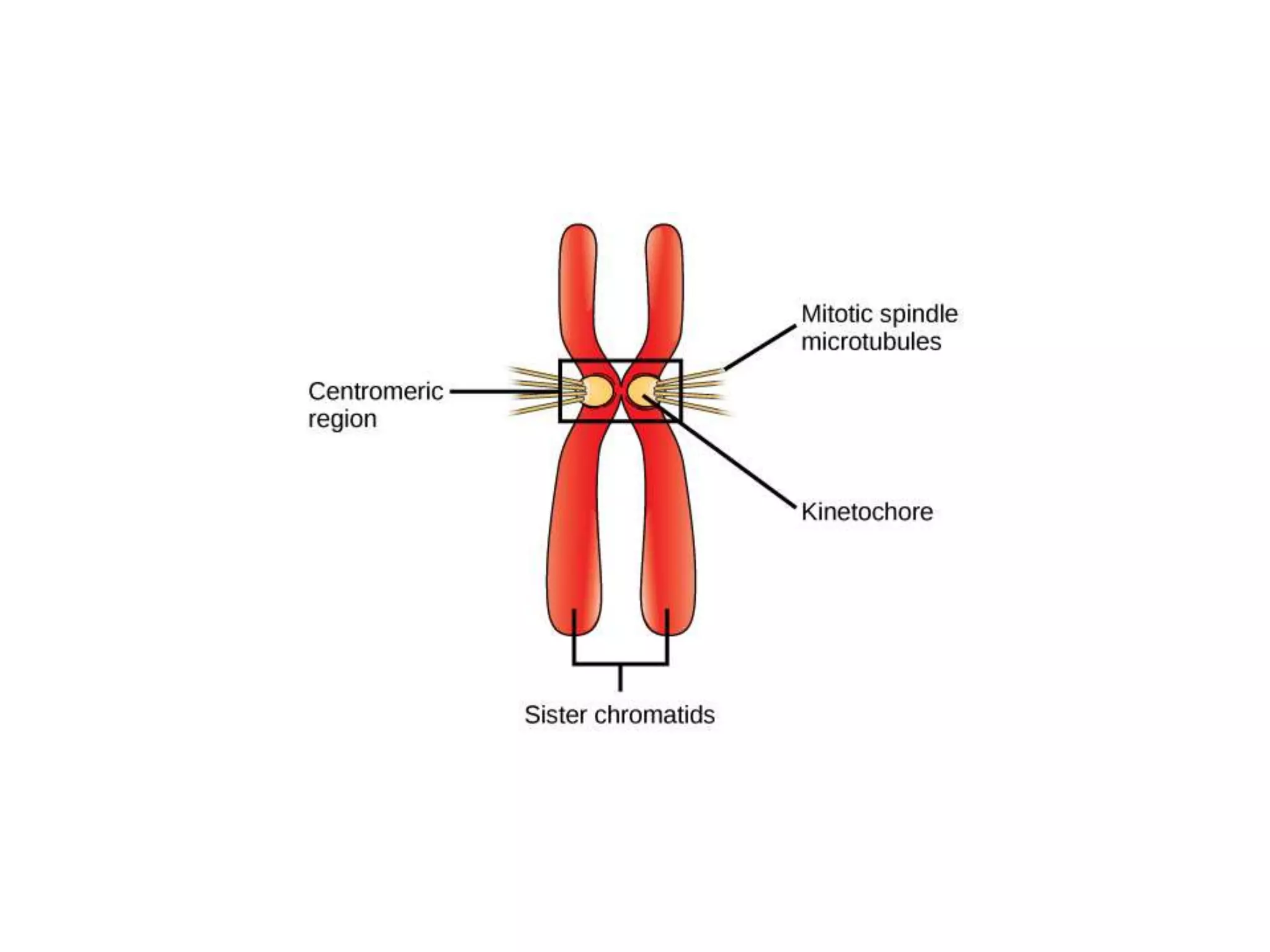
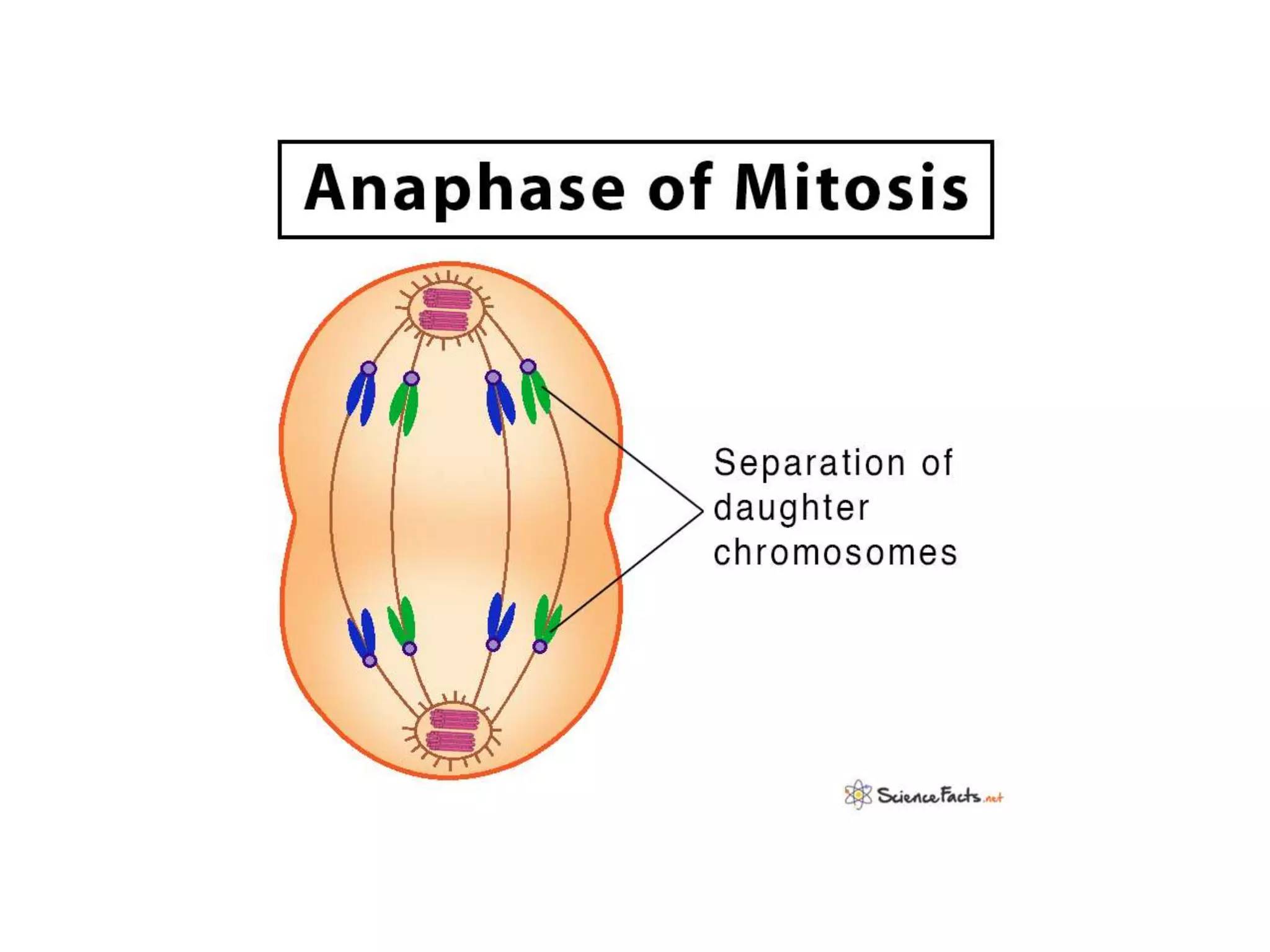
