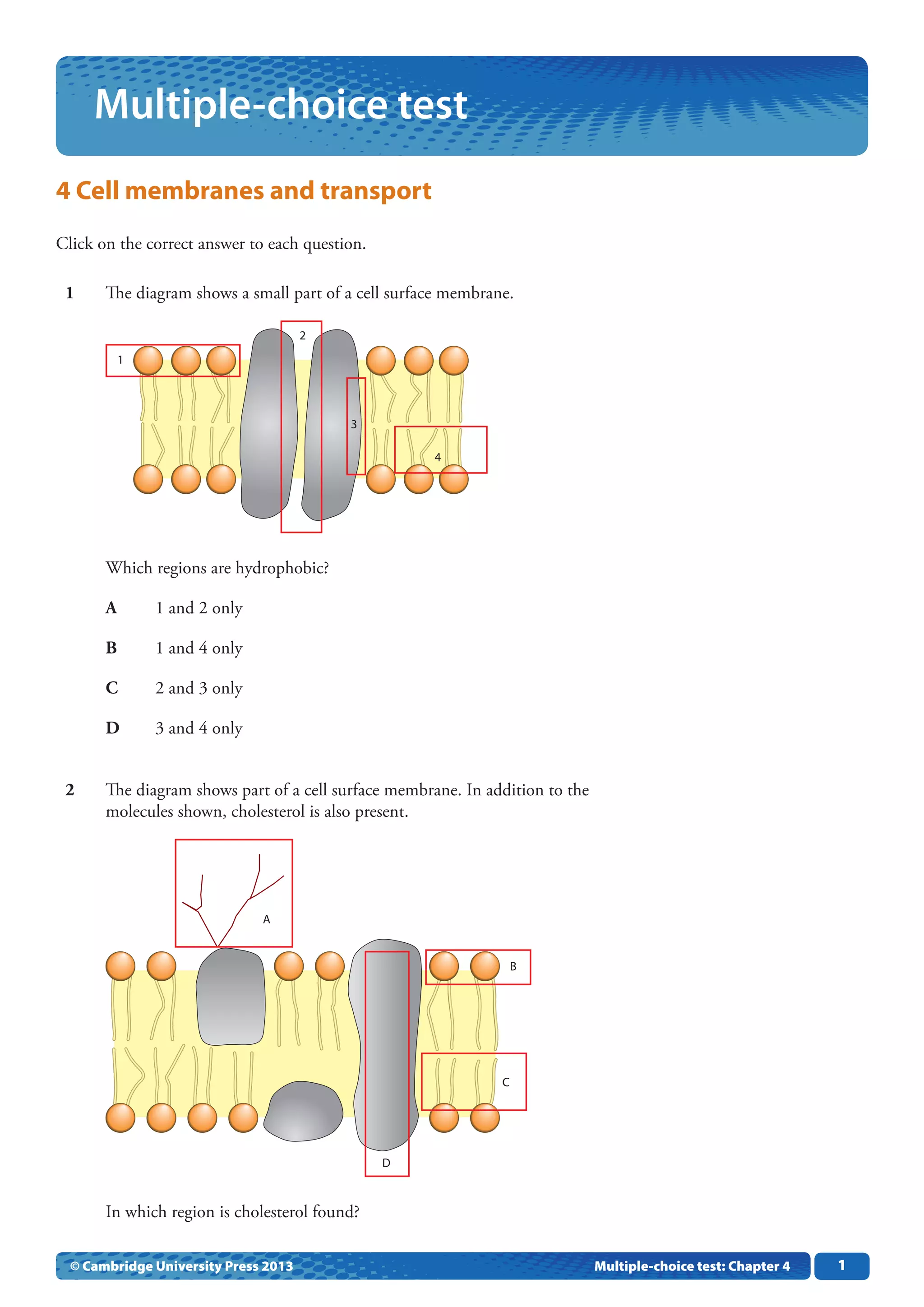
This document contains a 10 question multiple choice test about cell membranes and transport. The questions cover topics like:
- Which parts of the cell membrane are hydrophobic
- Where cholesterol is located in the membrane
- Which components allow ion movement
- Which molecules have specific functions like transporting ions or stabilizing layers
- Types of transport like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and osmosis
- Processes that require ATP energy like endocytosis and exocytosis
- The sequence of events in protein secretion by exocytosis
- Examples of exocytosis and endocytosis
- Determining water potential differences based on cell appearance after placement in solutions