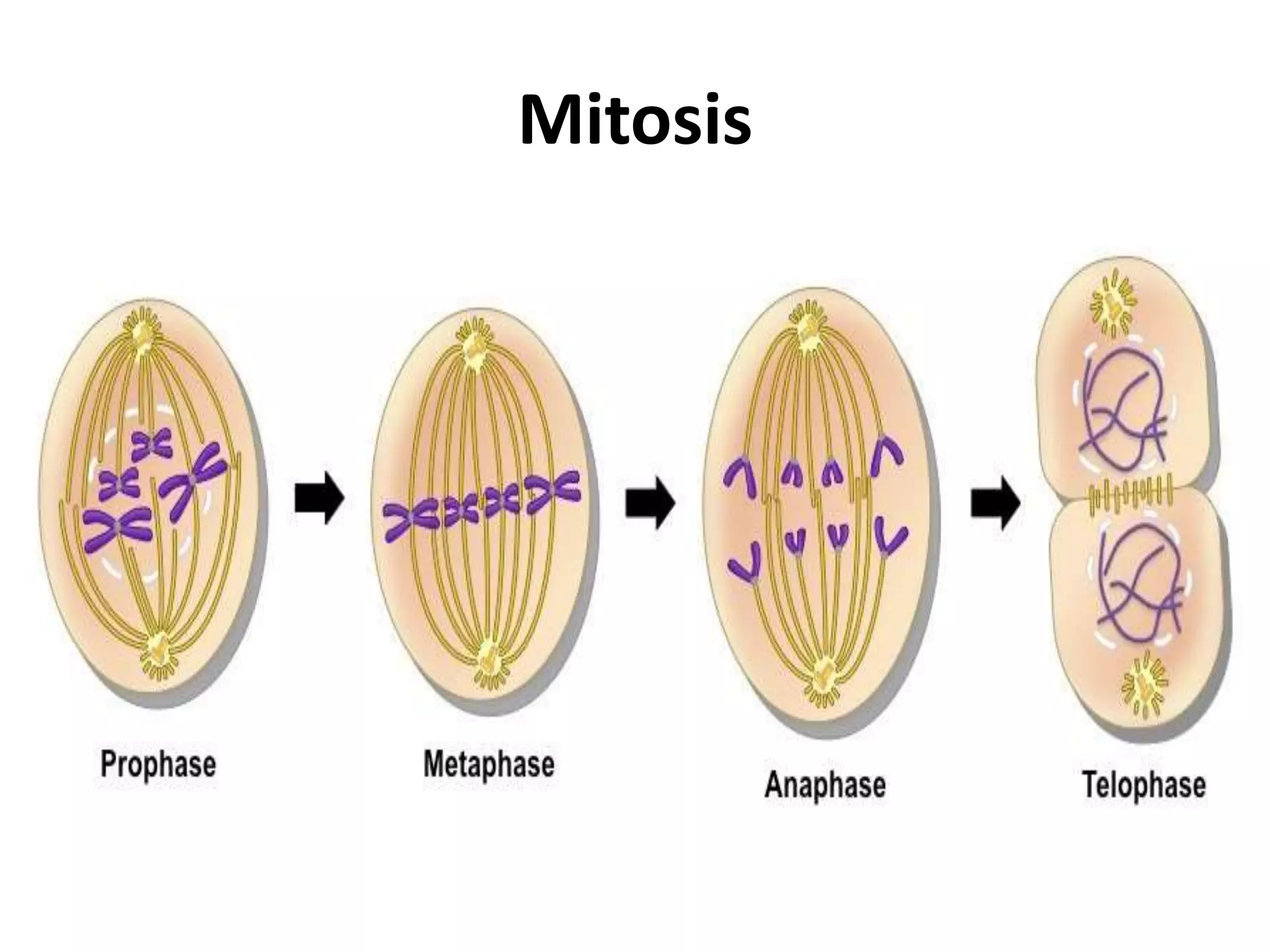
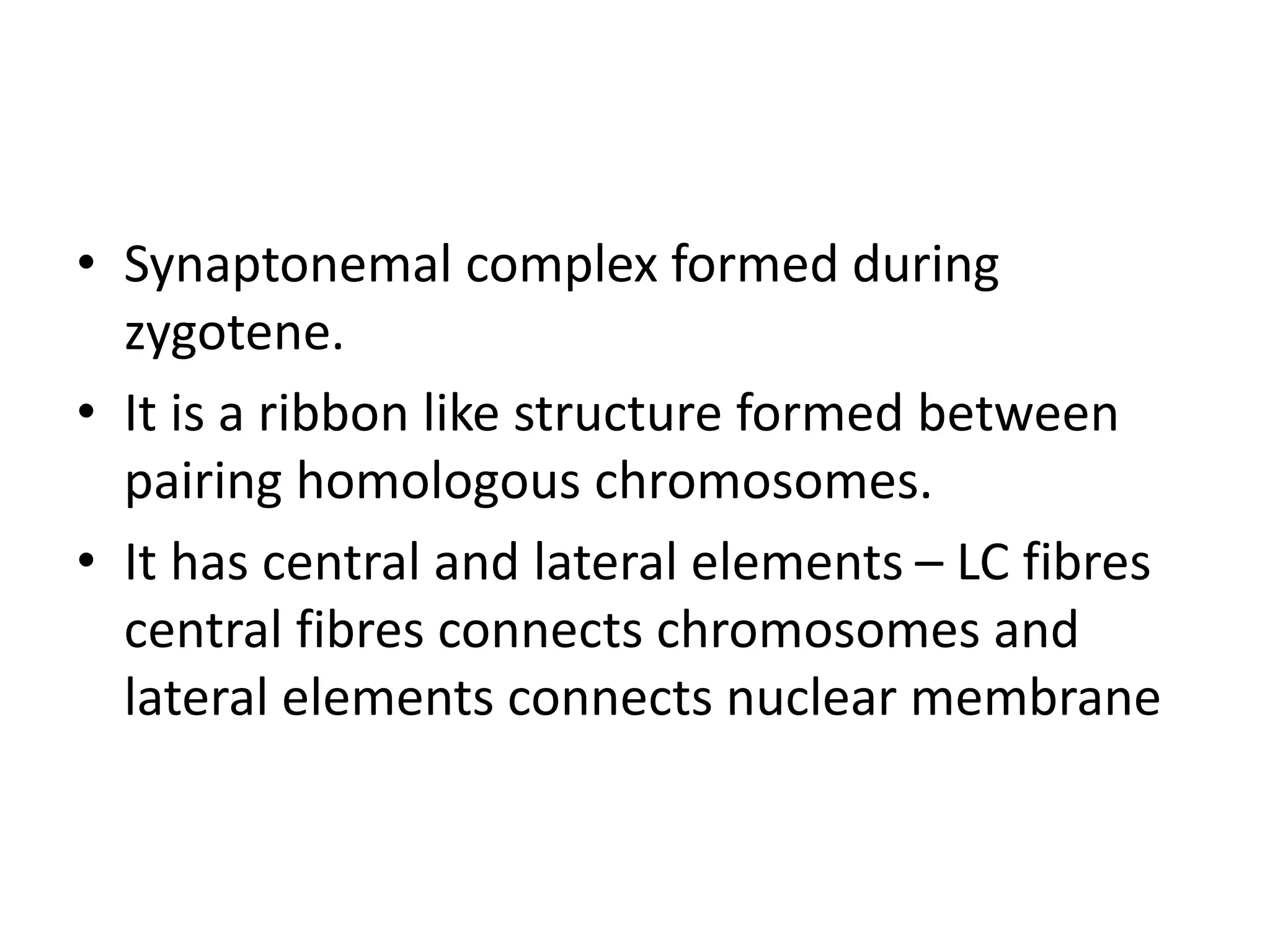
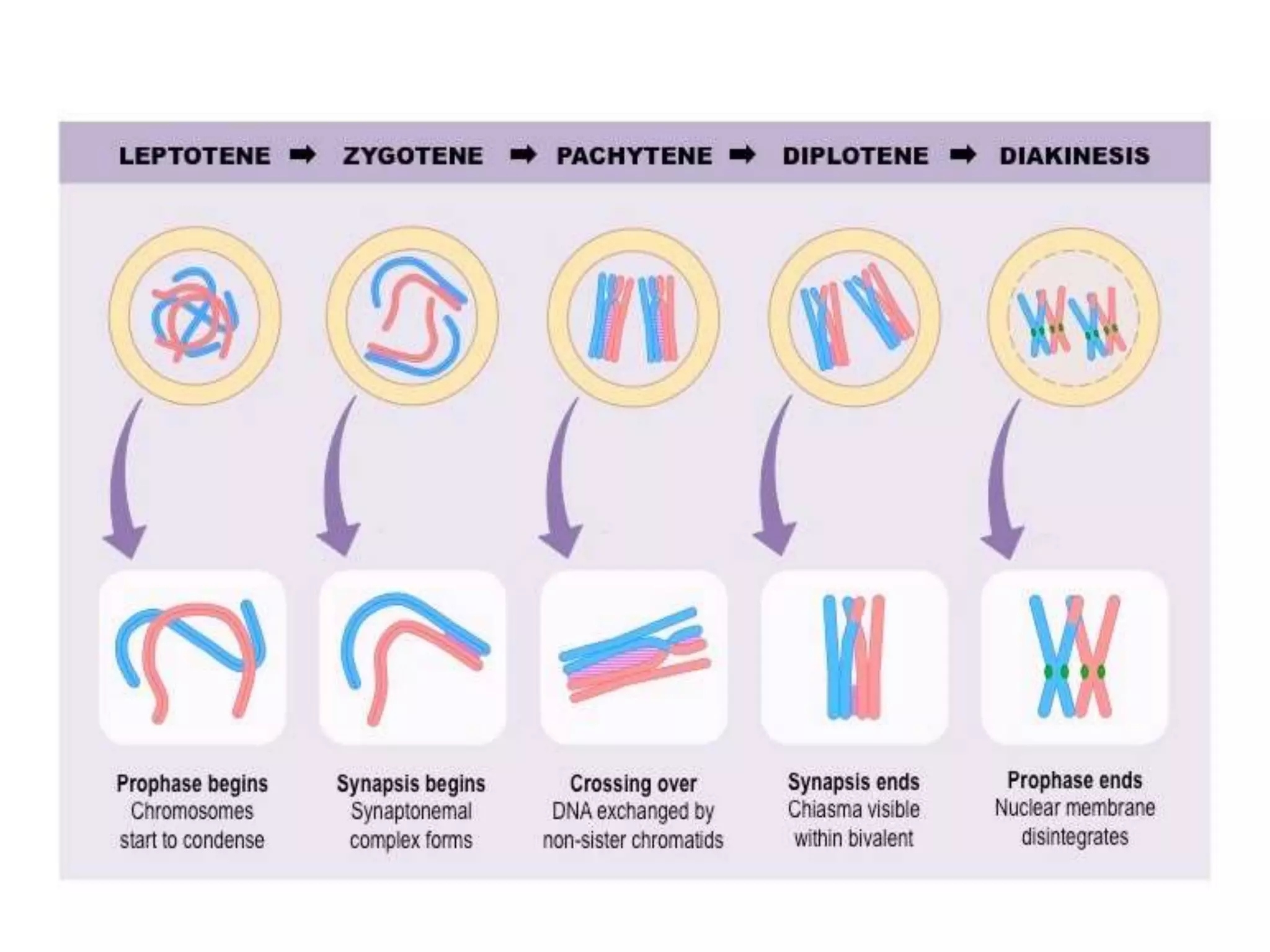
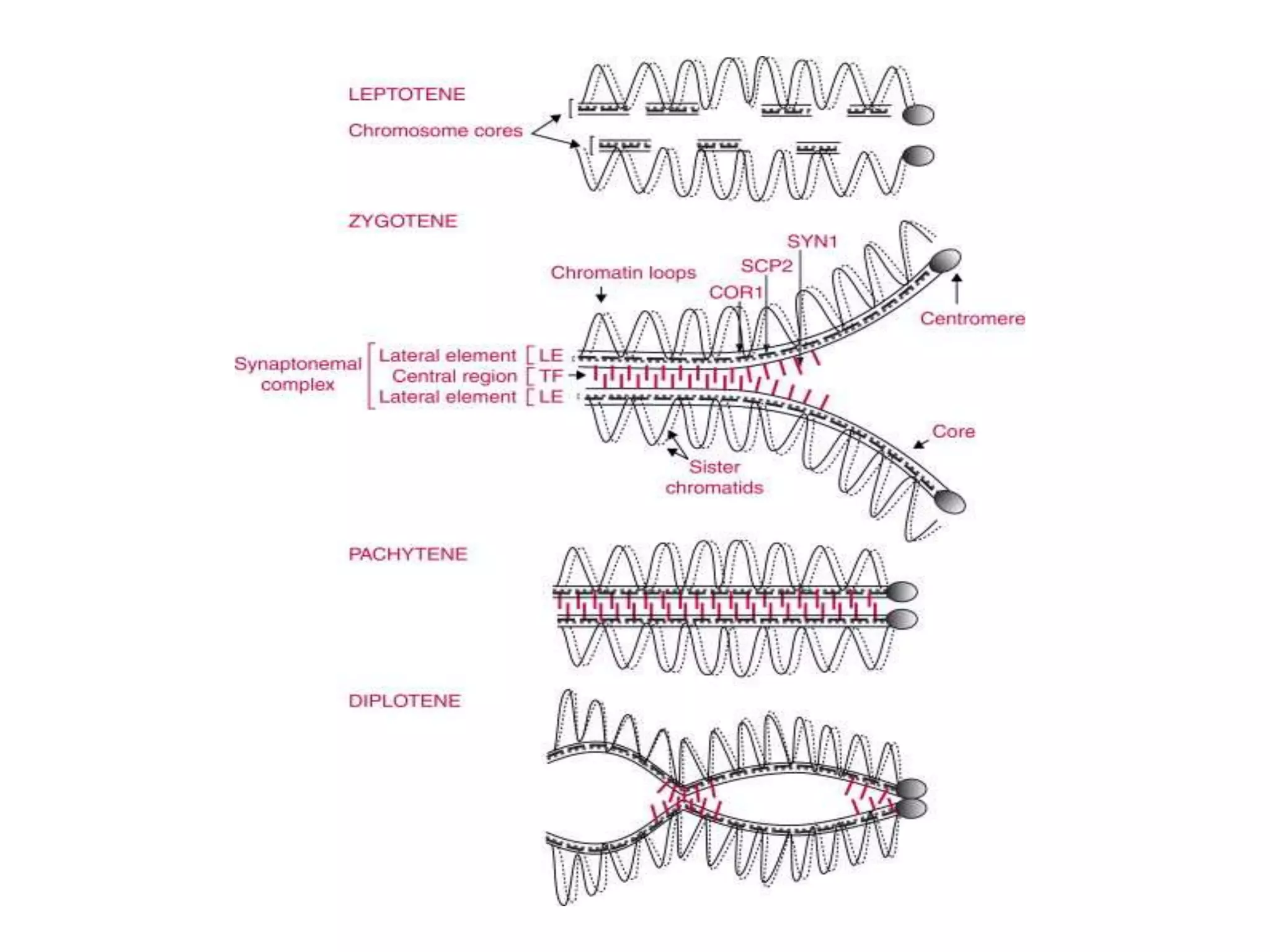
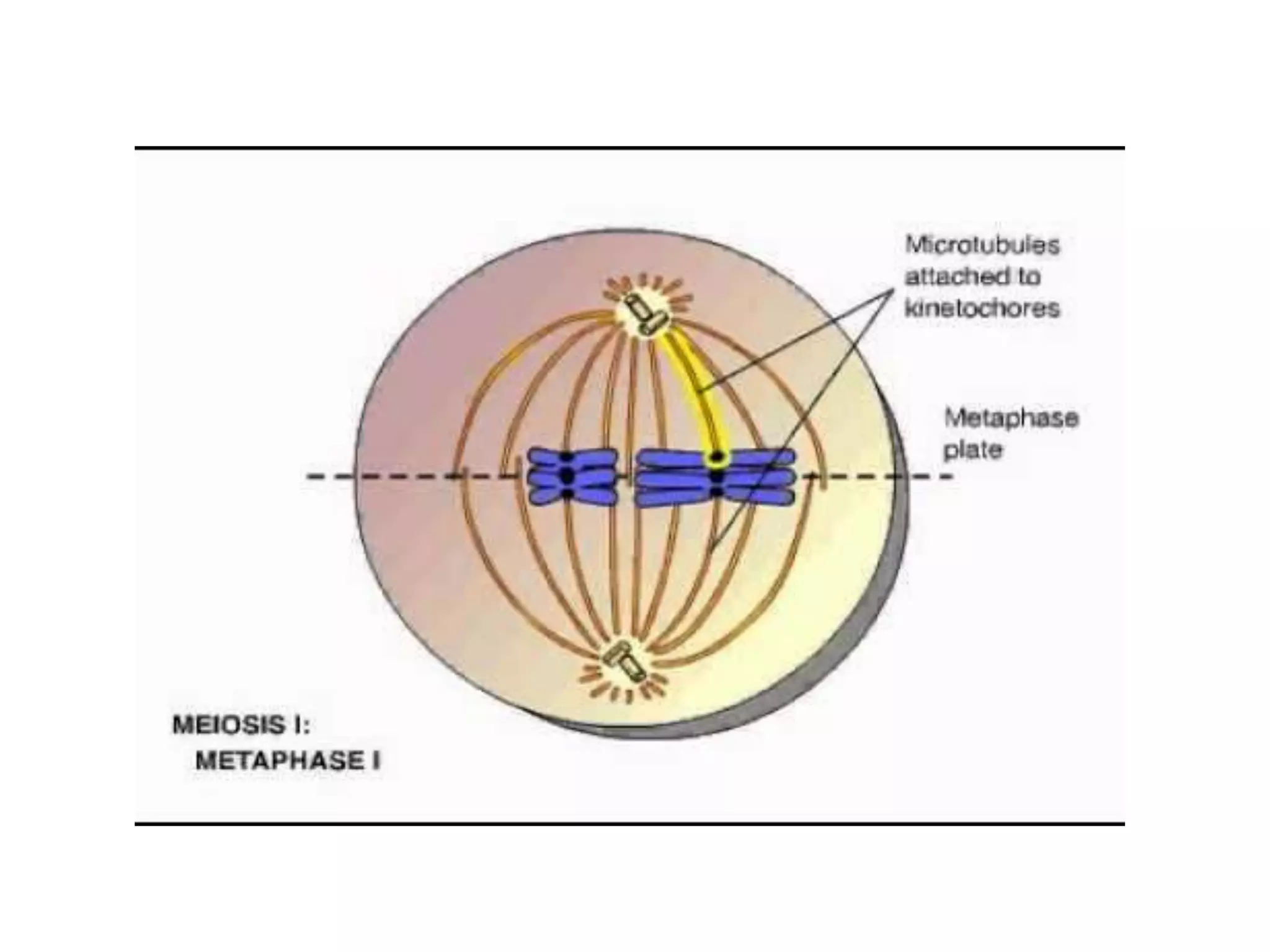
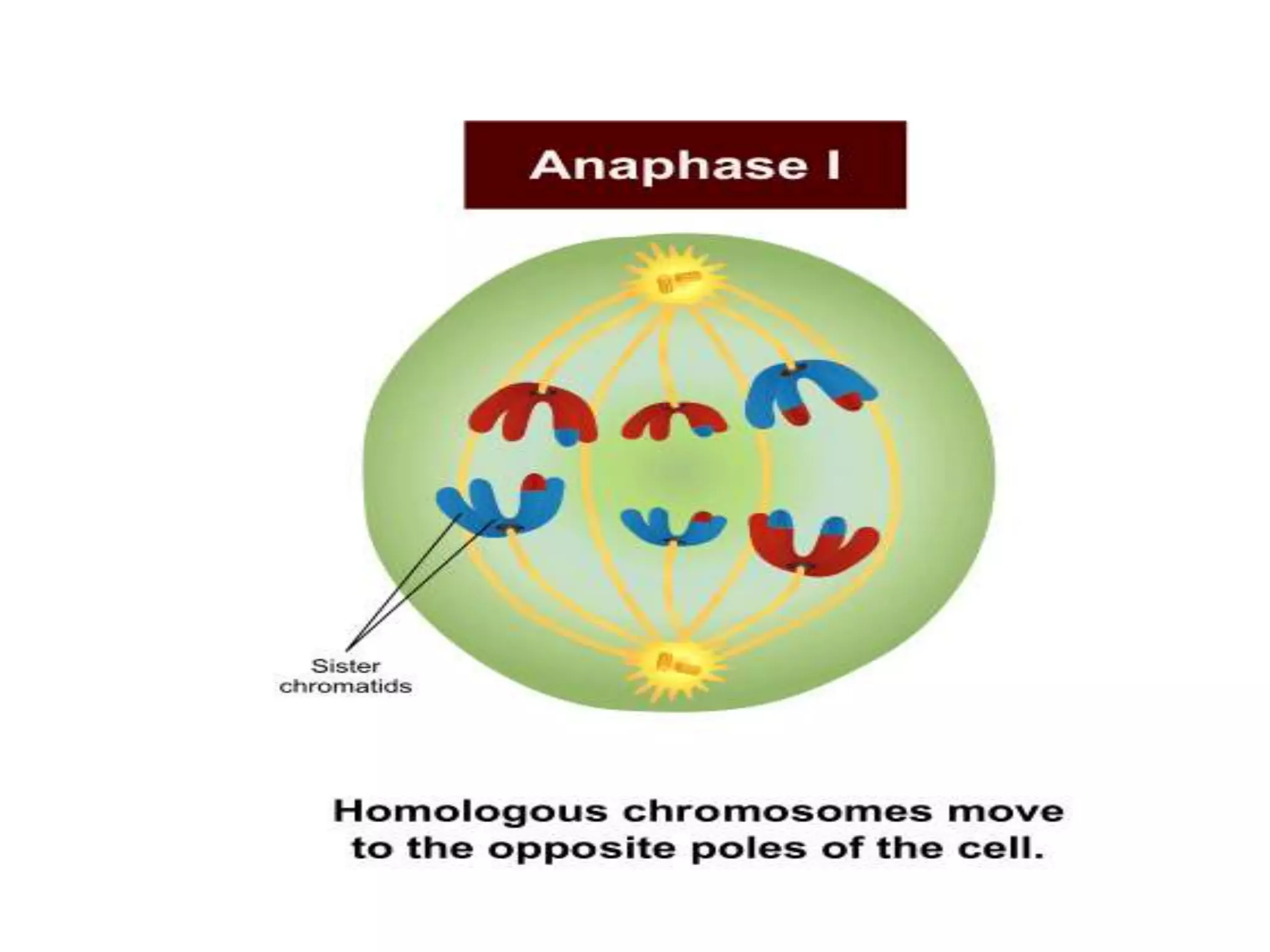
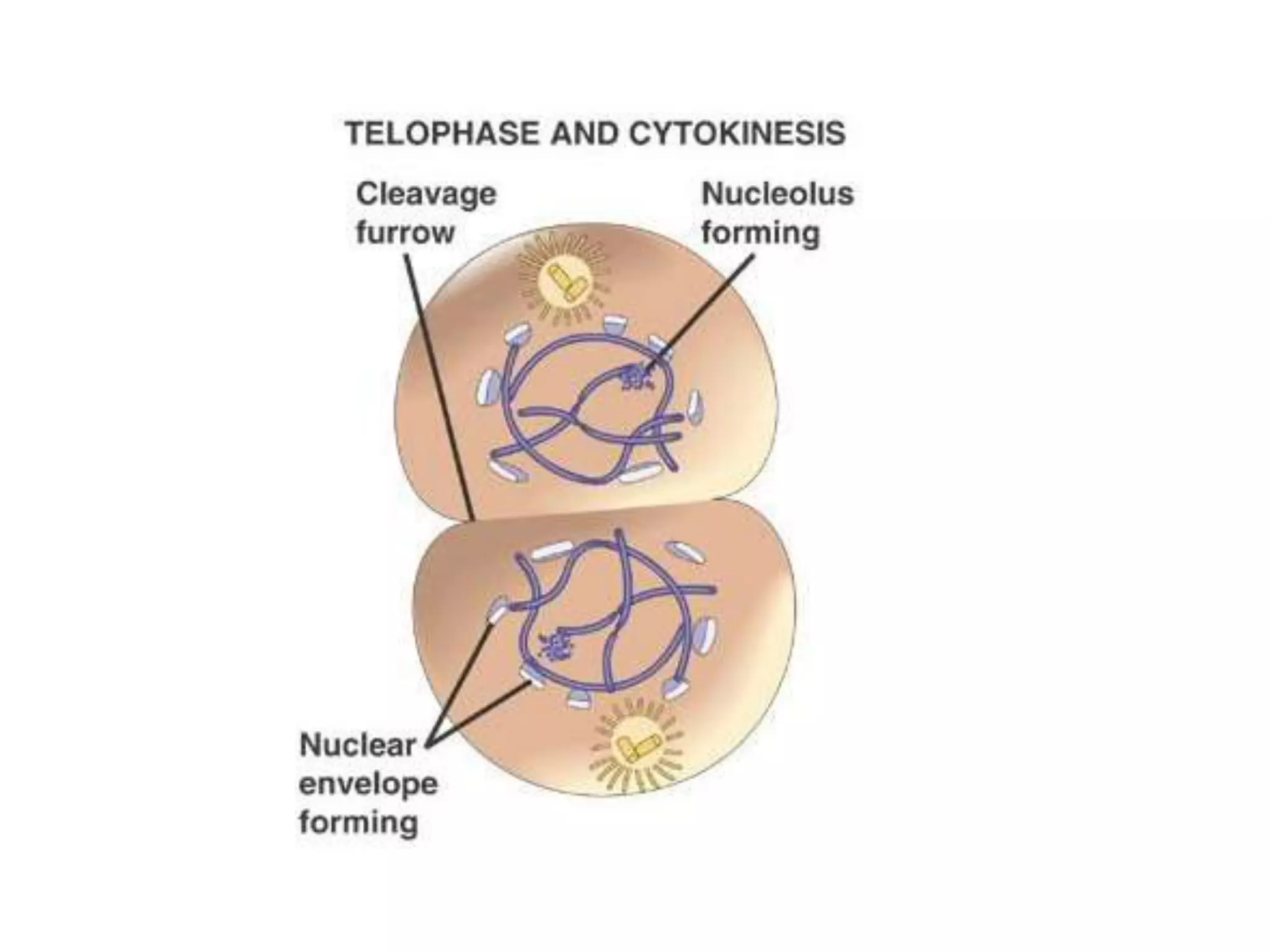
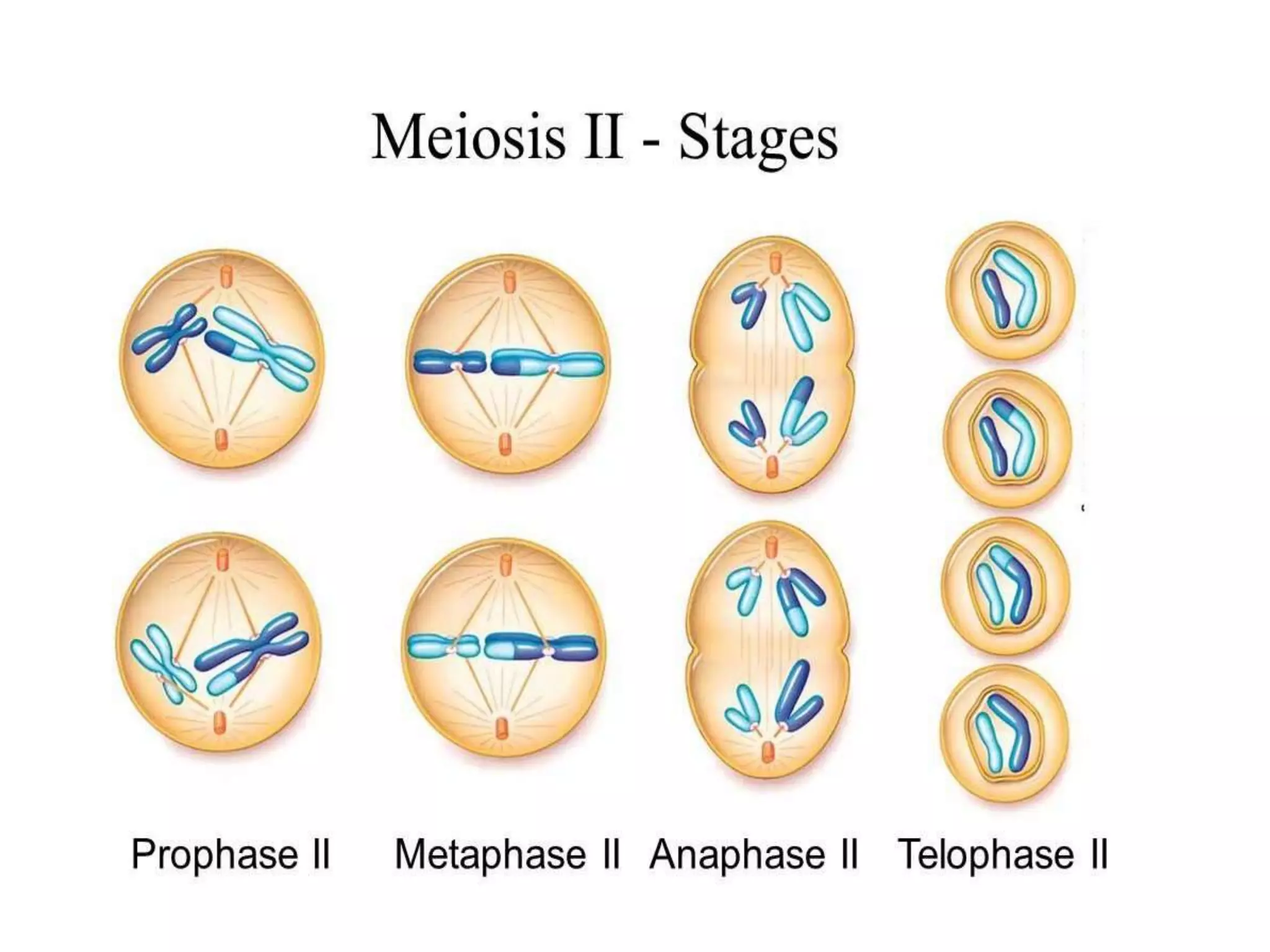
The document discusses the cell cycle and cell division, detailing historical developments and the phases of both mitosis and meiosis. It explains the significance of these processes in growth, development, and genetic variation in living organisms. Key terms and mechanisms such as interphase, karyokinesis, and the stages of meiosis are thoroughly elaborated.